Cardiovascular disease affects millions of Americans each year. It’s important to know the signs and symptoms early. This helps in getting the right treatment quickly.
Signs like chest discomfort and shortness of breath are warning signs. They tell us our heart might be stressed. Knowing these signs helps us take care of our heart health.
Cardiovascular disease shows different symptoms in different people. It’s key to know these signs to stay healthy. This helps prevent serious heart problems.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Cardiovascular Disease
Knowing the signs of heart problems can save lives. Cardiovascular disease often sneaks up on us. But knowing what to look for can make a big difference. Let’s explore the key indicators that might signal trouble with your heart health.
Early Warning Signs
Your body often sends subtle hints before a major cardiac event. Unexplained fatigue, even during everyday activities, can be a red flag. Shortness of breath, even with mild exertion, might indicate your heart’s struggling. Pay attention to these early warnings:
- Persistent tiredness
- Difficulty breathing during light activities
- Swelling in ankles or feet
- Irregular heartbeats or palpitations
Common Symptoms in Men vs Women
Heart disease doesn’t play favorites, but it can manifest differently based on gender. Men often experience classic symptoms like chest pain or discomfort. Women, on the other hand, might have more subtle signs:
| Men | Women |
|---|---|
| Crushing chest pain | Neck, jaw, or back pain |
| Left arm pain | Nausea or vomiting |
| Shortness of breath | Shortness of breath |
| Cold sweats | Extreme fatigue |
When to Seek Emergency Care
Some symptoms demand immediate attention. If you experience severe chest pain, difficulty breathing, or signs of a heart attack, don’t wait. Call emergency services right away. Remember, minutes matter when it comes to heart health.
“Listen to your body. If something feels off, and it’s accompanied by chest discomfort or breathing issues, seek medical help promptly.”
By staying alert to these signs and symptoms, you’re taking a critical step in protecting your heart. Don’t ignore what your body’s telling you – it could be a lifesaver.
Understanding Chest Pain and Discomfort
Chest pain is a common symptom that can signal heart problems. It’s important to know the different types of chest discomfort. Also, knowing when to seek medical help is key.
Types of Chest Pain
Chest pain can feel different. Some people feel a sharp stabbing, while others feel a dull ache or pressure. The pain’s location and how long it lasts can vary too.
Angina vs Heart Attack Pain
Angina and heart attack pain share some similarities. Angina usually happens when you’re active or stressed and goes away with rest. Heart attack pain is more severe, lasts longer, and can happen anytime, even when you’re resting.
| Characteristic | Angina | Heart Attack |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Usually less than 15 minutes | Often lasts 30 minutes or more |
| Trigger | Physical activity or stress | Can occur at any time |
| Relief | Responds to rest or medication | Persistent despite rest |
Related Symptoms
Chest pain can come with other symptoms that might mean a heart problem. These include:
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
- Sweating
- Pain radiating to the arm, jaw, or back
If you have severe chest pain or discomfort with these symptoms, get emergency medical care right away. Quick action can save lives in heart attack cases.
Breathing Difficulties and Cardiovascular Health
Breathing troubles can be a sign of heart problems. Many people don’t know that shortness of breath might mean their heart is at risk. This symptom often starts with mild discomfort during everyday tasks.
When your heart can’t pump blood well, it affects your lungs. This can make you feel out of breath even after light exercise or while resting. If you have persistent breathing problems, it’s important to pay attention to these warning signs and get medical advice.
Cardiovascular disease can show up in many ways, but shortness of breath is common. It might happen:
- When lying down
- During physical activity
- At rest, if it’s sudden
Don’t ignore these symptoms as just being out of shape. They could mean serious heart issues like heart failure or coronary artery disease. Catching these problems early is key to managing heart health.
“Breathlessness that comes on suddenly or gets worse over time should never be ignored. It’s your body’s way of saying something isn’t right.”
Regular check-ups and lifestyle changes can help prevent and manage heart disease. HealthWith.com offers resources to understand your symptoms better and take control of your heart health. Remember, your breath is linked to your heart – listen to what it’s telling you.
Fatigue and Exercise Intolerance as Warning Signs
Fatigue and exercise intolerance can signal heart disease early. These signs often start slowly and are easy to miss. It’s important to know how they work and their effects to catch them early.
Physical Exhaustion Patterns
Those with heart issues might feel tired that doesn’t go away with rest. This tiredness is different from usual exhaustion. It can start suddenly or get worse over time.
Exercise intolerance often goes hand in hand with this fatigue. It makes doing physical activities harder than before.

Impact on Daily Activities
Heart-related fatigue can really affect daily life. Even simple tasks like climbing stairs or carrying groceries become hard. Work and social activities might also suffer.
This decline in quality of life is a big reason to pay attention to these symptoms.
Recovery Time Concerns
How long it takes to recover from exercise is also key. People with heart disease often take longer to get back to normal. This longer recovery time is a warning sign, even if it’s new.
| Symptom | Normal | Potential Cardiovascular Issue |
|---|---|---|
| Fatigue Level | Improves with rest | Persistent, doesn’t improve with rest |
| Exercise Tolerance | Consistent or improving | Declining, activities become harder |
| Recovery Time | Quick return to normal | Extended, takes longer than usual |
If you see these signs of fatigue and exercise intolerance, see a doctor. Catching heart disease early can greatly improve your life and health.
Circulation Problems and Swelling Symptoms

Circulation issues often link to heart disease. When your heart can’t pump blood well, you might see swollen legs. This swelling, or edema, happens when fluid builds up in your body’s tissues.
Poor blood flow can make your ankles and feet swell. If you always have puffy ankles and feet, it could mean heart trouble. Swollen legs can feel heavy and tight, making it hard to move.
Other signs of poor circulation include:
- Cold hands and feet
- Numbness or tingling in extremities
- Skin discoloration
- Slow-healing wounds
If you have these symptoms and swollen legs, see a doctor. They can check your heart health and see if these signs mean something serious.
“Swelling in the legs can be a red flag for heart problems. Don’t ignore it – early detection can make a world of difference in managing cardiovascular disease.”
Remember, swollen legs and circulation problems don’t always mean heart disease. But they are warning signs that shouldn’t be ignored. By being careful and getting medical help early, you can protect your heart.
Heart Rhythm Abnormalities and Palpitations
Heart rhythm issues can be a sign of cardiovascular disease. Many people feel their heart racing, fluttering, or skipping beats. These feelings might be harmless, but they can also show a serious problem.
Types of Irregular Heartbeats
An irregular heartbeat, or arrhythmia, can take various forms:
- Tachycardia: Heartbeat faster than normal
- Bradycardia: Heartbeat slower than normal
- Premature contractions: Extra beats
- Fibrillation: Chaotic electrical signals
Triggers and Risk Factors
Several factors can trigger palpitations or increase your risk of developing an irregular heartbeat:
- Stress or anxiety
- Caffeine or alcohol consumption
- Certain medications
- Smoking
- High blood pressure
- Obesity
Monitoring Heart Rhythm
If you experience frequent palpitations or suspect an irregular heartbeat, your doctor may recommend monitoring your heart rhythm. This can be done through:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Holter monitor
- Event recorder
- Implantable loop recorder
Remember, while occasional palpitations are common, persistent irregular heartbeats could signal cardiovascular disease. Always consult your healthcare provider if you have concerns about your heart rhythm.
High Blood Pressure: The Silent Indicator
High blood pressure is often called “the silent killer” because it doesn’t show symptoms. It can harm your heart and blood vessels before you even notice. That’s why it’s important to get your blood pressure checked regularly.
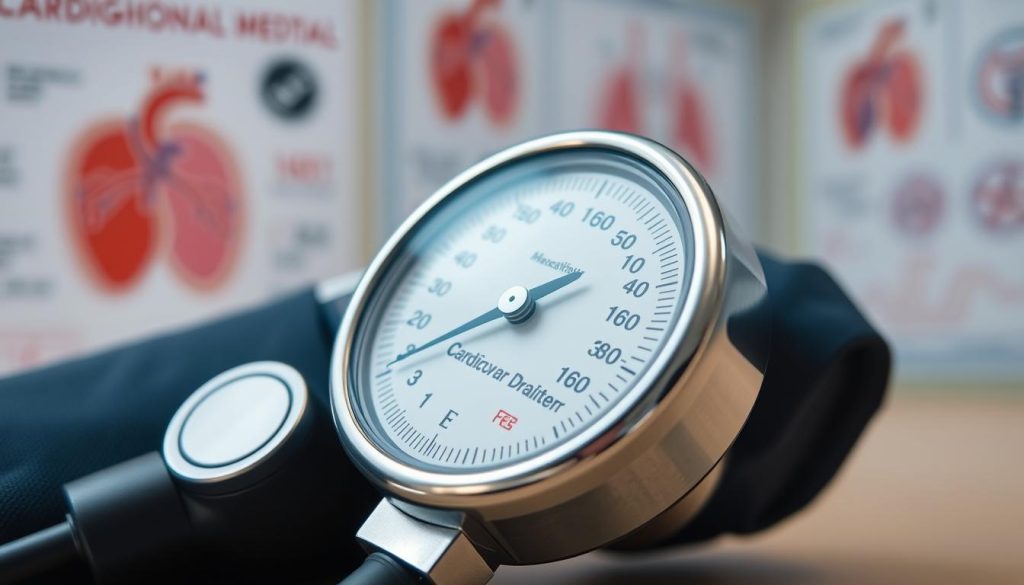

Blood pressure has two numbers. The top number shows the force when your heart beats. The bottom number shows the pressure between beats. Here’s what your numbers mean:
| Category | Systolic (mmHg) | Diastolic (mmHg) |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | Less than 120 | Less than 80 |
| Elevated | 120-129 | Less than 80 |
| Stage 1 Hypertension | 130-139 | 80-89 |
| Stage 2 Hypertension | 140 or higher | 90 or higher |
If not treated, high blood pressure can cause heart attacks and strokes. It’s vital to watch your blood pressure and keep it in check. You can do this by eating well, exercising, and managing stress.
High blood pressure is a major risk for heart disease. By controlling your blood pressure, you’re protecting your heart.
Cholesterol Levels and Heart Disease Connection
It’s important to know how cholesterol affects your heart. Cholesterol is a substance in your blood that’s vital but can be harmful if levels get too high.
Understanding Good vs Bad Cholesterol
Cholesterol isn’t all the same. HDL, or “good” cholesterol, helps clean your blood. LDL, or “bad” cholesterol, can clog your arteries and increase heart disease risk.
Diet Impact on Cholesterol
Your diet greatly affects your cholesterol levels. Foods with saturated and trans fats can increase LDL cholesterol. Eating more fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins can lower your cholesterol risk.
Treatment Options
If you have high cholesterol, your doctor might suggest lifestyle changes or meds. Statins are often used to lower LDL and prevent heart problems. Other treatments include bile acid sequestrants, cholesterol absorption inhibitors, and PCSK9 inhibitors.
“Managing your cholesterol is a key step in protecting your heart. Regular check-ups and a heart-healthy lifestyle can make a significant difference in your cardiovascular health.”
High cholesterol often has no symptoms. So, getting regular blood tests is key to keeping your heart healthy and preventing heart disease.
Recognizing Heart Attack Warning Signs
Knowing the warning signs of a heart attack can save lives. Chest pain is often the first symptom people think of, but it’s not always present. Some experience a crushing sensation or pressure in their chest that lasts more than a few minutes.
Shortness of breath is another key indicator. You might feel like you can’t catch your breath, even when resting. This can occur with or without chest discomfort.
- Cold sweats
- Nausea
- Lightheadedness
- Pain in one or both arms
- Jaw or back discomfort
Women may experience different symptoms than men. They’re more likely to feel extreme fatigue, shortness of breath, and nausea without chest pain.
| Common Symptoms | Men | Women |
|---|---|---|
| Chest Pain | Very common | Less common |
| Shortness of Breath | Common | Very common |
| Nausea | Less common | Common |
| Fatigue | Less common | Very common |
If you suspect a heart attack, call emergency services immediately. Quick action can prevent permanent heart damage and save your life.
Understanding Stroke Symptoms and Risk Factors
Stroke is a serious condition that needs quick action. Knowing the signs and managing risks can save lives. Let’s look at how to stay aware and prevent strokes.
FAST Assessment Method
The FAST method helps spot stroke symptoms fast:
- Face drooping
- Arm weakness
- Speech difficulty
- Time to call 911
Risk Factor Management
Many things can raise your stroke risk. By managing these, you can lower your chances of a stroke:
| Risk Factor | Management Strategy |
|---|---|
| High blood pressure | Regular monitoring, medication if needed |
| Smoking | Quit smoking programs, nicotine replacement |
| Diabetes | Blood sugar control, diet, exercise |
| High cholesterol | Diet changes, medication if necessary |
Prevention Strategies
Preventing stroke means making lifestyle changes and getting regular check-ups. Important steps include:
- Eating a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables
- Exercising regularly, aiming for 150 minutes per week
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques
By knowing the signs of stroke and managing risks, you can prevent this serious disease. Regular health check-ups and lifestyle changes are key to protecting yourself from stroke.
Prevention and Lifestyle Modifications
It’s important to take care of your heart to prevent cardiovascular disease. Making small changes in your daily life can have a big impact. Eating a diet full of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins helps keep your arteries clear.
Regular exercise is also key. Even a 30-minute brisk walk each day can strengthen your heart. This makes it more resilient and able to handle stress better.
Managing stress is also vital for heart health. Try deep breathing or meditation to relax your mind and body. Quitting smoking and drinking less alcohol are also important steps to protect your heart.
These changes not only lower your risk of heart disease but also boost your overall health. It’s a win-win situation.
Don’t forget the importance of regular health check-ups. They help catch problems early and prevent them from getting worse. Keep an eye on your blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and weight. Work with your doctor to make a plan that’s right for you.
Remember, it’s never too late to start making positive changes for your heart. Every step you take towards a healthier lifestyle is a step in the right direction.
FAQ
Q: What are the most common signs and symptoms of cardiovascular disease?
A: Common signs include chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue. You might also feel an irregular heartbeat or swelling in your legs. Symptoms can vary, depending on the condition and whether you’re a man or woman.
Q: How can I differentiate between angina and a heart attack?
A: Angina causes chest discomfort that goes away with rest or medicine. Heart attack pain is more severe and lasts longer. It might also come with nausea or shortness of breath. If unsure, seek medical help right away.
Q: When should I be concerned about fatigue as a symptom of heart disease?
A: Unusual, persistent, or activity-interfering fatigue could signal heart disease. If you’re tired all the time, and it’s not normal, see your doctor. This is true if you also have shortness of breath or chest pain.
Q: How does high blood pressure relate to cardiovascular disease?
A: High blood pressure, or hypertension, is often silent but deadly. It raises your risk of heart disease and stroke. Regular checks are key to catching and managing it early.
Q: What’s the connection between high cholesterol and heart disease?
A: High LDL (bad) cholesterol can clog arteries, leading to heart disease and stroke. Keeping cholesterol levels healthy through diet, exercise, and sometimes meds is vital.
Q: How can I recognize the signs of a stroke?
A: Use the FAST method: Face drooping, Arm weakness, Speech difficulty, Time to call emergency services. Other signs include sudden confusion, trouble seeing, dizziness, or severe headache. Quick action is critical in stroke cases.
Q: Are heart attack symptoms different for women?
A: Yes, women often have different or less obvious symptoms. While chest pain is common, women might also experience shortness of breath, nausea, back or jaw pain, and fatigue. It’s important for women to know these differences.
Q: How can lifestyle changes help prevent cardiovascular disease?
A: A heart-healthy lifestyle can greatly reduce your risk. Eat well, exercise regularly, manage stress, quit smoking, and limit alcohol. These steps help control blood pressure, cholesterol, and weight, all important for heart health.
Q: What are the risk factors for cardiovascular disease?
A: Major risks include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, obesity, diabetes, and physical inactivity. An unhealthy diet, excessive alcohol, age, gender, and family history also play a part. Knowing your risks helps in preventing heart disease.
Q: How often should I have my heart health checked?
A: Get a heart health check every two years if over 45 (or 30 for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples). If you have risk factors or heart conditions, your doctor might suggest more frequent checks.