Dealing with inguinal pain as a woman can be scary and confusing. Female groin discomfort on the left side raises many health questions. This article aims to uncover the reasons behind left inguinal pain in women and how to find relief.
We focus on women’s unique body needs. We’ll look at medical issues and lifestyle changes that help. Our goal is to help you understand and manage this pain.
This guide aims to help you understand and prevent future pain. We’ll walk you through finding the cause and offer solutions. We want to give you the tools to deal with this common issue.
Understanding Female Inguinal Pain
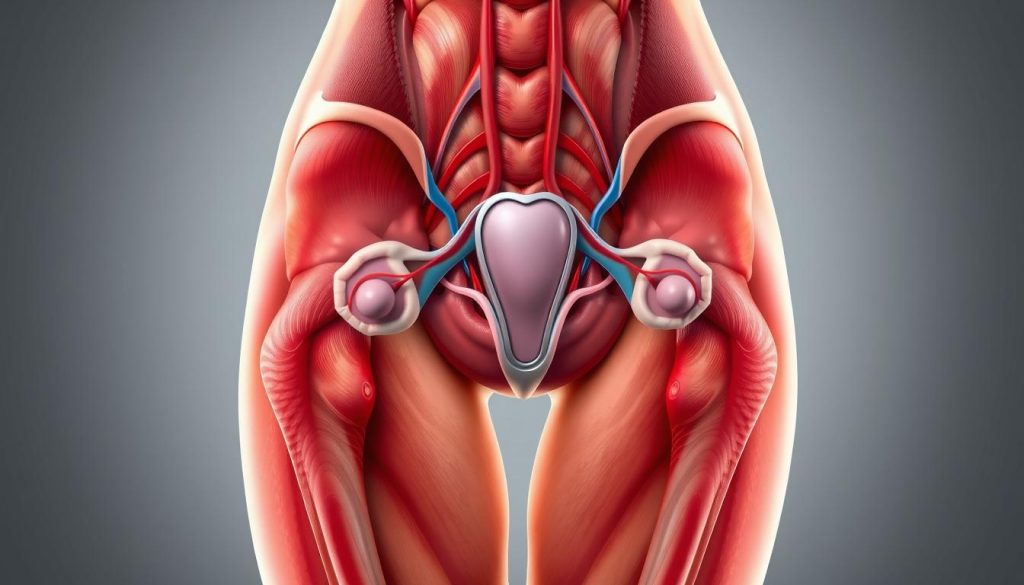
To fully understand inguinal area pain in females, knowing the anatomy of the female groin is key. This knowledge helps spot issues and grasp the symptoms of this pain.
Anatomy of the Female Groin Area
The female groin area has layers like skin, fat, muscles, and connective tissues. These layers protect nerves, blood vessels, and lymphatics. The round ligament of the uterus, running through the groin, is a common pain point.
Common Symptoms Associated with Inguinal Pain
Symptoms of inguinal pain in women are clear and can signal what’s wrong. Common signs include:
- Sharp or stabbing pain during activities like coughing, bending, or lifting heavy objects
- A dull ache that gets worse by the end of the day or after standing for a long time
- Visible swelling or bulge in the groin, which might mean a hernia
- Redness and warmth, signs of inflammation or infection
- Burning or discomfort in the groin, getting worse with activity
Spotting these signs early helps in diagnosing and treating pain in the left inguinal area. This approach can greatly improve the lives of many women suffering from this pain.
Potential Causes of Pain in Left Inguinal Area Female
Understanding the causes of female groin discomfort is key to managing this common issue. Knowing what causes female groin pain left side can improve life quality and guide treatment. We explore both common and rare causes of inguinal pain in women.
- Musculoskeletal issues: Often due to overuse or strain during physical activities.
- Gynecological conditions: Includes ovarian cysts or, in more severe cases, ectopic pregnancies.
- Intestinal disorders: Such as hernias or bowel obstructions, which directly press on the groin area.
- Urinary tract problems: Including infections or kidney stones that can refer pain to the groin.
This list is just a start for understanding inguinal pain in women. It shows why getting a medical diagnosis and treatment is so important.
| Condition | Description | Commonality |
|---|---|---|
| Musculoskeletal Strain | Strain or injury to muscles or tendons in the groin region. | Highly common in physically active individuals. |
| Ovarian Cysts | Fluid-filled sacs within or on the surface of an ovary. | Common in women of reproductive age. |
| Inguinal Hernia | A portion of the intestine bulges through the abdominal wall in the groin area. | Less common in women than men, but a notable cause. |
The table shows main medical conditions that can cause causes of female groin discomfort. Each condition affects women in unique ways. So, getting personalized medical advice is vital for managing and recovering from these issues.
Diagnosing Left Inguinal Pain in Women
Finding the cause of left inguinal pain in women needs a detailed check-up and imaging tests. It’s key to know what’s causing the pain to treat it well.
Physical Examination Procedures
Healthcare providers start by feeling the area for swelling or tenderness during the physical examination groin pain. They then check if moving around makes the pain worse. Special tests help pinpoint the pain, helping to understand female groin discomfort better.
Imaging Tests and Their Role in Diagnosis
If the physical check-up doesn’t show enough, doctors might use imaging tests inguinal pain. These tests show the soft tissues, bones, and organs in the groin. An ultrasound for groin pain is often first because it’s good at showing soft tissues and doesn’t hurt.
For a closer look, an MRI for female groin discomfort might be needed. It gives a detailed view that can spot problems ultrasound can’t.
| Test Type | Utilization | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Ultrasound | Initial assessment | Non-invasive, no radiation |
| MRI | Detailed imaging | Comprehensive view, high contrast resolution |
Inguinal Pain Women: When to Seek Medical Attention
If you have female left inguinal pain concerns, knowing when to get medical help for inguinal pain is key. This guide helps you know when to visit a doctor for groin pain. It also tells you when normal discomfort turns into a serious issue.
- Severity of Pain: Severe pain that makes daily tasks hard or impossible means it’s time to see a doctor.
- Sudden Onset: Pain that starts suddenly and without warning needs quick medical check-up. This could be a sign of hernias or infections.
- Accompanying Symptoms: Feeling feverish, nauseous, or vomiting with groin pain could mean an infection or urgent issue.
- Persistent Discomfort: Pain that doesn’t get better with rest or over-the-counter meds in a few days needs a doctor’s look.
Knowing when to see a doctor for groin pain is key to staying healthy and avoiding bigger problems. Ignoring severe or ongoing pain can make things worse. This might need more serious treatments.
| Signal | Description | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Pain | Constant discomfort no matter the position or time | Seek immediate medical consultation |
| Increasing Intensity | Pain gets worse over a short time | Visit emergency room or urgent care |
| Impaired Movement | Hard or impossible to walk, sit, or lie down comfortably | Consult healthcare provider promptly |
Waiting too long to get medical help for inguinal pain can cause serious problems. This is true for pain linked to reproductive or digestive issues. If unsure about symptoms, always talk to a doctor for a proper diagnosis.
Common Conditions Leading to Female Groin Pain Left Side
It’s important to know why women get groin pain. Issues like inguinal hernias and ovarian cysts can really hurt and affect daily life. Both can make it hard to enjoy everyday activities.
Hernias and Their Impact on Females
An inguinal hernia in females is not as common as in men but is a big worry. It happens when something inside pushes through a weak spot in the muscle or tissue. A left side groin hernia in women can hurt a lot, making it hard to lift or stand for long.
Things like pregnancy, coughing a lot, and lifting heavy can increase the risk of getting a hernia. It’s key to catch it early and treat it to avoid bigger problems like when the blood supply gets cut off.
Ovarian Cysts: A Hidden Culprit
Ovarian cysts are like fluid-filled bags on the ovaries. They might not cause any symptoms, but big ones can hurt a lot. The correlation between ovarian cysts and left inguinal pain happens when a cyst presses on nearby tissues, causing pain in the groin or femoral area.
These cysts can mess with how the ovaries work and sometimes lead to serious problems like twisting or bursting. If you have sudden, bad female groin discomfort, get checked out fast to make sure it’s not something serious.
Knowing about these issues and their symptoms helps women get help sooner. This way, they can find relief from the female groin pain caused by these common problems.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Inguinal Area Pain in Females
Looking into non-surgical options is key for treating female groin pain well. This part talks about treatments for inguinal pain that don’t need surgery. It covers ways to ease pain and help the groin area heal without surgery.
Physical Therapy as a Treatment Option
Physical therapy is a big help for groin pain. It uses special exercises to make muscles stronger and more flexible. This helps lessen pain. Other methods like ultrasound and electrical stimulation can also help speed up healing.
Pain Management Techniques
There are many ways to ease inguinal pain without surgery. Anti-inflammatory drugs, ice packs, and heat therapy are some of them. Also, making lifestyle changes like avoiding painful activities and doing gentle exercises can help manage symptoms well.
| Technique | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Therapy | Includes exercises and manual therapy | Strengthens muscles, reduces pain |
| Medication | Anti-inflammatories and pain relievers | Reduces inflammation and pain levels |
| Heat/Ice Therapy | Application of heat packs or ice packs | Alleviates acute pain and reduces swelling |
| Lifestyle Changes | Modifications in daily activities | Prevents aggravation of symptoms |
Trying these non-surgical methods helps manage female groin pain. It also boosts pelvic health, improving life quality for those with inguinal pain.
Surgical Interventions for Left Inguinal Region Pain
Surgery is a key option for severe or chronic left inguinal region pain. Healthcare professionals may suggest different surgeries based on the pain’s cause. This section will look at the available surgeries, what patients can expect, and how much relief they might get.
Types of Surgeries and Expected Outcomes
For women with persistent groin pain, surgery is often a necessary step. Procedures like hernia repair and tissue removal can greatly reduce inguinal pain. Each surgery aims to fix specific issues causing the pain, helping patients live better lives.
These surgeries usually lead to less pain, better movement, and fewer future problems. How well surgery works depends on the patient’s condition and the surgeon’s skill.
Recovery Process Post-Surgery
After groin surgery, following your doctor’s advice is key for healing. Care includes managing pain, avoiding infections, and slowly getting back to daily activities.
Good care means regular check-ups, managing pain, and physical therapy. Doctors may also suggest changes to your lifestyle to aid healing.
The time it takes to recover varies, but most see improvements in weeks. Full recovery usually takes months. Proper care after surgery is vital for a smooth return to daily life.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies for Left Inguinal Pain in Women
Making lifestyle changes and using home remedies can help with left inguinal pain. Changing your diet and exercise routine can be very helpful. These steps can prevent pain and work well with medical treatments.
Dietary Adjustments for Pain Relief
Changing your diet can greatly help with groin pain. Here are some tips for nutritional advice for inguinal discomfort:
- Eat foods that fight inflammation like berries, fatty fish, and leafy greens. They can help reduce pain.
- Stay away from foods that cause inflammation, such as refined sugars, processed meats, and high-fat dairy.
- Think about taking magnesium or vitamin D. They help muscles and nerves, which can manage inguinal pain with food.
This table shows important nutrients and where to find them for groin pain relief:
| Nutrient | Sources | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Salmon, chia seeds, flaxseeds | Reduces inflammation |
| Vitamin D | Milk, sunlight, fortified cereals | Improves muscle function |
| Magnesium | Nuts, whole grains, dark chocolate | Supports nerve function |
Exercise and Strength Training Benefits
Doing regular exercise for inguinal pain is good for your health. It also helps strengthen the pelvic area. Here’s how fitness and inguinal discomfort relief are linked:
- Try exercises like pelvic tilts and light stretching. They can relax muscles and improve blood flow.
- Strength training female groin area is very effective. It strengthens muscles that support the pelvic organs, which can reduce pain risk.
Combining flexibility exercises with strength training under a professional can really help manage inguinal discomfort.
How Pregnancy Contributes to Groin Pain
It’s important for expecting mothers to know how pregnancy affects their bodies. Pregnancy-related groin pain is a common issue. This pain comes from the growing uterus and hormonal changes that relax muscles.
The growing uterus puts pressure on muscles and nerves. This can cause pain, often on the left side. As the baby grows, the pain can get worse.
- Increased relaxin hormone levels which cause ligaments to stretch.
- Weight distribution and posture changes.
- Pressure exerted by the enlarging uterus.
Managing inguinal discomfort during pregnancy can be simple. Home remedies and lifestyle changes help a lot. Prenatal exercises, support garments, and pillows can ease the pain. But, if pain is severe, see a healthcare professional. Learn more at this health resource.
In summary, pregnancy-related groin pain is common due to body changes. Knowing the causes and how to manage it can make pregnancy more comfortable.
Left Inguinal Discomfort due to Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a common but often misunderstood condition. It can cause significant female groin discomfort endometriosis. This section will explore how endometriosis leads to endometriosis causing groin pain. We will also look at different strategies for management of endometriosis groin pain.
Understanding Endometriosis
Endometriosis is when tissue like the uterus lining grows outside the uterus. This can cause pain and infertility. The inguinal area is a rare but possible place for this tissue to grow. Women with understanding inguinal pain from endometriosis often feel pain that gets worse during their period. Knowing these patterns is key for diagnosis and treatment.
Managing Endometriosis-Related Groin Pain
Managing endometriosis groin pain requires medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgery. Here are some practical steps and therapies to help with pain relief endometriosis groin pain and improve life quality:
- Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage pain.
- Hormonal therapies: These can help reduce the growth of endometrial tissue and prevent new implantation.
- Physical therapy: Focused on pelvic floor relaxation techniques to reduce left inguinal pain endometriosis.
- Surgical options: In severe cases, laparoscopic surgery may be needed to remove endometrial patches.
| Management Strategy | Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Medication (NSAIDs) | Reduces inflammation and pain | Regular assessment for side effects needed |
| Hormonal Therapies | Slows growth of lesions | Long-term option, possible hormonal side effects |
| Physical Therapy | Improves pelvic floor tension | Must be done consistently for effectiveness |
| Surgical Intervention | Can provide significant relief from pain | Consider recovery time; possible need for repeat procedures |
The Role of Physical Activity in Aggravating Female Groin Discomfort
It’s important for women to know how physical activity effect on groin pain. Certain exercises can make the pain worse if not done carefully. Making smart choices can help avoid pain during workouts.
Exercise-induced female groin discomfort often happens in activities that are hard on the body. Knowing which activities to avoid and how to change them can help. This makes workouts safer and less painful.
- High-Impact Sports: Running, jumping, or quick changes in direction can put a lot of stress on the groin.
- Weightlifting: Lifting heavy things the wrong way can strain the groin muscles.
- Intense Stretching: Stretching too much or doing high leg raises can pull on the groin muscles too hard.
To manage and prevent symptoms from getting worse, it’s key to make changes in your workout:
- Try switching to low-impact activities like swimming or cycling to reduce stress.
- Do gentle warm-ups and cool-downs with stretching to improve flexibility without overdoing it.
- Get advice from a physical therapist for exercises that support groin health while keeping you fit.
| Activity Type | Risk Level | Modification Suggestions |
|---|---|---|
| Running | High | Alter pace or switch to brisk walking |
| CrossFit | Moderate to High | Reduce weight load and avoid high-leg kicks |
| Yoga | Low to Moderate | Focus on poses that do not overextend the groin area |
By knowing which exercises might be bad and making the right changes, you can stay active without pain. This keeps you healthy and ensures your workouts don’t cause more harm or injury.
Hormonal Changes and Their Effects on Lower Abdominal Pain in Female Groin Area
Many women face hormonal fluctuations groin pain during important times like the menstrual cycle or menopause. Knowing how these changes affect us can help us find ways to feel better.
The way hormones affect inguinal pain in women can cause discomfort that interferes with our daily lives. For example, menstrual cycle groin discomfort gets worse because of prostaglandins. These substances cause inflammation and pain.
- Prostaglandins increase before menstruation starts, making pain sharper.
- Changes in estrogen levels can make symptoms worse from one cycle to another.
- Lower estrogen levels during menopause can make inguinal discomfort worse.
To ease these symptoms, we need to try different things. This includes medical treatments and changes in our lifestyle:
- Pain relief medicines given by a doctor.
- Regular physical therapy to strengthen pelvic muscles.
- Eating foods that reduce inflammation.
- Making lifestyle changes, like drinking more water and managing stress.
It’s important to understand why we have hormonal fluctuations groin pain to manage it well. Seeing a healthcare provider regularly is key. They can create a treatment plan that fits our unique hormonal needs and symptoms.
Prevention Strategies for Chronic Groin Pain in Women
Preventing female groin pain requires a detailed plan. This includes regular health checks and careful practices. Taking action early can stop chronic pain from getting worse.
Importance of Regular Physical Exams
Regular physical exams are vital in mitigating chronic inguinal discomfort. They help doctors keep an eye on pelvic joints and other areas. This early detection is key to preventing pain and keeping the area healthy.
Best Practices for Muscle and Joint Health
Keeping pelvic joints and muscles healthy is essential. Doing exercises that target the pelvic area can help. Also, making lifestyle changes like staying at a healthy weight can reduce strain on these areas.
- Engage in regular low-impact exercises to enhance flexibility and strength.
- Avoid sudden movements that can overextend the groin area.
- Utilize proper techniques in physical activities to minimize risk.
Navigating Menopause and Associated Groin Pain
Menopause changes a woman’s life in many ways. It’s important to understand groin pain during this time. The drop in estrogen weakens pelvic muscles and tissues, causing pain.
This pain can feel like a dull ache or a sharp pain when moving. It often comes from the hormonal changes of menopause. These changes can make the groin area hurt.
To ease this pain, a mix of lifestyle changes, medical help, and self-care is needed. Staying active with gentle exercises can help. These exercises should strengthen the pelvic muscles without making the pain worse.
Also, hormone replacement therapy might help. A healthcare professional can guide you on this. Being proactive about your health can lessen the pain in your groin.
Every woman’s experience with menopause is different. If groin pain is constant or bothers you, see a doctor. They can suggest ways to manage the pain. Understanding and addressing groin pain during menopause can make this stage easier.
FAQ
Q: What are the possible causes of left inguinal pain in women?
A: Left inguinal pain in women can stem from several sources. It might be due to muscle strain or gynecological issues like ovarian cysts or endometriosis. Hernias are also a common cause of this pain.
Q: When should I seek medical attention for inguinal pain?
A: Seek medical help if the pain is severe, sudden, or accompanied by a fever. Also, if you notice a lump or experience other symptoms like gastrointestinal issues or unexplained weight loss.
Q: What types of imaging tests might be used to diagnose the cause of female groin discomfort?
A: Doctors might use ultrasounds, X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. These tests help see inside the groin area to find the pain’s source.
Q: Can pregnancy contribute to left inguinal pain in women?
A: Yes, pregnancy can lead to left inguinal pain. The growing uterus and added weight can strain muscles and ligaments in the groin.
Q: How is an inguinal hernia related to left-side female groin pain?
A: An inguinal hernia happens when tissue bulges through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles. This can cause pain in the groin, often on the right but sometimes on the left.
Q: Are there any non-surgical treatments for inguinal area pain in females?
A: Non-surgical options include physical therapy and pain management with medication or heat/cold therapy. Acupuncture or chiropractic care might also help.
Q: What lifestyle adjustments can help relieve left inguinal pain in women?
A: To ease left inguinal pain, maintain a healthy weight and strengthen core and pelvic muscles. Avoid activities that worsen the pain and eat anti-inflammatory foods.
Q: How can hormonal changes affect the lower abdominal area and potentially lead to groin pain?
A: Hormonal shifts during the menstrual cycle or menopause can lead to bloating and tenderness. These symptoms can cause lower abdominal pain and groin discomfort.
Q: What are the best practices for preventing chronic groin pain in women?
A: Prevent chronic groin pain by staying active, maintaining good posture, and avoiding repetitive strain. Regular physical exams and following ergonomic guidelines are also key.
Q: Can endometriosis cause left inguinal discomfort?
A: Yes, endometriosis can cause left inguinal discomfort. This happens if endometrial tissue implants near nerves in the groin or forms cysts that press on pelvic structures.
Q: What role does physical activity play in aggravating female groin discomfort?
A: Physical activities, like sudden movements or heavy lifting, can make groin pain worse. They can also trigger new pain in some people.
Q: Can dietary adjustments improve inguinal pain in women?
A: Yes, eating anti-inflammatory foods and staying hydrated can help improve inguinal pain. These changes support pelvic health and reduce inflammation.
Q: How is the recovery process managed after surgery for left inguinal region pain?
A: Recovery involves following your surgeon’s instructions, attending physical therapy, and managing pain with medication. Gradually return to normal activities as you heal.
Q: What signs should I look for to know if I might have an ovarian cyst causing left inguinal pain?
A: Look for irregular menstrual cycles, pelvic pain, bloating, and pain during sex. Large or ruptured cysts can cause sharp, severe pain.