Spotting prostate cancer early is key to effective treatment. As men get older, prostate issues become a big concern. Knowing the signs is the first step to protecting your health.
Prostate cancer symptoms can be hard to notice at first. This makes it important to be aware. Changes in how you pee or feeling pain without reason are signs. Knowing these signs helps men get medical help early. This guide will cover the main signs, risk factors, and how to get checked for prostate cancer. It’s all about taking care of your health.
Understanding Prostate Cancer and Its Impact on Men’s Health
Prostate cancer is a big worry for men’s health. It happens in the prostate, a small gland that’s key for making sperm. Knowing about prostate cancer helps find it early and prevent it.
What is the Prostate and Its Function
The prostate is a small gland, like a walnut, below the bladder. It makes seminal fluid, which helps sperm. If cancer grows in the prostate, it can mess with its work and harm men’s health.
Risk Factors for Developing Prostate Cancer
There are several things that make prostate cancer more likely:
- Age (risk goes up after 50)
- Family history of prostate cancer
- African American ethnicity
- Certain genetic mutations
- Diet full of red meat and fatty foods
Age Groups Most Affected by Prostate Cancer
Older men are mostly hit by prostate cancer. The risk grows with age, as shown below:
| Age Group | Risk of Prostate Cancer |
|---|---|
| Under 40 | 1 in 10,000 |
| 40-59 | 1 in 41 |
| 60-69 | 1 in 16 |
| 70 and older | 1 in 8 |
Knowing these risks and age stats is key for keeping the prostate healthy. Regular check-ups and screenings are vital for men’s health, especially as they get older.
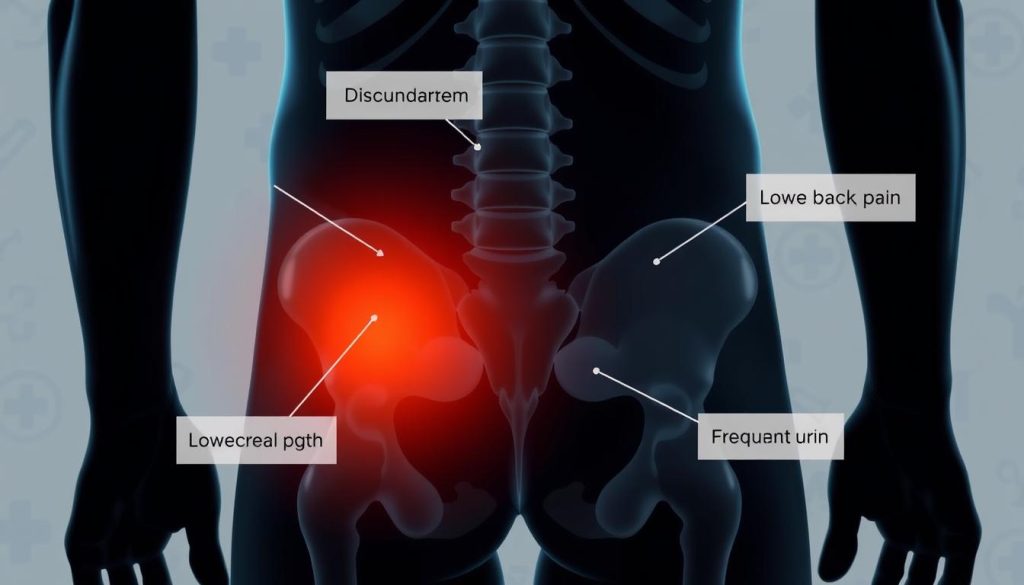
How to Tell if You Have Prostate Cancer: Common Warning Signs
Spotting prostate cancer symptoms early is key to effective treatment. Some men might not notice anything at first. But others might see small changes. Knowing these signs can lead to quick medical help.

Urinary changes are often the first signs of prostate cancer. Men might find themselves needing to pee more, especially at night. They might also struggle to start or stop peeing, have a weak flow, or feel burning while peeing.
Pain in the pelvic area, lower back, or hips could also mean prostate cancer. Some men might feel pain during ejaculation or have trouble getting an erection. These symptoms are important to pay attention to.
Unexplained weight loss or feeling very tired could also be signs. While these can mean many things, seeing a doctor is important if they keep happening.
| Common Signs of Prostate Cancer | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Urinary changes | Very common |
| Pelvic discomfort | Common |
| Sexual function changes | Sometimes present |
| Unexplained weight loss | Less common |
Seeing these symptoms doesn’t mean you definitely have prostate cancer. Many other things can cause similar signs. If you notice any changes, talk to your doctor for a check-up and tests.
“Early detection is key in managing prostate cancer. Don’t hesitate to discuss any unusual symptoms with your doctor, even if they seem minor.”
Early Physical Symptoms That Shouldn’t Be Ignored
Spotting early signs of prostate cancer is key for quick treatment. Some men might not notice anything, but others will see physical changes. It’s vital to watch for these signs and see a doctor if they keep happening.
Urinary Changes and Difficulties
Urinary problems are common signs of prostate cancer. Men might see:
- Frequent urges to urinate, especially at night
- Weak or interrupted urine flow
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination
- Blood in urine or semen

Pain and Discomfort Signals
Pain or discomfort in certain areas might mean prostate cancer:
- Lower back pain
- Hip or pelvic discomfort
- Bone pain, particularly in advanced stages
While many things can cause these symptoms, ongoing pain is a reason to see a doctor.
Sexual Function Changes
Sexual problems can be an early sign of prostate cancer. Men might find it hard to:
- Get or keep an erection
- Feel less interested in sex
- Experience pain or discomfort during ejaculation
These issues can hurt your relationship and life quality. It’s important to talk about them quickly.
Seeing these symptoms doesn’t mean you definitely have prostate cancer. Many other things can cause similar problems. If you notice these changes, see your doctor for a check-up and to feel better.
Prostate Cancer Screening Methods and Detection
Prostate cancer screening is key to finding the disease early. Regular checks can spot cancer before symptoms show. This can lead to better treatment results. Let’s look at the main ways doctors screen for prostate cancer.
Digital Rectal Examination (DRE)
A DRE is a physical check where a doctor feels the prostate gland. They use a gloved, lubricated finger in the rectum. This quick, painless check gives important info.
PSA Blood Test Understanding
The PSA blood test checks PSA levels in the blood. High levels might mean prostate cancer, but other issues can also cause them. Your doctor will look at your PSA levels, age, and health to understand them.
| PSA Level (ng/mL) | Risk Category |
|---|---|
| 0-2.5 | Low |
| 2.6-4.0 | Slightly Elevated |
| 4.1-10.0 | Moderately Elevated |
| Above 10.0 | High |
Advanced Screening Technologies
New tech is making prostate cancer detection better. MRI-guided biopsies take more precise samples. Genetic tests also help figure out cancer risk. These new tools work with old methods to make diagnosis more accurate.
“Early detection through regular screening is key to successful prostate cancer treatment. Don’t hesitate to discuss screening options with your healthcare provider.”
Important Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
When doctors think prostate cancer might be present, they use special tests to find out for sure. These tests help figure out if cancer is there and what treatment should be.
Prostate Biopsy Process
A prostate biopsy is a major step in finding out if you have prostate cancer. Doctors take small tissue samples from the prostate using thin needles. They then look at these samples under a microscope for cancer cells.
Even though it might sound scary, the biopsy is usually quick. It’s done with local anesthesia to make you comfortable.
Imaging Tests for Diagnosis
Imaging tests are very important in finding prostate cancer. MRI scans give detailed pictures of the prostate. They help doctors find any areas that look suspicious.
CT scans show if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. These tests are painless and give doctors important information about the disease.
Interpreting Test Results
It’s important to understand your test results. Doctors use a grading system called the Gleason score to see how aggressive the cancer is. This score, along with other factors, helps figure out the cancer stages.
Working closely with your healthcare team is key. They can help you understand your results and make the best treatment choices.
FAQ
Q: What are the early signs of prostate cancer?
A: Early signs of prostate cancer include frequent urination and weak urine flow. You might also have trouble starting or stopping urination. Blood in urine or semen and pelvic pain are other signs. But, many men with early prostate cancer don’t show symptoms.
Q: At what age should men start getting screened for prostate cancer?
A: Men should talk to their doctor about prostate cancer screening at 50 if they’re at average risk. If you’re African American or have a family history, start the conversation at 45.
Q: What is a PSA test?
A: A PSA test is a blood test that checks for prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels. PSA is a protein made by the prostate gland. High levels can mean cancer or other issues. A doctor must interpret the results.
Q: Can prostate cancer be detected through a urine test?
A: Traditional urine tests don’t find prostate cancer. But, new tests like the PCA3 test analyze urine for cancer markers. They’re used with other tests, not alone.
Q: What happens during a Digital Rectal Examination (DRE)?
A: A DRE involves a doctor feeling the prostate gland through the rectum. They look for size, shape, or texture changes that might show cancer. It’s brief and helps check prostate health.
Q: How accurate is a prostate biopsy?
A: A prostate biopsy is the most surefire way to diagnose cancer. But, its accuracy can vary. Newer methods, like MRI-guided biopsies, might be more accurate. Talk to your doctor about the benefits and risks.
Q: Can lifestyle changes reduce the risk of prostate cancer?
A: Some risk factors can’t be changed, like age and genetics. But, lifestyle choices can help. Eating well, exercising, and avoiding red meat and high-fat dairy might lower risk.
Q: What’s the difference between prostate cancer stages?
A: Prostate cancer stages range from I to IV. Stage I is early and confined to the prostate. Stage II is more advanced but still in the prostate. Stage III means the cancer has spread but not far. Stage IV indicates cancer in distant organs or lymph nodes.
Q: Are there any new technologies for prostate cancer detection?
A: Yes, new technologies are coming. Advanced MRI, PET scans, and genetic tests are being developed. They aim to find cancer early and reduce biopsies.
Q: How often should prostate cancer screening be done?
A: Screening frequency depends on your risk and PSA test results. If PSA is low, screening every 2 years might be okay. Higher levels might need annual checks. Always talk to your doctor for the best plan.