Atherosclerosis is a major concern for heart health. It happens when plaque builds up in arteries. Knowing what causes atherosclerosis is key to managing heart disease risk and keeping our hearts healthy.
Atherosclerosis is a silent disorder that affects millions. It narrows arteries, cutting off blood to important organs. This can lead to serious problems, making it a focus in preventing and treating heart disease.
Seeing atherosclerosis as a heart disease helps us tackle its effects on heart health. Many things, like lifestyle and genetics, play a part in its development. By looking into these, we can learn how to protect our blood vessels and lower heart disease risk.
Understanding Atherosclerosis as a Cardiovascular Disease
Atherosclerosis is a major heart disease affecting millions globally. It causes plaque buildup in arteries, narrowing them and reducing blood flow. Let’s look at how it fits into heart-related issues.
Definition and Classification of Cardiovascular Diseases
Cardiovascular diseases include many heart and blood vessel conditions. These include:
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart valve disorders
- Arrhythmias
- Heart failure
- Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is special because it directly affects the arterial walls.
The Role of Atherosclerosis in Heart Health
Atherosclerosis is key to heart health because it affects blood flow. As plaque builds up, it narrows arteries, making the heart work harder. This strain can lead to serious problems:
| Complication | Description |
|---|---|
| Heart Attack | Blocked coronary artery |
| Stroke | Blocked cerebral artery |
| Peripheral Artery Disease | Reduced blood flow to limbs |
Impact on the Circulatory System
Atherosclerosis affects more than just the heart. It impacts the whole circulatory system, reducing oxygen and nutrient delivery. This can cause muscle pain and even organ damage.
“Atherosclerosis is like rust in your pipes. It builds up slowly but can cause major problems if left unchecked.”
It’s vital to understand atherosclerosis as a heart disease. Recognizing its role in heart health and its effects on the circulatory system helps us prevent and treat it. This way, we can keep our arteries healthy and overall well-being.
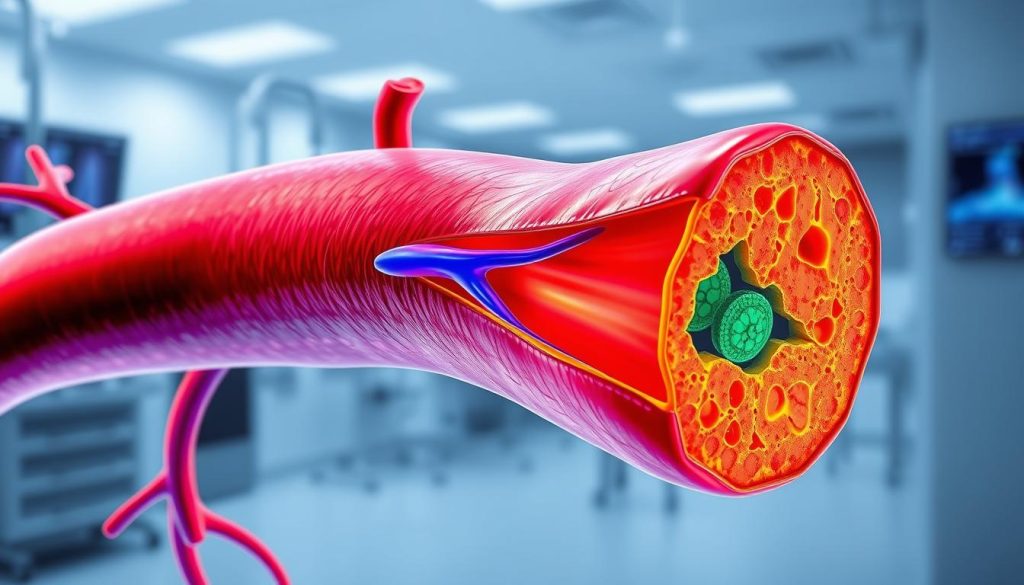
How Plaque Buildup Affects Arterial Health
Plaque buildup in arteries is a silent threat to your heart health. This process, known as atherosclerosis, gradually narrows blood vessels and impairs circulation. It’s important to understand how plaque forms and impacts your arteries to keep your heart and vascular system healthy.
Plaque starts as fatty deposits on artery walls. Over time, these deposits grow, attracting calcium, cellular debris, and fibrous tissue. As plaque accumulates, it reduces the artery’s inner diameter, restricting blood flow. This restriction can lead to serious cardiovascular issues, including heart attacks and strokes.
The effects of plaque buildup on arterial health include:
- Reduced oxygen supply to vital organs
- Increased blood pressure
- Weakened arterial walls
- Higher risk of blood clots
Plaque can become unstable and rupture, triggering immediate blood clot formation. This sudden blockage can cause acute events like heart attacks or strokes. This shows why managing your cardiovascular health is so important.
| Artery Condition | Blood Flow | Cardiovascular Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Healthy Artery | Normal | Low |
| Mild Plaque | Slightly Reduced | Moderate |
| Severe Plaque | Significantly Reduced | High |
Regular check-ups, a heart-healthy diet, and exercise can help prevent plaque buildup. By taking these steps, you can reduce your risk of atherosclerosis and maintain optimal cardiovascular function.
Primary Causes and Risk Factors of Atherosclerosis
Knowing what causes atherosclerosis is key to avoiding heart disease. This condition comes from many factors, like genes and lifestyle.
Genetic Predisposition to Atherosclerosis
Some people are born with genes that make them more likely to get plaque in their arteries. If your family had heart disease early, you might be at risk too. These genes can mess with your cholesterol, blood pressure, and fat processing.
Environmental and Lifestyle Triggers
Our choices in life also play a big part in getting atherosclerosis. Smoking harms blood vessels and causes inflammation. Eating too much saturated fat and not enough fruits and veggies helps plaque grow. Not moving enough and drinking too much alcohol are also big risks.
Medical Conditions That Accelerate Plaque Formation
Some health problems can make atherosclerosis worse. High blood pressure makes arteries work too hard and get damaged. Diabetes messes with cholesterol use, leading to more plaque. Being overweight and having high cholesterol also add to the problem.
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- High cholesterol
By changing our lifestyle and getting medical help, we can lower our risk of atherosclerosis. This can help prevent serious heart disease.
The Connection Between Cholesterol and Arterial Disease
Cholesterol is very important for heart health. Knowing how it affects arteries is key to keeping the heart and blood vessels healthy. Let’s look at how cholesterol levels affect artery health.
HDL vs LDL Cholesterol Balance
The right balance between HDL (good) and LDL (bad) cholesterol is critical. HDL helps clean out arteries, while LDL can clog them. Keeping cholesterol levels in check is vital to avoid artery disease.
Triglycerides and Their Impact
Triglycerides, another blood fat, can also clog arteries when levels are high. They work with LDL to increase artery disease risk. Keeping triglyceride levels in check is important for heart health.
Dietary Influences on Blood Lipids
What we eat greatly affects our blood lipids. Eating foods high in saturated and trans fats can increase LDL cholesterol. On the other hand, foods rich in omega-3s and fiber can boost HDL. Eating a balanced diet is essential for healthy cholesterol levels and artery health.
| Food Type | Effect on Cholesterol | Impact on Cardiovascular Health |
|---|---|---|
| Saturated Fats | Raises LDL | Negative |
| Trans Fats | Raises LDL, Lowers HDL | Very Negative |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Raises HDL | Positive |
| Fiber | Lowers LDL | Positive |
Is Atherosclerosis a Cardiovascular Disease: Expert Insights
Top cardiologists and researchers agree that atherosclerosis is a cardiovascular disease. They base this on studies about how plaque buildup impacts heart health and cardiovascular health.
Dr. Sarah Johnson, a well-known cardiologist at Mayo Clinic, says, “Atherosclerosis is a main cause of cardiovascular diseases. It makes arteries narrow, cutting off blood to important organs.” Many experts share this view.
Recent studies show a clear link between atherosclerosis and other heart conditions. A study with 2,580 participants found that those with early atherosclerosis were at higher risk for heart disease.
“Atherosclerosis is not just a risk factor; it’s a progressive cardiovascular disease that requires early intervention and management.”
Dr. Michael Chen, the lead researcher at Johns Hopkins, emphasizes the seriousness of atherosclerosis for heart health. He and others stress the need for lifestyle changes and regular health checks to keep the heart healthy and stop atherosclerosis from getting worse.
| Expert Opinion | Key Point |
|---|---|
| Dr. Sarah Johnson | Atherosclerosis narrows arteries, reducing blood flow |
| Dr. Michael Chen | Early intervention is key for managing atherosclerosis |
| Mayo Clinic Research | There’s a strong link between atherosclerosis and heart disease risk |
Inflammation’s Role in Atherosclerosis Development
Inflammation is key in atherosclerosis growth. It affects heart health a lot. Knowing how inflammation and atherosclerosis link helps manage heart disease risks.
Inflammatory Markers and Disease Progression
Some blood proteins show inflammation. These signs can tell us how atherosclerosis will grow. For example, high C-reactive protein levels mean higher heart risk. Doctors use these signs to check heart health and decide treatments.
Studies link inflammation and atherosclerosis closely. Chronic inflammation harms artery walls, making them prone to plaque. This speeds up atherosclerosis, risking heart problems.
Immune System Response in Plaque Formation
The immune system is key in plaque growth. When artery walls get hurt, immune cells go there. These cells get stuck in the plaque, making it bigger. This can lead to unstable plaques that might burst.
- White blood cells accumulate in artery walls
- Immune cells release substances that promote plaque growth
- Chronic inflammation sustains the atherosclerotic process
Controlling inflammation is vital for heart health. Changing lifestyle and using anti-inflammatory drugs can slow atherosclerosis. By tackling inflammation and other risk factors, we can protect our hearts.
Modern Diagnostic Methods for Atherosclerosis
Finding atherosclerosis early is vital for heart health. Today, doctors have advanced tools for diagnosing it. Let’s look at these methods and how they check heart and blood vessel health.
Imaging Technologies and Their Applications
Doctors now have powerful tools to see inside arteries. These include:
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to create pictures of arteries
- CT scans: Provide detailed cross-sections of blood vessels
- MRI: Gives clear images of soft tissues and blood flow
These tests help spot plaque buildup before symptoms start. They’re vital for early atherosclerosis diagnosis and treatment planning.
Blood Tests and Biomarkers
Simple blood tests can reveal a lot about cardiovascular health. Doctors check for:
| Biomarker | What It Measures | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Cholesterol levels | LDL, HDL, total cholesterol | High levels increase atherosclerosis risk |
| C-reactive protein | Inflammation in the body | Can indicate artery inflammation |
| Lipoprotein(a) | Specific type of LDL | Linked to higher heart disease risk |
Physical Examination Techniques
Hands-on checks are also important. Doctors listen to heart sounds, check pulses, and look for signs of poor circulation. These simple steps, combined with advanced tests, create a full picture of a person’s cardiovascular health.
By using these methods, healthcare providers can catch atherosclerosis early. This early detection is key to preventing serious heart problems and keeping arteries healthy.
Treatment Approaches and Medical Interventions
Doctors aim to slow or stop plaque buildup in atherosclerosis. They start with lifestyle changes for heart health. This includes a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, and quitting smoking.
Medication is also key. Statins help lower cholesterol levels. Blood pressure medicines reduce artery wall strain. Blood thinners prevent clots in narrowed arteries.
Surgical procedures are needed in severe cases. Angioplasty and stenting open blocked arteries. Bypass surgery creates a new blood flow path. New therapies, like targeted anti-inflammatory drugs, are also being explored.
Managing atherosclerosis long-term is vital. Regular check-ups, ongoing medication, and lifestyle changes are essential. Working with healthcare providers helps patients manage their condition and improve heart health.
FAQ
Q: Is atherosclerosis considered a cardiovascular disease?
A: Yes, atherosclerosis is a cardiovascular disease. It happens when plaque builds up in arteries. This affects the heart and blood vessels.
Atherosclerosis is often the main cause of other heart diseases. This includes coronary artery disease and peripheral artery disease.
Q: What are the main causes of atherosclerosis?
A: Atherosclerosis is caused by genetics, lifestyle, and some medical conditions. High cholesterol and blood pressure are big factors. Smoking, obesity, diabetes, and not exercising also play a role.
A diet full of saturated fats and chronic inflammation also contribute. Oxidative stress is another important factor.
Q: How does plaque buildup affect arterial health?
A: Plaque buildup in arteries is a big problem. It narrows the arteries and cuts down blood flow. This can harm vital organs.
It can lead to heart attacks and strokes. If the plaque ruptures, it can cause blood clots. These clots can block arteries and be deadly.
Q: What’s the connection between cholesterol and atherosclerosis?
A: Cholesterol is key in atherosclerosis. High LDL cholesterol helps form plaque in arteries. HDL cholesterol helps remove excess cholesterol.
An imbalance of LDL cholesterol increases atherosclerosis risk. High triglycerides also play a part in the disease.
Q: How does inflammation contribute to atherosclerosis?
A: Inflammation is a big player in atherosclerosis. It damages artery linings, making them more prone to plaque. It also makes plaques grow and become unstable.
High levels of inflammatory markers like CRP in the blood are linked to atherosclerosis risk. They also increase the chance of heart events.
Q: What diagnostic methods are used to detect atherosclerosis?
A: To find atherosclerosis, doctors use several methods. They include:
– Imaging technologies like coronary calcium scans and CT angiography
– Blood tests to check cholesterol and inflammatory markers
– Physical exams to measure blood pressure and listen for artery sounds
– Stress tests to see how the heart works during exercise
– Angiograms for detailed blood vessel images
Q: What are the main treatment options for atherosclerosis?
A: Treating atherosclerosis involves lifestyle changes and medicine. Important steps include:
– Eating a heart-healthy diet and exercising regularly
– Quitting smoking and managing stress
– Taking statins to lower cholesterol and blood pressure medications
– In severe cases, surgery like angioplasty or bypass surgery may be needed
– Regular check-ups to monitor the disease and adjust treatment
Q: Can atherosclerosis be reversed?
A: Atherosclerosis can’t be completely reversed. But, with the right treatment, its progress can be slowed or stopped. Lifestyle changes and medicine can help stabilize plaques and improve blood flow.
In some cases, aggressive treatment can even reduce plaque buildup. But, prevention and early treatment are key to managing atherosclerosis.
Q: Are there any natural remedies that can help prevent or manage atherosclerosis?
A: Natural remedies can help with atherosclerosis, but always talk to a doctor first. A Mediterranean diet, regular exercise, and stress reduction can help. Omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidant-rich foods are also beneficial.
Remember, these should be used along with, not instead of, professional medical advice and treatment.