Prostate cancer is a serious health issue that affects many men worldwide. It develops in the prostate gland, a small organ key to the male reproductive system. Knowing what prostate cancer is and its symptoms can save lives.
As men get older, their chance of getting prostate cancer goes up. It’s the second most common cancer in men worldwide. Spotting symptoms early is crucial for treatment success. Symptoms include changes in how you pee and discomfort in the pelvic area.
This article will dive into what prostate cancer is, its common symptoms, and why knowing about it is crucial for men’s health. By learning about prostate cancer, you can take steps towards early detection and treatment if needed.
Understanding Prostate Cancer: Definition, Types, and Basic Overview
Prostate cancer is a serious disease that affects many men. To understand it, we must learn about the prostate gland and how cancer develops there.
The Role and Function of the Prostate Gland
The prostate is a small gland in the male body. It makes fluid that helps sperm. It’s located below the bladder and surrounds part of the urethra, which carries urine out.
Different Types of Prostate Cancer
Most prostate cancers are adenocarcinomas, starting in gland cells. Rare types include small cell carcinomas and neuroendocrine tumors. The type of cancer affects treatment and how well you might do.
| Type | Description | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Adenocarcinoma | Starts in gland cells | 95% of cases |
| Small Cell Carcinoma | Rare, aggressive form | 1% of cases |
| Neuroendocrine Tumors | Arise from neuroendocrine cells | Less than 1% of cases |
How Prostate Cancer Develops and Spreads
Prostate cancer starts with DNA changes in prostate cells. These cells grow and divide fast, forming a tumor. The cancer can spread to nearby tissues or distant parts of the body through the bloodstream or lymph system.
“Understanding what prostate cancer is and how it develops is crucial for early detection and effective treatment.”
Early Warning Signs and Common Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
Spotting prostate cancer symptoms early is key to effective treatment. Many men show no signs in the early stages. That’s why regular prostate cancer screening is crucial. Symptoms can vary from person to person.
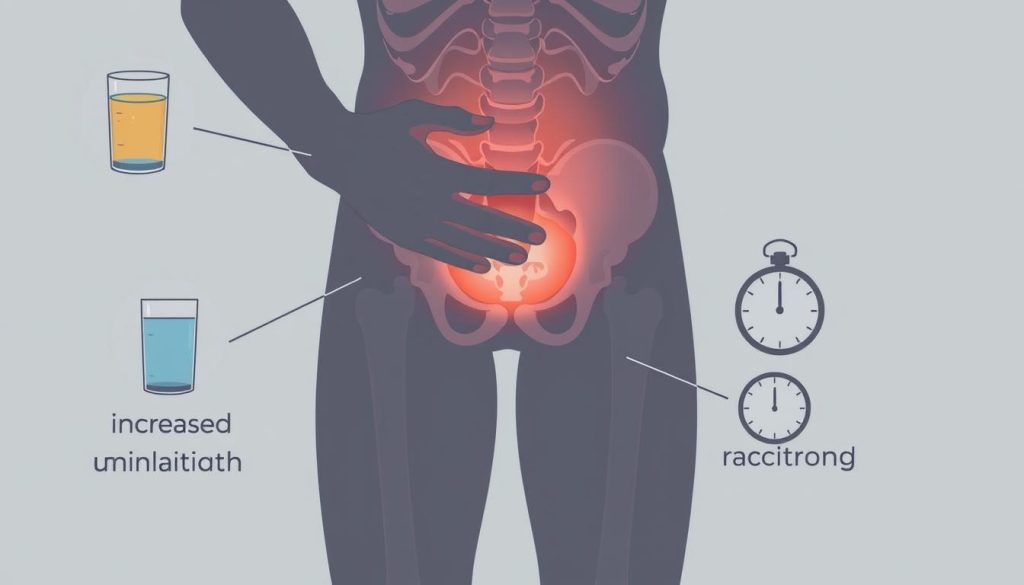
Physical Symptoms and Changes
Physical changes include unexplained weight loss, bone pain, or discomfort in the pelvic area. Some men feel tired more often or have weak legs. These signs can start off small but get worse over time.
Urinary-Related Warning Signs
Urinary issues are common symptoms of prostate cancer. Men might notice:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination
- Weak or interrupted urine flow
- Blood in urine or semen
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you notice these symptoms, don’t worry. They can have other causes too. But seeing a doctor quickly is important. Early detection through screening can improve outcomes. Your doctor might suggest tests like a PSA blood test or digital rectal exam.
Remember, prostate cancer often has no symptoms in its early stages. Regular check-ups are key to catching it early.
By paying attention to your body and talking to your healthcare provider, you can help protect your prostate health.
What is Prostate Cancer: Risk Factors and Causes
It’s important to know about prostate cancer causes and risk factors. This knowledge helps in early detection and prevention. Some factors we can’t control, but lifestyle choices can help.
Age is a big factor in prostate cancer risk. Men over 50 are more likely to get it. Family history also plays a role, especially if a relative had prostate cancer.
Race is another important factor. African American men face a higher risk and often get more aggressive forms of prostate cancer. On the other hand, Asian men have lower rates.
- Diet high in red meat and fat
- Lack of exercise
- Obesity
- Smoking
Lifestyle choices can increase prostate cancer risk. Eating more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may help lower the risk.
“Regular screenings are vital for men at high risk. Early detection can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes.”
Some studies link certain chemicals or radiation to prostate cancer risk. But, more research is needed to confirm these findings.
| Risk Factor | Level of Risk | Modifiable? |
|---|---|---|
| Age (over 50) | High | No |
| Family History | High | No |
| Race (African American) | High | No |
| Diet | Moderate | Yes |
| Physical Inactivity | Moderate | Yes |
Knowing about prostate cancer risk factors helps men make better choices. Regular check-ups and talking to healthcare providers are key steps in prevention and early detection.
Diagnosis Methods and Screening Procedures
Finding prostate cancer early is key to treating it well. Doctors use many ways to spot it, from simple blood tests to high-tech scans. Knowing about these steps can help men get ready for their doctor’s visits and make smart health choices.
PSA Testing and Digital Rectal Examination
The first steps in finding prostate cancer often include a PSA test and a digital rectal exam. PSA is a protein made by the prostate gland. High levels might mean cancer, but can also show other issues. A digital rectal exam lets doctors check the prostate’s size and feel for any odd textures.
Biopsy Procedures and Imaging Tests
If tests suggest a problem, your doctor might suggest a biopsy or imaging tests. A biopsy takes small tissue samples for lab checks. Tests like MRI or CT scans give clear pictures of the prostate. These help doctors find and understand cancer’s spread.
Understanding Your Test Results
After these tests, your doctor will talk about what they mean for your health. This might include talking about the cancer’s stage if found. It’s crucial to understand your test results to choose the right treatment. Always ask questions and get clear on any part of your prostate cancer diagnosis you’re unsure about.
FAQ
Q: What is prostate cancer?
A: Prostate cancer is a type of cancer that grows in the prostate gland. This gland is small and shaped like a walnut. It’s found in men and helps make seminal fluid. It’s common in men over 50 and can often be treated if caught early.
Q: What are the common symptoms of prostate cancer?
A: Symptoms include needing to urinate a lot, especially at night. You might also have trouble starting or stopping urination. Other signs are erectile dysfunction and blood in urine or semen. But, early prostate cancer often has no symptoms, making screenings important.
Q: What causes prostate cancer?
A: We don’t know all the causes of prostate cancer. But, risk factors include age, race, family history, obesity, and certain genetic mutations. Most cases happen in men over 50, especially African American men.
Q: How is prostate cancer diagnosed?
A: Doctors use several tests to diagnose prostate cancer. These include a PSA blood test, digital rectal exam (DRE), and a biopsy. Imaging tests like MRI or CT scans may also be used.
Q: What are the stages of prostate cancer?
A: Prostate cancer is staged from I to IV. Stage I is early cancer in the prostate. Stages II and III are more advanced but still localized. Stage IV means the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Q: How is prostate cancer treated?
A: Treatment depends on the cancer’s stage and the patient’s health. Options include active surveillance, surgery, radiation, hormone therapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy.
Q: What is the survival rate for prostate cancer?
A: The survival rate for prostate cancer is good, especially if caught early. For localized cancer, the 5-year survival rate is nearly 100%. But, for advanced stages, the rate drops. Early detection and treatment are key.
Q: Can prostate cancer be prevented?
A: Preventing prostate cancer is not guaranteed. But, you can lower your risk by staying healthy, exercising, and eating well. Regular screenings are also important, especially for those at higher risk.
Q: At what age should men start getting screened for prostate cancer?
A: Men should talk to their doctor about screening at age 50. African American men or those with a family history should start this conversation earlier, around age 45.
Q: What is a PSA test?
A: A PSA test is a blood test that measures PSA levels. PSA is a protein from the prostate gland. High levels can mean prostate cancer, but other conditions can also cause it.
Go to the full page to view and submit the form.