Prostate cancer is a serious disease that affects many men around the world. In its late stages, it can be very harmful. As terminal prostate cancer gets worse, it poses big challenges for those affected and their families.
When prostate cancer reaches its final stages, it spreads to other parts of the body. This can cause serious problems as cancer cells attack important organs. It’s important for patients to understand how advanced prostate cancer affects the body.
We will look at how prostate cancer progresses from early to late stages. We’ll also talk about where cancer often spreads and how long it takes to get there. We’ll discuss how it affects bones, organs, and overall quality of life. This will help shed light on the complexities of this tough condition.
Understanding the Progression of Terminal Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer can become lethal, leading to death. Knowing how it progresses helps patients and caregivers prepare for what might happen.
From Early-Stage to Metastatic Disease
Prostate cancer begins in the prostate gland. As it grows, cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body. This marks the start of metastatic disease, a major cause of death from prostate cancer.
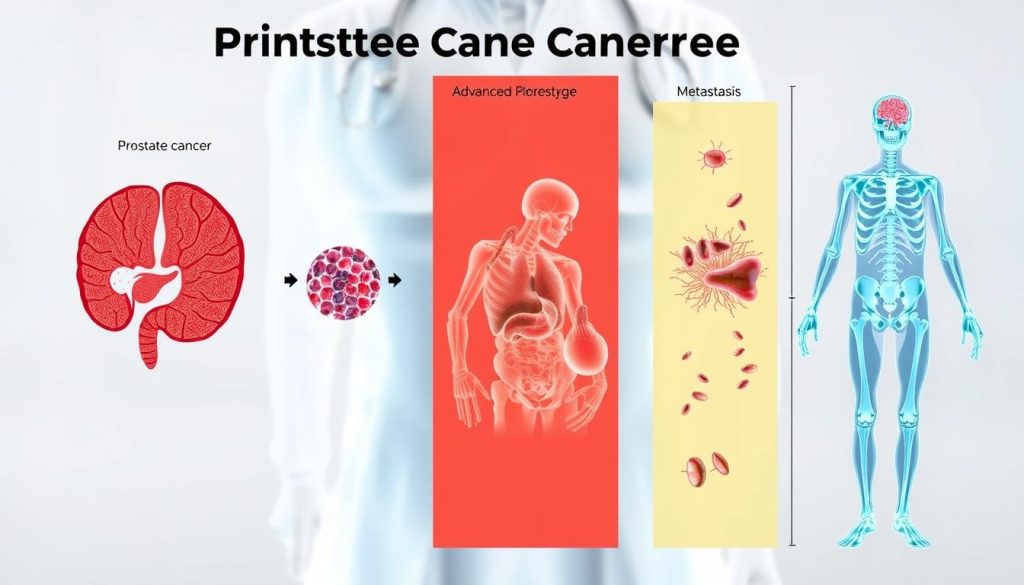
Common Sites of Prostate Cancer Spread
When prostate cancer spreads, it often goes to certain areas:
- Bones (especially spine and pelvis)
- Lymph nodes
- Liver
- Lungs
These tumors can harm organ function, leading to death from prostate cancer.
Timeline of Disease Advancement
How fast prostate cancer progresses varies. Some cases move quickly, while others grow slowly over years. Regular check-ups help track the disease’s progress.
| Stage | Description | Typical Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Localized | Cancer confined to prostate | Months to years |
| Locally Advanced | Spread to nearby tissues | 1-2 years |
| Metastatic | Spread to distant organs | 2-5 years |
Understanding this progression is key. It helps spot signs of worsening disease and make choices about treatment to possibly slow down lethal prostate cancer.
Bone Metastasis and Its Life-Threatening Complications
Bone metastasis is a serious issue when prostate cancer spreads to bones. It can change a patient’s life forever managing end-of-life prostate cancer. Let’s look at how bone metastasis affects patients.
Pathological Fractures and Mobility Issues
Prostate cancer in bones makes them weak, raising the chance of fractures. These breaks can happen during simple tasks, making it hard to move around. Patients might need help walking or even stay in bed, losing their independence and quality of life.
Bone Pain and Quality of Life Impact
Bone metastasis often leads to severe, ongoing pain. This pain can make everyday tasks hard. Managing pain is key in end-of-life care, aiming to keep patients comfortable and dignified.
Spinal Cord Compression Risks
Spinal cord compression is a big risk with bone metastasis. It happens when cancer in the spine presses on the spinal cord, possibly causing paralysis. Finding and treating it early is crucial to avoid lasting nerve damage.
| Complication | Impact | Management Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Pathological Fractures | Reduced mobility, increased pain | Surgical intervention, physical therapy |
| Bone Pain | Decreased quality of life, emotional distress | Pain medication, radiation therapy |
| Spinal Cord Compression | Potential paralysis, neurological deficits | Emergency radiation, steroids, surgery |
Knowing about these complications helps create better care plans for advanced prostate cancer patients. It’s important to tackle both physical and emotional needs in end-of-life care.
Organ Failure Due to Advanced Prostate Cancer
End-stage prostate cancer can spread to vital organs, leading to severe complications and organ failure. As the disease progresses, it impacts the liver, lungs, and brain. This significantly affects their functions and contributes to prostate cancer mortality.

The liver, a crucial organ for detoxification, becomes compromised when cancer cells invade. This invasion can cause:
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes)
- Abdominal swelling
- Severe fatigue
When prostate cancer spreads to the lungs, breathing difficulties arise. Patients may experience shortness of breath, persistent coughing, and chest pain. These symptoms worsen as the disease advances, making everyday activities challenging.
Brain metastases, though less common, can have devastating effects. They may cause:
- Severe headaches
- Seizures
- Cognitive impairment
- Vision problems
As organ function deteriorates, the body’s systems begin to fail, leading to a cascade of complications. This progression significantly impacts quality of life and survival rates, underlining the importance of early detection and treatment in prostate cancer cases.
“Organ failure in advanced prostate cancer is a complex process that requires comprehensive care and support for patients and their families.”
Understanding these complications helps in managing end-stage prostate cancer. It provides appropriate care to improve patients’ comfort and dignity during this challenging time.
Managing Pain and Symptoms in Terminal Stages
When prostate cancer reaches its final stages, the goal is to improve comfort and quality of life. Palliative care is key, offering specialized care to ease pain and symptoms. It aims to enhance the well-being of patients and their families during this tough time.
Pain Management Approaches
Controlling pain is a major focus in the final stages of prostate cancer. Doctors use various treatments, like opioids, nerve blocks, and radiation therapy. These methods help patients stay comfortable and maintain their dignity as the disease advances.
Quality of Life Considerations
In the terminal stages, keeping quality of life high is essential. This includes managing fatigue, urinary issues, and mobility. Palliative care teams work with patients to create personalized treatments. They focus on meeting patients’ goals and values, ensuring the best quality of life until the end.
Emotional and Psychological Support
The emotional impact of advanced prostate cancer can be huge. Support groups, counseling, and spiritual care are crucial. They help patients and families deal with anxiety, depression, and grief. These services offer comfort and a sense of connection during this challenging journey.
FAQ
Q: How does prostate cancer typically progress to its terminal stage?
A: Prostate cancer starts in the early stages and can spread. It first goes to nearby lymph nodes, then to bones. Finally, it reaches vital organs like the liver, lungs, or brain. This can take years, but it varies for everyone.
Q: What are the most common sites of prostate cancer metastasis?
A: The most common places for prostate cancer to spread are bones, especially the spine, pelvis, and ribs. It also goes to lymph nodes, liver, and lungs. Rarely, it reaches the brain.
Q: How does bone metastasis affect a patient’s quality of life?
A: Bone metastasis can cause a lot of pain and increase fracture risk. It also limits how well you can move. This can lead to paralysis and requires pain management and care to stay comfortable.
Q: What are the main complications of advanced prostate cancer?
A: Advanced prostate cancer can cause bone pain and fractures, spinal cord compression, and organ failure. It can also lead to urinary problems and severe fatigue. These issues greatly affect a patient’s health and quality of life.
Q: How does organ failure contribute to mortality in end-stage prostate cancer?
A: Organ failure is a major cause of death in end-stage prostate cancer. Cancer in vital organs like the liver or lungs can fail them. This can lead to multi-organ failure and death.
Q: What pain management approaches are used in terminal prostate cancer?
A: Pain management for terminal prostate cancer includes many methods. This includes opioids, non-opioids, nerve blocks, and radiation therapy. The goal is to reduce pain and side effects, using a mix of treatments for each patient.
Q: What role does palliative care play in managing end-of-life prostate cancer?
A: Palliative care is key in managing end-of-life prostate cancer. It focuses on relieving symptoms, pain, and improving quality of life. It also addresses emotional, psychological, and spiritual needs of patients and their families. Palliative care teams aim to ensure comfort and dignity at the end of life.
Q: How can families prepare for the end-of-life stage of prostate cancer?
A: Families should talk openly with healthcare providers about the prognosis and care options. It’s important to discuss and document the patient’s wishes for treatment and end-of-life care. Seeking emotional support, arranging hospice care, and addressing legal and financial matters are also crucial steps.