Understanding the link between cerebrovascular accidents (CVAs) and heart disease is key to heart health. CVAs, or strokes, affect blood vessels in the brain. But how do they relate to heart disease?
Strokes and heart problems are closely connected. Both deal with the cardiovascular system, which includes the heart and blood vessels. This article looks into the connection between CVAs and heart health. It highlights their shared risk factors and prevention strategies.
Exploring the facts about cerebrovascular accidents and their effect on heart health is our goal. We aim to give valuable insights for those worried about their heart and brain health. Let’s find out the truth about CVAs and their role in cardiovascular diseases.
Understanding CVA: Definition and Medical Classification
Cerebrovascular accident, or stroke, is a serious brain condition. It affects the brain’s blood supply. This section will cover what CVA means, its types, and related medical terms.
What Cerebrovascular Accident Means
A cerebrovascular accident happens when blood flow to the brain is cut off or reduced. This lack of blood and oxygen kills brain cells quickly. The term “cerebrovascular” talks about the brain’s blood vessels. “Accident” shows it happens suddenly.
Types of CVA and Their Characteristics
CVA can be divided into two main types:
- Ischemic stroke: This is when a blood vessel in the brain gets blocked.
- Hemorrhagic stroke: It’s caused by a blood vessel in the brain bursting.
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA), or mini-stroke, is a short blockage of brain blood flow. Its symptoms are like a stroke but last less than 24 hours.
Medical Terms and Common Names for CVA
In medical talk, CVA is called a “stroke.” Other names include:
- Brain attack
- Cerebral infarction (for ischemic stroke)
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (for hemorrhagic stroke)
Knowing these terms helps patients and caregivers understand medical talks and plans better.
Is CVA a Cardiovascular Disease: Understanding the Connection
CVA, or cerebrovascular accident, is closely tied to cardiovascular disease. Both affect the circulatory system, impacting heart health and blood flow. It’s key to understand this connection for prevention and treatment.
The cardiovascular system includes the heart and blood vessels. When we talk about cardiovascular disease, we often think of heart attacks. But CVA, or stroke, is also part of this group.
CVA happens when blood flow to the brain is disrupted. This can be due to a blockage (ischemic stroke) or bleeding (hemorrhagic stroke). Both types are linked to blood vessel health and overall heart function.
“Understanding the connection between CVA and cardiovascular disease is key to protecting both brain and heart health.”
Risk factors for CVA often overlap with heart disease. These include:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Diabetes
By tackling these risk factors, you can boost your heart health. This reduces the risk of heart disease and CVA. Regular check-ups, a healthy diet, and exercise are vital for strong blood vessels and a healthy heart.
The Relationship Between Heart Health and Cerebrovascular Events
Heart health is key to avoiding cerebrovascular events. Our heart and brain are connected through our blood vessels. This connection is essential for our overall health. Let’s look at how we can keep both organs in top shape.
How Heart Function Affects Brain Blood Flow
A healthy heart pumps blood well to the brain. If the heart weakens, blood flow to the brain can drop. This can cause serious problems. Keeping your heart healthy ensures your brain gets the oxygen and nutrients it needs.
Shared Risk Factors Between CVA and Heart Disease
Many factors that increase the risk of stroke and heart disease are the same. These include high blood pressure, smoking, being overweight, and diabetes. By tackling these issues, you can boost your heart health and lower stroke risk.
| Risk Factor | Impact on Heart | Impact on Brain |
|---|---|---|
| High Blood Pressure | Strains heart muscle | Damages blood vessels |
| Smoking | Narrows arteries | Reduces oxygen supply |
| Obesity | Increases workload | Affects blood flow |
Cardiovascular System’s Role in Stroke Prevention
A strong heart is vital for preventing strokes. Regular exercise makes your heart stronger and improves blood flow. It also helps keep blood pressure healthy. Adding a healthy diet to your routine can greatly reduce your risk of heart disease and strokes.
Looking after your heart is a big step towards protecting your brain. By focusing on heart health, you’re also working on preventing strokes and improving your overall health.
Common Risk Factors Leading to CVA Development
Knowing about CVA risk factors is key to preventing strokes and heart disease. Many things can raise your risk of having a cerebrovascular accident. Let’s look at these factors to help you stay healthy.
Age and genetics are big factors in CVA risk. As we age, our risk goes up. If your family has a history of stroke or heart disease, you might be at higher risk too.
Our lifestyle choices also play a big part. Smoking, drinking too much alcohol, and not being active are big risks. Eating too much saturated fat and sodium can lead to high blood pressure and hardening of arteries, making things worse.
Medical conditions can also raise your risk. High blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol are big culprits. These conditions can damage blood vessels, making them more likely to block or burst.
| Risk Factor | Impact on CVA Risk | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Hypertension | High | Regular blood pressure checks, medication if needed |
| Smoking | High | Quit smoking programs, nicotine replacement therapy |
| Obesity | Moderate | Balanced diet, regular exercise |
| Diabetes | High | Blood sugar management, healthy lifestyle |
By tackling these risk factors, you can lower your chance of having a CVA. Regular health checks, eating right, and staying active are important for preventing strokes.
Identifying Early Warning Signs of CVA
Spotting CVA symptoms early can be a lifesaver. It’s key to know the signs for quick emergency care. Let’s look at the warning signs and when to get help.
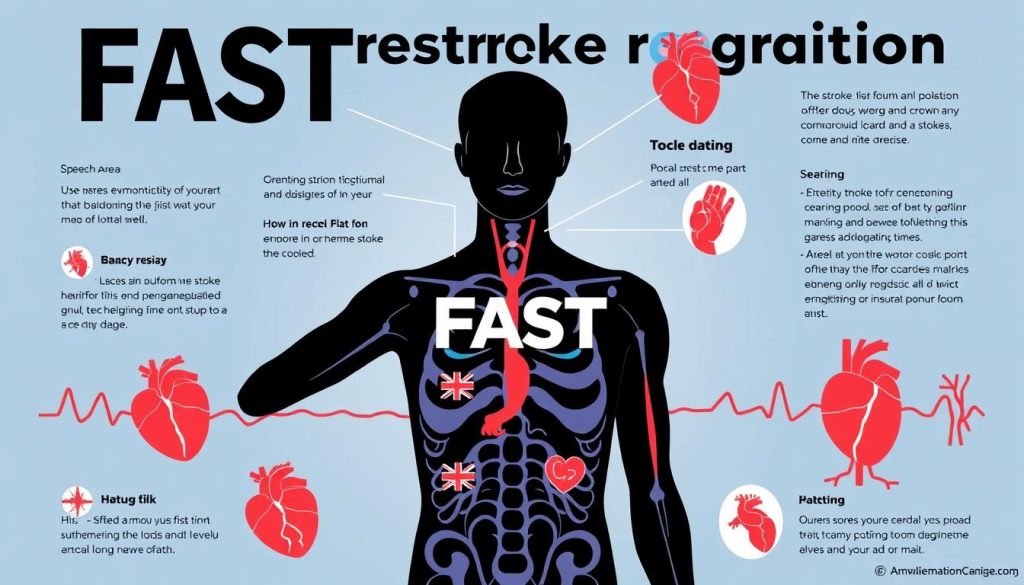
FAST Method for Stroke Recognition
The FAST method is a simple way to spot stroke symptoms:
- Face: Ask the person to smile. Does one side of the face droop?
- Arms: Can they raise both arms? Does one arm drift downward?
- Speech: Is their speech slurred or strange?
- Time: If you observe any of these signs, call 911 immediately.
Lesser-Known Symptoms to Watch For
While FAST covers major signs, other CVA symptoms include:
- Sudden severe headache
- Unexplained dizziness or loss of balance
- Sudden confusion or trouble understanding
- Vision problems in one or both eyes
When to Seek Emergency Care
If you think someone might be having a stroke, don’t wait. Every minute is critical for treatment. Call 911 if you see any stroke symptoms, even if they seem minor. Quick emergency care can greatly help CVA patients.
| Symptom | Action |
|---|---|
| Any FAST signs | Call 911 immediately |
| Sudden severe headache | Seek emergency care |
| Unexplained dizziness | Contact medical help |
| Sudden vision problems | Go to ER promptly |
Prevention Strategies for CVA and Heart Disease
Preventing CVA and heart disease is key to staying healthy. Making lifestyle changes can greatly reduce your risk. By adopting healthy habits, you can lower your chances of getting these conditions.
Eating a balanced diet with lots of fruits, veggies, and whole grains is good for your heart. It’s also important to cut down on saturated fats and salt. Aim for at least 150 minutes of exercise each week to strengthen your heart and improve blood flow.
Quitting smoking is a big step in preventing heart disease. Smokers are at a higher risk for CVA and heart problems. If you’re trying to quit, talk to your doctor about ways to help.
Keeping a healthy weight is also important. Being overweight can put extra strain on your heart. Regular health screenings can catch problems early, just like with colon cancer.
“Prevention is better than cure. Small changes in your daily routine can make a big difference in your heart health.”
Managing stress is often overlooked but is very important. Activities like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga can help. Getting enough sleep is also key for heart health.
| Prevention Strategy | Benefits | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Healthy Diet | Lowers cholesterol and blood pressure | Eat more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains |
| Regular Exercise | Strengthens heart and improves circulation | 150 minutes of moderate activity per week |
| Quit Smoking | Reduces risk of CVA and heart disease | Seek support from healthcare providers |
| Weight Management | Decreases strain on cardiovascular system | Maintain a BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 |
| Stress Reduction | Lowers blood pressure and heart rate | Practice meditation or deep breathing daily |
By making these lifestyle changes, you can improve your heart health. Remember, small steps can lead to big improvements in your overall well-being.
Treatment Approaches for CVA Patients
CVA treatment includes many steps, from emergency care to long-term rehab. The main goal is to lessen brain damage and help with stroke recovery. Let’s look at the different stages of care for CVA patients.
Emergency Medical Interventions
When a CVA happens, time is very important. Emergency care aims to get blood flowing to the brain again. This might involve drugs to dissolve clots or surgery to remove blockages. Quick action can greatly improve results and lessen damage.
Long-term Recovery Methods
After the emergency, treatment moves to long-term recovery. This phase includes managing medications, making lifestyle changes, and regular medical check-ups. Patients work with healthcare teams to prevent future strokes and handle related health problems.
Rehabilitation Options and Timeline
Rehabilitation is key for stroke recovery. It helps patients regain lost skills and adjust to new challenges. The rehab timeline varies but usually starts soon after the stroke and can last for months or years.
| Rehabilitation Type | Focus Area | Typical Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Therapy | Motor skills, balance | 3-6 months |
| Occupational Therapy | Daily living activities | 2-4 months |
| Speech Therapy | Communication, swallowing | 4-8 months |
| Cognitive Therapy | Memory, problem-solving | 6-12 months |
Every patient’s journey through CVA treatment and rehab is different. Success depends on the stroke’s severity, the patient’s health, and their dedication to recovery. With the right care and support, many CVA survivors regain independence and improve their quality of life.
Lifestyle Modifications to Reduce CVA Risk
Changing your daily habits can greatly lower your risk of a cerebrovascular accident (CVA). A healthy lifestyle is essential for good heart health and stroke prevention.
Eating a balanced diet is a key way to reduce CVA risk. Include lots of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. It’s also important to limit salt, saturated fats, and processed foods for your heart’s sake.
Regular exercise is also vital. Try to do at least 150 minutes of moderate activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity weekly. Activities like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling are great options.
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques or meditation
- Get enough sleep – aim for 7-9 hours per night
- Keep your weight in a healthy range
- Control chronic conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes
By making these lifestyle changes, you can significantly lower your CVA risk. Remember, even small steps can make a big difference in your heart health over time.
Latest Medical Advancements in CVA Treatment
The field of CVA treatment is growing fast, giving new hope to stroke survivors. Recent years have brought big steps forward in stroke therapy and medical innovations. These changes are making a big difference in how patients are cared for and their outcomes.
Innovative Therapeutic Approaches
New therapies are changing how we treat strokes. Neuromodulation techniques help the brain heal better. Virtual reality rehabilitation helps patients get back motor skills in fun, interactive ways.
New Medications and Their Effects
New medicines are bringing hope to CVA patients. New anticoagulants lower stroke risk with fewer side effects. Neuroprotective drugs protect brain cells during strokes, reducing damage. Stem cell therapies might help grow back damaged brain tissue.
Technological Breakthroughs in Treatment
Medical innovations are changing stroke care. New imaging techniques help doctors diagnose and treat more accurately. Robotic-assisted surgery makes complex procedures safer. AI helps find strokes early and tailor treatments.
| Technology | Application | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| AI Imaging | Rapid Stroke Detection | Faster Diagnosis |
| Robotic Surgery | Minimally Invasive Procedures | Reduced Recovery Time |
| VR Therapy | Motor Skill Rehabilitation | Improved Engagement |
These new treatments in CVA care offer hope for better recovery and life quality for stroke survivors. As research keeps going, the future of stroke therapy looks very promising.
Impact of CVA on Overall Cardiovascular Health
A cerebrovascular accident (CVA) can affect a person’s heart health a lot. The damage from a stroke can spread to the whole circulatory system. This means patients are at a higher risk for more heart problems, making ongoing care very important.
The heart and brain work together closely. Damage to one can hurt the other. CVA survivors might see changes in heart rhythm and blood pressure. These changes can increase the risk of heart disease.
To keep the heart healthy after a CVA, a full plan is needed. This includes regular doctor visits, taking medicine as prescribed, and making lifestyle changes. Doctors suggest eating heart-healthy foods, exercising, and finding ways to reduce stress. Taking care of both brain and heart health can improve a patient’s life a lot.
Knowing how CVA affects heart health helps patients and their families. It shows the need for a complete care plan and preventive steps. With the right care and support, many CVA survivors can lower their risk of more heart problems and stay healthier.
FAQ
Q: Is CVA considered a cardiovascular disease?
A: Yes, CVA (Cerebrovascular Accident) is a cardiovascular disease. It affects the brain’s blood vessels. It’s closely linked to heart health, sharing many risk factors with other heart conditions.
Q: What’s the difference between CVA and stroke?
A: There is no difference. CVA (Cerebrovascular Accident) is another term for a stroke. Both refer to brain damage from interrupted blood flow.
Q: What are the main types of CVA?
A: There are two main types of CVA. Ischemic stroke is caused by a blood clot. Hemorrhagic stroke is caused by a blood vessel rupture.
Q: How does heart function affect the risk of CVA?
A: Heart function greatly affects CVA risk. Poor heart health can lead to conditions like atrial fibrillation. These increase the risk of blood clots and stroke.
Q: What are the common risk factors for CVA?
A: Common risk factors include high blood pressure and smoking. Diabetes, high cholesterol, and obesity also increase risk. Physical inactivity and family history of stroke or heart disease are factors too.
Q: How can I recognize the signs of a CVA?
A: Use the FAST method to spot CVA signs: Face drooping, Arm weakness, Speech difficulty. Time to call emergency services is key. Other signs include sudden severe headache and vision problems.
Q: Can CVA be prevented?
A: While not all CVAs can be prevented, you can lower your risk. Maintain a healthy lifestyle and manage conditions like hypertension. Exercise regularly, eat well, and don’t smoke.
Q: What are the immediate treatment options for CVA?
A: Immediate treatment varies by type. For ischemic strokes, clot-busting drugs or mechanical thrombectomy may be used. Hemorrhagic strokes focus on controlling bleeding and reducing brain pressure.
Q: How long does recovery from a CVA typically take?
A: Recovery time varies by stroke severity and location. Initial recovery happens in months, but ongoing therapy can take years.
Q: Are there any new treatments for CVA?
A: Yes, new treatments are emerging. Advances include better clot-busting drugs and faster diagnosis with advanced imaging. New rehab technologies like robotic therapy and virtual reality are also being explored.
Q: How does having a CVA affect long-term cardiovascular health?
A: A CVA can significantly affect long-term heart health. It raises the risk of future strokes and may cause blood pressure or heart rhythm issues. Ongoing management and lifestyle changes are key to maintaining heart health post-CVA.