Prostate cancer is a serious health concern for men worldwide. Knowing the early signs and symptoms is key for early diagnosis and treatment. This guide will cover the main indicators, risk factors, and why screening is important.
As men get older, their chance of getting prostate cancer goes up. Regular check-ups and knowing the symptoms are crucial for prostate health. Learning about warning signs and screening options helps you protect your health.
We will explore important facts, common symptoms, and screening methods for prostate cancer. This information helps you make informed health decisions and seek medical help when needed.
Understanding Prostate Cancer: Essential Facts and Statistics
Prostate cancer is a serious health concern affecting men worldwide. This section explores key facts, statistics, and the global impact of this disease.
What is Prostate Cancer and Who Does it Affect
Prostate cancer develops in the prostate gland, a small organ below the bladder in men. It mainly affects older men, with risk increasing after 50. While prevention strategies exist, they’re not perfect. Regular screenings, like the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test, are key for early detection.
Current Statistics and Prevalence Rates
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide. In the United States, about 1 in 8 men will get prostate cancer. The importance of early detection is huge, as it greatly improves treatment chances.
| Age Group | Prevalence Rate |
|---|---|
| 40-49 | 1 in 500 |
| 50-59 | 1 in 50 |
| 60-69 | 1 in 15 |
| 70+ | 1 in 7 |
Impact on Men’s Health Globally
The global burden of prostate cancer is huge. It impacts millions of men, their families, and healthcare systems worldwide. While death rates have dropped in many places, thanks to better treatments and early detection, it’s still a big challenge in areas with poor healthcare.
“Prostate cancer is a global health issue that requires increased awareness, research, and access to quality care.”
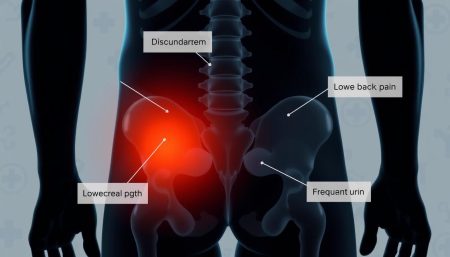
How Do I Know If I Have Prostate Cancer
Finding prostate cancer early is key to good treatment. Some men might not feel any symptoms. But others might notice changes that mean they should see a doctor. Knowing the signs and getting regular checks can help catch it early.

- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination
- Weak or interrupted urine flow
- Blood in urine or semen
Other signs might be:
- Erectile dysfunction
- Pain or discomfort in the pelvic area
- Unexplained weight loss
If you notice any of these, talk to your doctor. They might suggest tests like:
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) blood test
- Digital Rectal Examination (DRE)
- Prostate biopsy
Keep in mind, these signs can also mean other health issues. Men over 50 or those at higher risk should get regular checks. Early detection can greatly improve treatment results and life quality.
“Knowledge is power. Understanding your body and staying vigilant about changes can make all the difference in early prostate cancer detection.”
Early Warning Signs and Common Symptoms
Spotting prostate cancer symptoms early is key to good treatment. Many cases are caught through screening before symptoms show. Knowing the signs helps you watch your health closely.
Urinary Changes and Complications
Urinary changes are often the first sign of prostate problems. You might notice:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination
- Weak or interrupted urine flow
- Painful or burning sensation while urinating
Physical Discomfort and Pain Symptoms
As the disease gets worse, you might feel:
- Pain or discomfort in the pelvic area
- Bone pain, especially in the hips, spine, or ribs
- Pressure or pain in the rectum
Changes in Sexual Function
Prostate cancer can also affect your sex life. Look out for:
- Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection
- Painful ejaculation
- Blood in semen
General Health Changes to Watch For
Sometimes, prostate cancer symptoms are subtle and affect your overall health:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue or weakness
- Swelling in legs or feet
If you’re wondering “how do I know if I have prostate cancer,” these signs can guide you. Remember, these symptoms can also mean other health issues. Always talk to a healthcare provider for a proper check-up and diagnosis.
Risk Factors for Developing Prostate Cancer
Knowing about prostate cancer risk factors is key to preventing and catching it early. Age is a big factor, with men over 50 at higher risk. If your family has a history of prostate cancer, you’re more likely to get it too.
Race also plays a part. African American men are at higher risk than others. They often get more aggressive forms of the disease at a younger age.
Your diet and lifestyle can affect your risk. Eating a lot of red meat and high-fat foods might increase your risk. But, eating more fruits, vegetables, and fish can help prevent prostate cancer.
Being overweight can lead to more aggressive prostate cancers. Staying healthy through exercise and good nutrition can lower your risk. Quitting smoking is also crucial for preventing prostate cancer.
“Knowledge of risk factors empowers men to make informed decisions about their health and screening options.”
Some chemicals, like pesticides or heavy metals, might raise your risk. If you work with these, be careful and take precautions.
While some risks can’t be changed, many can. By focusing on these, men can take steps to prevent prostate cancer and improve their health.
Prostate Cancer Screening Methods and Tests
Early detection is key in fighting prostate cancer. Doctors use different methods to spot signs of the disease. Let’s look at the main ways to screen for prostate cancer.
PSA Testing: Understanding Your Results
The prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test checks PSA levels in your blood. High levels might mean prostate cancer. But, other things can also change PSA levels.
| PSA Level (ng/mL) | Risk Category | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| 0-2.5 | Low | Regular screening |
| 2.6-4.0 | Slightly Elevated | Additional testing |
| 4.1-10.0 | Moderately Elevated | Further evaluation |
| >10.0 | High | Immediate biopsy |
Digital Rectal Examination Process
The digital rectal exam is a physical check. A doctor feels for oddities in the prostate gland. This quick check can find lumps or odd shapes that need more looking into.
Advanced Screening Technologies
New tech is making prostate cancer screening better. This includes MRI scans and biomarker tests. These tools give more detailed info about the prostate. They help doctors make more accurate diagnoses and avoid too many biopsies.
“Advances in screening technologies are transforming how we detect and diagnose prostate cancer, leading to more personalized and effective care for patients.”
Diagnostic Procedures and Confirmation Tests
Diagnosing prostate cancer involves several steps. These steps help confirm if cancer cells are present. Let’s look at the main diagnostic procedures used by healthcare providers.
Prostate Biopsy Procedure
A prostate biopsy is a key test for prostate cancer. It involves taking tiny tissue samples from the prostate gland. These samples are then checked under a microscope for cancer cells.
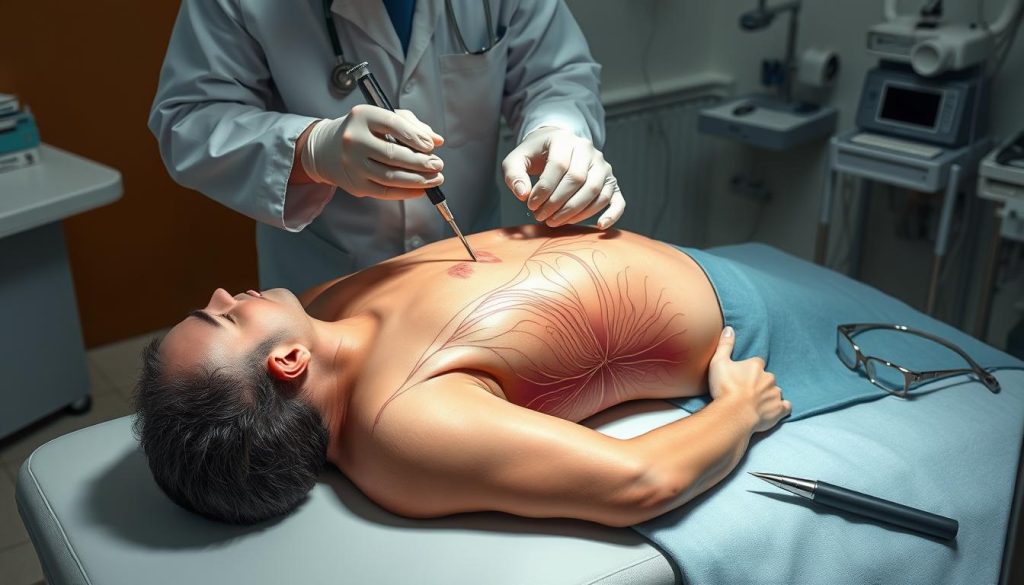
- Numbing the area with local anesthesia
- Inserting a thin needle through the rectum or perineum
- Collecting multiple tissue samples from different parts of the prostate
- Sending samples to a lab for analysis
Imaging Tests and Their Role
Imaging tests are vital in diagnosing prostate cancer. They help doctors see the prostate gland and the tissues around it.
| Imaging Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) | Provides detailed images of the prostate and helps guide biopsies |
| Transrectal Ultrasound | Creates images of the prostate using sound waves |
| CT Scan | Checks if cancer has spread beyond the prostate |
Understanding Test Results
After prostate cancer tests, it’s important to understand the results. Your doctor will explain the findings, including the Gleason score. This score shows how aggressive the cancer is. This information helps decide the best treatment for you.
“A prostate cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming, but understanding the process helps patients make informed decisions about their care.”
When to See a Healthcare Provider
It’s important to know when to see a doctor about prostate cancer. If you’re wondering if you have prostate cancer, it’s time to make an appointment. Men should talk to their doctor about prostate cancer screening around age 50. This is especially true for those at higher risk.
Don’t ignore signs that might mean prostate cancer. Changes in urination, like going more often or having trouble starting or stopping, need a doctor’s check. Pain in the lower back, hips, or pelvis is also a sign to see a doctor. Remember, prostate cancer in its early stages often doesn’t show symptoms, making regular check-ups key.
Your doctor will decide the best screening methods for you. They might suggest a PSA test or a digital rectal exam. If you notice any unusual changes, contact your doctor right away.
FAQ
Q: What are the early signs of prostate cancer?
A: Early signs of prostate cancer include frequent urination and weak urine flow. You might also have trouble starting or stopping urination. Blood in urine or semen and erectile dysfunction are other signs. Pain or discomfort in the pelvic area is also a symptom.
But, many men with early-stage prostate cancer don’t show symptoms. That’s why regular screening is so important.
Q: Who is at risk for developing prostate cancer?
A: Several factors increase your risk of prostate cancer. Age is a big one, especially after 50. African American men are at higher risk. Family history, obesity, and certain genetic mutations also play a role.
Men with these risk factors should talk to their healthcare provider about screening options.
Q: How is prostate cancer diagnosed?
A: Doctors use a few tests to diagnose prostate cancer. The prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test measures PSA levels in the blood. A digital rectal exam (DRE) checks the prostate gland for abnormalities.
If needed, a prostate biopsy takes tissue samples for cancer cell examination. Imaging tests like MRI might also be used.
Q: What is the PSA test and what do the results mean?
A: The PSA test checks prostate-specific antigen levels in the blood. Higher levels might mean prostate cancer, but they can also be caused by other conditions. Normal levels are under 4 ng/mL, 4-10 ng/mL are suspicious, and over 10 ng/mL are high risk.
But, a healthcare professional should interpret these results, considering other factors.
Q: How often should men be screened for prostate cancer?
A: Screening frequency depends on your risk factors. Men should talk to their doctor about screening starting at age 50. African Americans or those with a family history might start earlier, around age 45.
How often you’re screened depends on your PSA levels and overall health.
Q: Can prostate cancer be prevented?
A: There’s no surefire way to prevent prostate cancer, but lifestyle choices can help. Eating well, exercising, and maintaining a healthy weight are good. Some studies suggest certain medications might also help, but talk to a healthcare provider first.
Q: What are the treatment options for prostate cancer?
A: Treatment options vary based on the cancer’s stage, PSA level, and your health. Choices include active surveillance, surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. The best plan is decided with healthcare professionals.
Q: What is active surveillance and who is it suitable for?
A: Active surveillance means watching the cancer without immediate treatment. It’s for men with low-risk, slow-growing cancer. This approach includes regular PSA tests, DREs, and biopsies.
It helps avoid treatment side effects while catching cancer early for effective treatment if needed.