Knowing how to diagnose cardiovascular disease is key to keeping your heart healthy. This guide will cover the different ways doctors find and check heart problems. We’ll look at everything from first tests to detailed diagnostic exams.
Spotting symptoms and risk factors early is important for cardiovascular disease diagnosis. Learning about warning signs and screening options helps you take care of your heart. Let’s dive into the important parts of heart disease screening and the steps that come after.
We’ll talk about the tests doctors use to check your heart health. This includes simple physical exams and advanced imaging. Knowing this helps you work better with your doctor and make smart choices for your heart.
Understanding Cardiovascular Disease and Its Warning Signs
It’s important to know the signs of heart disease early. Heart disease can be diagnosed by spotting warning signs. Let’s look at common symptoms, risk factors, and when to seek medical help right away.
Common Symptoms of Heart Disease
Heart disease symptoms can be different for everyone. Some common signs include:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Irregular heartbeat
- Fatigue
- Swelling in legs, ankles, or feet
Risk Factors That Indicate Need for Screening
Some things can make you more likely to get heart disease. If you have any of these, you should get checked:
| Modifiable Risk Factors | Non-Modifiable Risk Factors |
|---|---|
| High blood pressure | Age (65+ for women, 55+ for men) |
| High cholesterol | Family history of heart disease |
| Smoking | Ethnicity |
| Obesity | Gender (higher risk in males) |
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Some heart disease symptoms need quick help. Call emergency services if you have:
- Severe chest pain lasting more than a few minutes
- Difficulty breathing with lightheadedness
- Sudden weakness or numbness in face, arm, or leg
- Severe headache with no known cause
Knowing these signs is key to catching heart problems early. If you see any concerning symptoms, see a doctor for a proper diagnosis.
Initial Physical Examination for Heart Disease
A physical exam is the first step to check your heart health. Doctors use it to find problems and see if more tests are needed.
- Check your blood pressure
- Listen to your heart with a stethoscope
- Examine your neck for enlarged veins
- Look at your skin color
- Check for swelling in your legs and feet
Doctors use a stethoscope to listen to your heart sounds. They look for any unusual sounds. They also check your pulse to see if it’s strong and steady.
“A thorough physical exam can reveal valuable clues about your heart’s health, guiding our next steps in diagnosis and treatment.”
Your doctor might ask you to do simple exercises. They want to see how your heart handles stress. They’ll watch for any signs of trouble, like breathing hard or feeling pain in your chest.
| Examination Component | What It Reveals |
|---|---|
| Blood Pressure Check | Risk of hypertension |
| Heart Auscultation | Presence of murmurs or irregular rhythms |
| Neck Vein Examination | Signs of heart failure |
| Skin Color Assessment | Circulation issues |
| Extremity Check | Fluid retention or circulation problems |
This first physical exam is key to understanding your heart health. It helps your doctor figure out if you need more tests or special care.
How Is Cardiovascular Disease Diagnosed: The Complete Process
Diagnosing cardiovascular disease starts with your first visit to the doctor. Knowing this process helps you get ready and take part in your health care.
First Medical Consultation Steps
Your first meeting with the doctor begins with talking about your symptoms and worries. They will ask about your lifestyle, diet, and how much you exercise. This helps them understand your health and possible risks.
Medical History Assessment
Looking at your medical history is very important. Your doctor will ask about past illnesses, surgeries, and medicines you’re taking. This can show patterns or conditions that might affect your heart.
Family History Evaluation
Your family’s heart health is also important. The doctor will ask about heart problems in your family. This helps find out if you might be at higher risk for certain heart conditions.
With this info, your doctor can decide what to do next. This might include physical exams, blood tests, or special heart scans. Remember, finding problems early is key to keeping your heart healthy.
Essential Blood Tests for Cardiovascular Assessment
Blood tests are key in finding and tracking heart problems. They give insights into your heart’s health. This helps doctors decide on the best treatment.
Cholesterol Panel Testing
A cholesterol panel checks different fats in your blood. It looks at:
- Total cholesterol
- LDL (bad) cholesterol
- HDL (good) cholesterol
- Triglycerides
High LDL and triglycerides raise heart disease risk. Doctors use these numbers to check your heart health.
Cardiac Biomarkers
Cardiac biomarkers are substances in the blood when the heart is hurt. They help spot heart attacks and other heart issues. Common biomarkers include:
| Biomarker | Function |
|---|---|
| Troponin | Detects heart muscle damage |
| CK-MB | Indicates recent heart attack |
| BNP | Assesses heart failure severity |
Blood Sugar and Other Relevant Tests
High blood sugar can harm blood vessels and raise heart disease risk. Doctors might test for diabetes with fasting blood glucose or an A1C test. Other tests include:
- C-reactive protein (CRP) to measure inflammation
- Homocysteine levels to assess blood vessel health
- Lipoprotein(a) to evaluate genetic risk factors

These tests give a full picture of your heart health. Your doctor will use these results to make a treatment plan just for you.
Advanced Cardiac Imaging Techniques
Modern cardiac imaging techniques are key in diagnosing heart disease. These tools give detailed views of the heart’s structure and function. This helps doctors spot and assess heart conditions with great accuracy.
Echocardiography uses sound waves to show the heart in real-time. It’s a non-invasive way to check heart valve function, blood flow, and chamber sizes. Cardiac computed tomography (CT) scans give detailed images of the heart and blood vessels. They’re great for finding coronary artery disease and checking the heart’s anatomy.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) gives high-resolution images of the heart. It’s best for seeing heart muscle damage, congenital heart defects, and cardiac masses. Nuclear imaging, like PET and SPECT scans, uses radioactive tracers to check blood flow and heart function.
| Imaging Technique | Primary Use | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Echocardiography | Heart valve assessment | Real-time imaging, non-invasive |
| Cardiac CT | Coronary artery evaluation | Quick, detailed anatomical images |
| Cardiac MRI | Heart muscle assessment | High-resolution soft tissue imaging |
| Nuclear Imaging | Blood flow analysis | Functional assessment of heart |
These advanced imaging techniques are vital for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. They help doctors create personalized treatment plans. This leads to better outcomes for patients.
Non-Invasive Diagnostic Procedures
Doctors use many non-invasive tests to find heart problems. These tests give important info without needing to cut into the body. They are safe and comfy for patients.
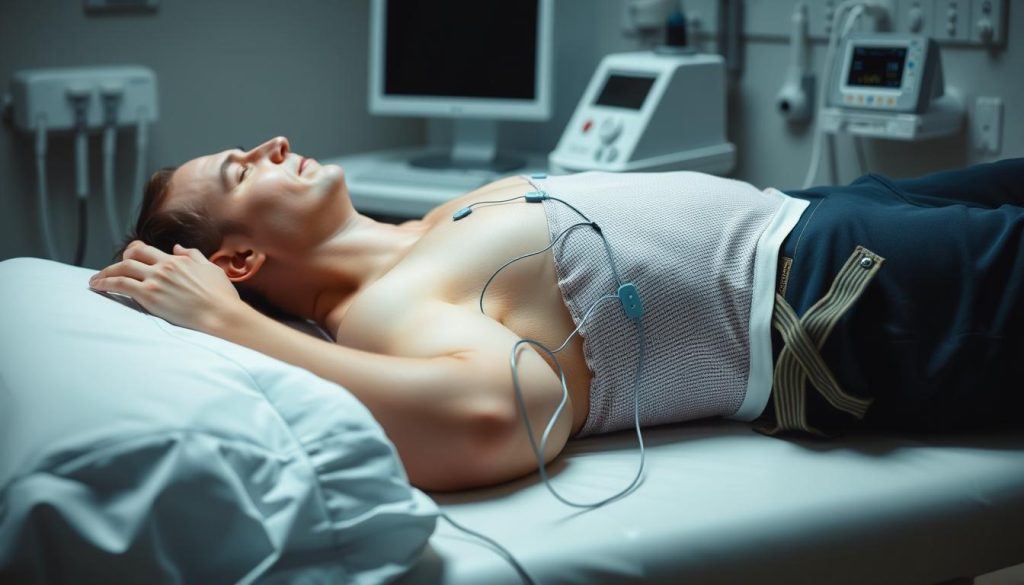
Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG)
An ECG checks the heart’s electrical signals. Small electrodes on the chest, arms, and legs pick up these signals. This test quickly spots heart issues like irregular beats and heart attacks.
Stress Testing Methods
Stress tests see how well the heart works when you’re active. You’ll walk on a treadmill or bike while an ECG tracks your heart. It shows if you have heart problems or how fit your heart is.
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart rhythm problems
- Overall cardiovascular fitness
If you can’t exercise, doctors might use medicine to stress the heart instead.
Holter Monitoring
A Holter monitor is a portable ECG worn for 24 to 48 hours. It records your heart’s activity all day. This helps find heart issues that a regular ECG might miss.
These tests are key for understanding heart health. They help doctors find problems early and create treatment plans that fit each patient’s needs.
Invasive Diagnostic Procedures for Heart Disease
When non-invasive tests aren’t enough, doctors might suggest invasive tests. These tests give a closer look at the heart and blood vessels. They help find and understand complex heart issues.
Cardiac catheterization is a major invasive test. It involves putting a thin tube (catheter) into a blood vessel. This is usually done in the groin or arm and guided to the heart. Doctors can then:
- Measure blood pressure in the heart chambers
- Look for blockages in coronary arteries
- Take tissue samples for biopsy
- Do treatments like angioplasty
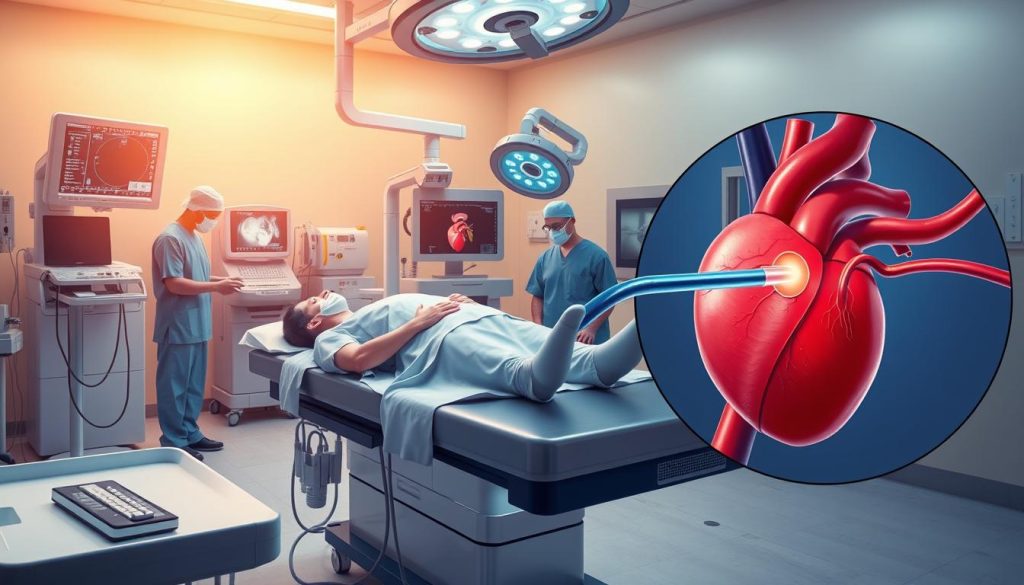
Coronary angiography is another invasive test. It uses X-rays and dye to show detailed images of blood vessels. This helps spot narrowed or blocked arteries that might cause chest pain or heart attacks.
“Invasive tests can be lifesaving when used appropriately. They provide critical information that guides treatment decisions for complex heart conditions.”
These procedures do come with some risks, like bleeding or infection. But, they are usually safe when done by skilled healthcare professionals. The benefits often outweigh the risks for those with serious heart issues.
| Procedure | Purpose | Typical Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiac Catheterization | Assess heart function and blood flow | 30-60 minutes |
| Coronary Angiography | Visualize coronary arteries | 1-2 hours |
| Electrophysiology Study | Evaluate heart rhythm problems | 2-4 hours |
Invasive cardiovascular tests are key in diagnosing and treating heart disease. They offer insights that help doctors make the best decisions for patient care.
Specialized Vascular Disease Screening Methods
Vascular disease screening is key to finding problems beyond the heart. Doctors use different methods to check blood vessels all over the body. These techniques help spot issues early, leading to better treatment.
Ultrasound Assessment
Ultrasound is a painless way to check blood flow. It uses sound waves to make images of arteries and veins. This test can find blockages or narrowing in blood vessels.
It’s often used to check the carotid arteries in the neck and the arteries in the legs.
Angiography Procedures
Angiography gives a detailed look at blood vessels. It involves injecting a special dye into the bloodstream. X-rays then capture images of the dye flowing through the vessels.
This helps doctors see any blockages or abnormalities. While more invasive than ultrasound, angiography provides valuable information for diagnosis.
Venous Testing Options
Venous testing focuses on the veins that return blood to the heart. These tests can find issues like blood clots or valve problems. Common methods include duplex ultrasound and venography.
These tests help doctors plan the right treatment for vein-related conditions.
FAQ
Q: What are the common symptoms of cardiovascular disease?
A: Symptoms of cardiovascular disease include chest pain or discomfort. You might also feel short of breath or have an irregular heartbeat. Fatigue, dizziness, and swelling in the legs or feet are other signs.
But, some people might not notice these symptoms, even in the early stages of heart disease.
Q: When should I seek immediate medical attention for possible heart problems?
A: If you have severe chest pain or trouble breathing, get help right away. Fainting or pain in the arm, jaw, or back are also urgent signs. These could mean you’re having a serious heart problem.
Q: What does a typical physical examination for heart disease involve?
A: A heart disease check-up starts with listening to your heart with a stethoscope. Your blood pressure and pulse are checked too. The doctor looks for signs of fluid buildup or circulation problems.
They might also check for risk factors like obesity and assess your overall health.
Q: How important is family history in diagnosing cardiovascular disease?
A: Family history is very important for heart disease. If your relatives got heart disease young, you might be at higher risk. Your doctor will look at this along with other factors to understand your risk.
Q: What blood tests are typically used to assess heart health?
A: Tests for heart health include a lipid panel for cholesterol and cardiac biomarkers like troponin. C-reactive protein (CRP) tests for inflammation, and blood glucose tests are also key. These tests help understand your risk and can spot heart damage.
Q: What is an echocardiogram and how does it help in diagnosing heart problems?
A: An echocardiogram is an ultrasound of the heart. It shows the heart’s structure and function. It helps find heart problems by checking the heart’s size, how well it works, and looking for damage or poor blood flow.
Q: What is the difference between non-invasive and invasive diagnostic procedures?
A: Non-invasive tests, like ECGs or stress tests, don’t need to go inside the body. They’re safer. Invasive tests, like cardiac catheterization, involve inserting tools into the body. They give more detailed information but are riskier.
Q: How does a stress test work in diagnosing heart disease?
A: A stress test checks how your heart works when you’re active. You’ll walk on a treadmill or bike while your heart is monitored. It shows problems with blood flow that might not show up when you’re resting.
Q: What is Holter monitoring and when is it used?
A: Holter monitoring is wearing a device that records your heart’s activity for 24 to 48 hours. It’s used when your doctor suspects irregular heartbeats or when symptoms don’t show up on a regular ECG.
Q: Are there any risks associated with cardiac catheterization?
A: Cardiac catheterization is usually safe but has some risks. These include bleeding, infection, and allergic reactions. There’s also a small chance of kidney damage, heart attack, or stroke. Your doctor will talk about the risks and benefits with you.