Prostate cancer is a big worry for men all over the world. It’s important to know how common it is and its effects. The burden of prostate cancer changes in different groups, so we need to look at it closely.
Looking into prostate cancer shows us many risk factors and trends. We’ll see how widespread this disease is and its big impact on health. Let’s dive into the numbers and find out who’s most likely to get it.
Prostate Cancer Global Prevalence and Incidence Rates
Prostate cancer is a common cancer in men around the world. It’s important to understand its impact globally. This includes looking at how common it is, how many new cases there are, and how many people die from it.
Worldwide Statistics and Regional Variations
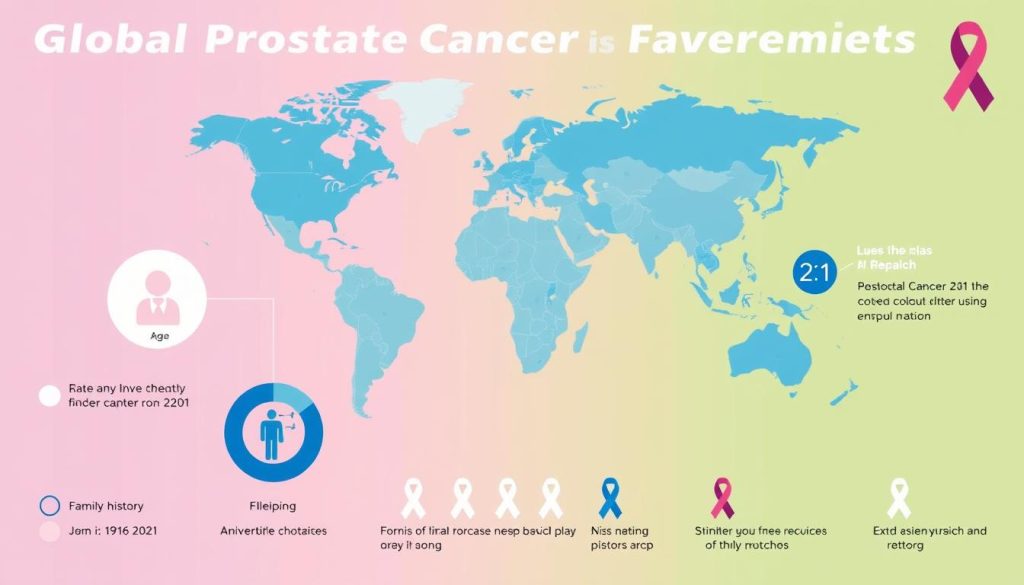
Prostate cancer is more common in some places than others. Countries with more resources and longer lives tend to see more cases. In 2020, over 1.4 million new cases were reported worldwide. North America and Europe had the highest rates.
Age-Adjusted Incidence Rates
Age-adjusted rates help compare prostate cancer risk fairly. They adjust for age differences, giving a clearer view of the disease’s impact. For example, in 2018, the U.S. had an age-adjusted rate of 106.4 per 100,000 men.
Mortality Rates Across Different Populations
Mortality rates show a different story. Prostate cancer survival rates are often lower in areas with less healthcare. In 2020, about 375,000 people died from prostate cancer worldwide. Africa and the Caribbean had the highest death rates.
| Region | Incidence Rate (per 100,000) | Mortality Rate (per 100,000) |
|---|---|---|
| North America | 73.7 | 7.8 |
| Europe | 62.1 | 11.3 |
| Asia | 11.5 | 3.8 |
| Africa | 26.6 | 14.9 |
These statistics show we need better screening and healthcare worldwide. This is to help reduce the gap in prostate cancer outcomes.
How Common Is Prostate Cancer in Different Demographics
Knowing who is at risk of prostate cancer helps us prevent it. The disease’s frequency changes with age, race, and where you live in the U.S.
Age Distribution and Risk Patterns
As men get older, the risk of prostate cancer goes up. Men over 50 are more likely to get it. The typical age for a diagnosis is 66. But, it’s rare for men under 40 to get it.

Racial and Ethnic Disparities
There are big differences in prostate cancer rates among races. African American men are 60% more likely to get it than white men. They also face more aggressive forms and higher death rates. Asian American and Hispanic men have lower rates.
Geographical Distribution in the United States
Prostate cancer rates vary by region. The Northeast and Mid-Atlantic have higher rates than the West and Southwest. Healthcare access, screening, and environment play a role in these differences.
| Region | Incidence Rate (per 100,000) |
|---|---|
| Northeast | 123.5 |
| Midwest | 115.7 |
| South | 107.2 |
| West | 101.8 |
These facts show why we need to focus on screening and awareness. Understanding these patterns helps doctors and policymakers work better. They aim to help all men by addressing these disparities.
Primary Risk Factors for Prostate Cancer Development
Knowing the risk factors for prostate cancer is key to catching it early and preventing it. Some risks we can’t change, but others we can manage with our lifestyle choices.
Age is a big factor in prostate cancer risk. Men over 50 are more at risk, with the risk going up as they age. If a close relative had prostate cancer, your risk might be higher too.
Race and ethnicity also play a part. African American men face a higher risk of prostate cancer. They are also more likely to get aggressive forms of the disease at a younger age.
- Diet high in red meat and dairy products
- Obesity
- Lack of regular exercise
- Smoking
These lifestyle choices can up your risk of getting prostate cancer. Eating healthy, staying active, and keeping a healthy weight can help lower your risk.
Being exposed to certain chemicals, like pesticides or heavy metals, might also raise your risk. Some studies link inflammation of the prostate to cancer development.
“Knowledge is power. Understanding your risk factors for prostate cancer empowers you to take control of your health.”
While you can’t change some risks, like age or genetics, you can work on others. Regular health check-ups and talking to your doctor are crucial for managing your prostate health.
Trends in Prostate Cancer Detection and Diagnosis
Prostate cancer detection and diagnosis have made big strides in recent years. These advances help find cancer early and treat it more effectively. This is good news for men dealing with this common health issue.
Early Detection Methods and Screening Rates
Doctors use several tools to find prostate cancer. The main ones are digital rectal exams (DRE) and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests. How often these tests are used can vary a lot. This depends on where you live and who you are.
Impact of PSA Testing on Diagnosis Rates
PSA testing has changed how we diagnose prostate cancer. This blood test checks for PSA levels, which can show if there’s a problem. Since it started, more men are being diagnosed with prostate cancer early.
| Year | PSA Tests Performed (millions) | Prostate Cancer Diagnoses |
|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 4.2 | 106,000 |
| 2000 | 17.8 | 180,000 |
| 2010 | 31.5 | 217,000 |
| 2020 | 29.7 | 191,000 |
Stage at Diagnosis Statistics
Thanks to better detection methods, more cancers are found early. This has greatly improved treatment results and survival rates. Now, about 77% of prostate cancers are caught early. This gives men a better chance of successful treatment.
Survival Rates and Treatment Outcomes
Understanding prostate cancer survival rates is crucial for patients and their families. The five-year relative survival rate is a key measure. It compares the survival of prostate cancer patients to the general population. For all stages combined, the five-year relative survival rate for prostate cancer is.
Prostate cancer treatment outcomes depend on several factors. The stage at diagnosis is a big factor in determining the prognosis. Men diagnosed with localized prostate cancer have a nearly 100% five-year survival rate. For those with regional spread, the rate is still high at 98%.
Even with distant metastases, the five-year survival rate is about 30%. This is higher than many other cancers at this stage.
Treatment choices greatly impact prostate cancer survival rates. Options like surgery, radiation therapy, and hormone therapy have improved outcomes over the years. Active surveillance for low-risk cases has also shown promising results.
It’s important to note that these statistics are based on past data. They may not reflect the most recent advances in treatment. Each case is unique, and patients should discuss their specific situation with their healthcare team. This way, they can understand their personal outlook and treatment options.
FAQ
Q: How common is prostate cancer globally?
A: Prostate cancer is a common cancer among men worldwide. It’s the second most diagnosed cancer in men, with over 1.4 million new cases each year. But, the rates vary a lot by region, with more cases in developed countries.
Q: What age group is most at risk for prostate cancer?
A: The risk of prostate cancer grows with age. Most cases are found in men over 65. It’s rare in men under 50, but the risk jumps up after 50. By 80, over 80% of men will have cancer cells in their prostate.
Q: Are there racial disparities in prostate cancer rates?
A: Yes, there are big racial differences in prostate cancer rates. African American men have the highest rates and are diagnosed younger and with more aggressive cancer. They also die more often from it than other racial groups in the U.S.
Q: What are the primary risk factors for developing prostate cancer?
A: Main risk factors include age, race, family history, and certain genetic mutations. Diet high in red meat and saturated fats, obesity, and lack of exercise may also increase risk.
Q: How has PSA testing affected prostate cancer diagnosis rates?
A: PSA testing, introduced in the late 1980s, led to more prostate cancer diagnoses. It found many cases early, but also raised concerns about overdiagnosis and overtreatment.
Q: What are the survival rates for prostate cancer?
A: Prostate cancer survival rates are high, especially if caught early. The 5-year survival rate for all stages is about 98%. For early-stage cancer, it’s nearly 100%. But, survival rates drop for advanced cancer.
Q: How do prostate cancer rates vary geographically in the United States?
A: Prostate cancer rates differ across the U.S. They’re higher in the Northeast and lower in the West. These differences might be due to screening, environment, lifestyle, and demographics.
Q: What impact has early detection had on prostate cancer mortality rates?
A: Early detection, like PSA testing, has greatly reduced prostate cancer deaths. Since the 1990s, deaths from prostate cancer have fallen by over 50%. But, the full effect of early detection on mortality is still debated.