Bile duct cancer, or cholangiocarcinoma, is a rare but serious form of cancer. It affects the bile ducts, which carry bile from the liver to the small intestine. This is vital for digestion. As it grows, it can cause symptoms and complications, making early detection and treatment key.
In this guide, we’ll cover the main points of bile duct cancer. We’ll look at early signs and advanced treatment options. Whether you’re a patient, caregiver, or just health-conscious, knowing about this complex condition is important. It helps you make informed decisions about your health.
We’ll explore risk factors, diagnostic procedures, and new therapies at top cancer centers. By the end, you’ll understand cholangiocarcinoma better. You’ll also know about the resources for those dealing with this tough disease.
What is Bile Duct Cancer (Cholangiocarcinoma)
Bile duct cancer, also known as cholangiocarcinoma, is a rare and serious form of cancer. It affects the bile ducts. These important structures carry bile from the liver to the small intestine.
Definition and Basic Anatomy
Cholangiocarcinoma develops in the cells lining the bile ducts. These thin tubes connect the liver, gallbladder, and small intestine. They form a network called the biliary system. When cancer strikes, it disrupts the normal flow of bile, impacting digestive processes.
Types of Bile Duct Cancer
Bile duct cancer comes in three main types:
- Intrahepatic: Occurs within the liver
- Perihilar: Develops where the bile ducts exit the liver
- Distal: Forms in the portion of the bile duct nearest to the small intestine
Role of Bile Ducts in Digestive Health
Bile ducts are vital for proper digestion. They transport bile, a fluid that helps break down fats in food. When cholangiocarcinoma interferes with this process, it can lead to various digestive issues and impact overall health. Understanding the importance of bile ducts highlights why early detection and treatment of this cancer are critical.
Early Warning Signs and Symptoms
Spotting bile duct cancer symptoms early can save lives. This rare cancer often starts with small signs that are easy to miss. It’s important to listen to your body and get medical help if something feels wrong.
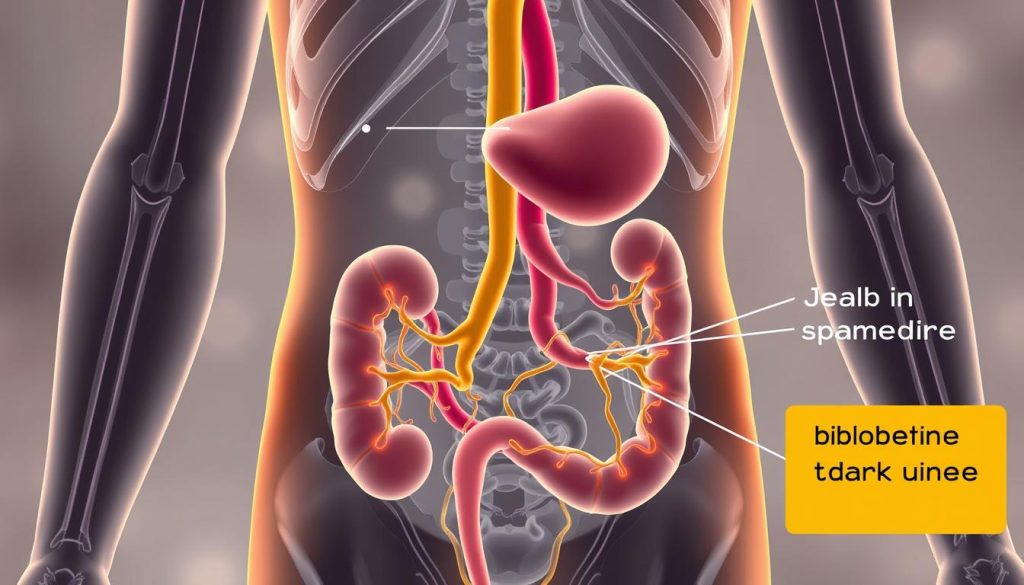
Jaundice is a clear sign, causing skin and eyes to turn yellow. This happens when bile builds up because of blocked ducts. You might also notice dark urine and pale stools.
Abdominal pain is another common symptom. It starts as a dull ache in the upper right abdomen and gets worse over time. Some people say it feels like a constant discomfort that gets worse after eating.
- Unexplained weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fever or night sweats
These symptoms can look like other, less serious problems, making it hard to diagnose. If you keep getting symptoms like jaundice or abdominal pain, see a doctor. Catching bile duct cancer early can greatly improve treatment chances.
Common Risk Factors for Bile Duct Cancer
Knowing the risk factors for bile duct cancer can help catch it early. Many things can increase your chance of getting this disease. These include your personal traits and things around you.
Age and Gender Considerations
Bile duct cancer often hits older adults, mainly those over 65. Men are slightly more likely to get it than women.
Genetic Predisposition
Some people are more likely to get bile duct cancer because of their genes. Conditions like Lynch syndrome and BAP1 tumor predisposition syndrome can raise your risk. If your family has had this cancer, you might be at higher risk too.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Things you do and the environment around you can affect your risk. Working with certain chemicals, like those in printing, can increase your risk. Being overweight and drinking too much alcohol can also play a part.
| Risk Factor | Impact Level | Preventable |
|---|---|---|
| Age (65+) | High | No |
| Genetic Predisposition | Moderate to High | No |
| Chemical Exposure | Moderate | Yes |
| Obesity | Low to Moderate | Yes |
| Alcohol Consumption | Low to Moderate | Yes |
While some risks can’t be changed, others can be managed. Making healthy lifestyle choices and staying informed can help catch bile duct cancer early. This can lead to better treatment outcomes.
The Connection Between Jaundice and Cholangiocarcinoma
Jaundice can be an early sign of cholangiocarcinoma, a rare but serious cancer. This cancer happens when bile ducts get blocked. This blockage stops bile from flowing from the liver to the small intestine.
Bilirubin builds up in the blood because of this blockage. This buildup causes the skin and eyes to turn yellow, a sign of jaundice.
Bile duct obstruction in cholangiocarcinoma can occur in several ways:
- Tumor growth within the bile ducts
- External pressure from nearby tumors
- Inflammation caused by cancer cells
Jaundice can be caused by many things, but in adults without liver disease, it’s a concern. Other symptoms of cholangiocarcinoma include:
- Itchy skin
- Dark urine
- Pale stools
- Abdominal pain
Not all jaundice means cancer. Hepatitis, gallstones, and some medicines can also cause it. If jaundice lasts, see a doctor right away for a check-up.
Diagnostic Procedures and Testing Methods
Diagnosing bile duct cancer needs a mix of tests. Doctors use different methods to find the disease and plan treatment.
Blood Tests and Tumor Markers
Blood tests look for tumor markers, substances cancer cells make. These markers help doctors find bile duct cancer early. Tests like CA 19-9 and CEA levels are common.
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies let doctors see inside the body without surgery. They help find tumors and see if cancer has spread.
| Imaging Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| CT Scan | Detailed cross-sectional images of organs |
| MRI | High-resolution images of soft tissues |
| Ultrasound | Real-time images of organs using sound waves |
Biopsy Procedures
A biopsy takes a small tissue sample for lab tests. It confirms cancer. Doctors use needle biopsies or endoscopic methods to get samples safely.
These tools work together to give a clear picture of the disease. Early and accurate diagnosis is vital for treating bile duct cancer effectively.
Understanding Cancer Staging
Cancer staging is key in figuring out how far bile duct cancer has spread. Doctors use the TNM system to check the tumor’s size, if lymph nodes are involved, and if cancer has spread. This info helps create a treatment plan that fits each patient’s needs.
- Stage I: The cancer is confined to the bile duct.
- Stage II: The tumor has grown into nearby tissues.
- Stage III: Cancer has spread to regional lymph nodes.
- Stage IV: The disease has metastasized to distant organs.
Getting the cancer stage right is essential for a treatment plan. Early-stage cancers often have more treatment choices and better chances of recovery. This is compared to cancers that have spread further.
| Stage | Treatment Options | 5-Year Survival Rate |
|---|---|---|
| I | Surgery, radiation | 30-50% |
| II | Surgery, radiation, chemotherapy | 20-30% |
| III | Chemotherapy, radiation, targeted therapy | 10-20% |
| IV | Chemotherapy, palliative care | Less than 5% |
Knowing about cancer staging helps patients and their families make better choices. It’s vital to talk about your staging with your healthcare team. This way, you can understand what it means for your future.
Surgical Treatment Options
Surgery is key in treating bile duct cancer. Doctors look at many factors to pick the best method. Let’s dive into the main surgical choices for patients.
Resection Surgery
Resection surgery cuts out the cancerous bile duct part. It tries to remove all tumor tissue. It’s often the first choice for early bile duct cancer.
The surgeon might also take out nearby lymph nodes. This helps check if cancer has spread.
Liver Transplantation
Liver transplantation is an option in some cases. It replaces the liver with a healthy one from a donor. This is for cancer that has spread but is only in the liver.
It can give patients a second chance at life.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
Minimally invasive procedures are becoming more common. They use small cuts and special tools. This leads to quicker recovery and less pain.
Examples include laparoscopic surgery and robotic-assisted procedures.
| Surgical Option | Best For | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|
| Resection Surgery | Early-stage cancer | 4-6 weeks |
| Liver Transplantation | Widespread liver involvement | 3-6 months |
| Minimally Invasive Procedures | Small, localized tumors | 2-4 weeks |
Each surgical method has its own pros and cons. Your doctor will choose the best one for you. Early detection and treatment are key to better outcomes for bile duct cancer patients.
Chemotherapy Protocols for Bile Duct Cancer
Chemotherapy is a major treatment for bile duct cancer, mainly in advanced stages. It uses drugs to kill cancer cells all over the body. Doctors mix different drugs to make treatment more effective.
Common chemotherapy protocols for bile duct cancer include:
- Gemcitabine plus cisplatin
- FOLFOX (leucovorin, fluorouracil, and oxaliplatin)
- Capecitabine
These drugs are given through an IV in cycles. There are breaks between treatments to let the body heal. How long and how often treatments happen depends on the plan and how well the patient responds.
Chemotherapy can be effective but has side effects. Common side effects include:
| Short-term Side Effects | Long-term Side Effects |
|---|---|
| Nausea and vomiting | Fatigue |
| Hair loss | Peripheral neuropathy |
| Decreased blood cell counts | Cognitive changes |
| Mouth sores | Fertility issues |
Doctors watch patients closely during treatment to manage side effects. They might give medicines to help with symptoms. This helps improve life quality during treatment.
New targeted therapies and combination treatments are showing promise. These aim to better outcomes and fewer side effects. They offer hope for those with this tough disease.
Radiation Therapy Approaches
Radiation therapy is key in treating bile duct cancer. It uses high-energy beams to kill cancer cells. We’ll look at two main ways radiation therapy is used for bile duct cancer.
External Beam Radiation
External beam radiation is a common method. It sends radiation from outside the body using a machine called a linear accelerator. The beams are aimed right at the tumor. Patients get treatment five days a week for weeks.
This method can make tumors smaller and ease symptoms in bile duct cancer patients.
Targeted Radiation Methods
Targeted radiation is more precise. Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is one example. It uses advanced imaging to focus high doses of radiation on specific areas. This way, it causes less harm to healthy tissue and can be done in fewer sessions.
For bile duct cancer, SBRT might be used when surgery isn’t possible.
Both external beam radiation and targeted radiation have their roles in treating bile duct cancer. The choice depends on the cancer stage, tumor location, and overall health. Your doctor will decide the best radiation therapy for you. Remember, radiation therapy can be used alone or with other treatments for the best results.
Palliative Care and Pain Management
Bile duct cancer patients often face tough symptoms that affect their daily lives. Palliative care is key in managing these issues and boosting well-being. It aims to enhance quality of life during treatment.
Pain management is a big part of palliative care. Doctors use different methods to help patients deal with pain, such as:
- Medication plans made just for each patient
- Nerve blocks to target pain in specific areas
- Physical therapy to improve mobility and lessen pain
Nutritional support is also vital. Cancer and treatments can mess with appetite and digestion. Dietitians help create meal plans that keep patients strong during treatment.
Psychological care is just as important. Dealing with bile duct cancer can be very tough emotionally. Mental health experts offer counseling and support to help patients and their families.
Palliative care aims to improve life quality for bile duct cancer patients. It covers physical, emotional, and spiritual needs. This approach ensures patients get all-around support during treatment.
Latest Advancements in Treatment
Bile duct cancer treatment has made big strides in recent years. New methods bring hope to those diagnosed. Let’s look at some of the latest options changing how we treat cholangiocarcinoma.
Immunotherapy Options
Immunotherapy uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. For bile duct cancer, scientists are looking into several promising treatments. These include checkpoint inhibitors and CAR T-cell therapy. Early studies suggest they could lead to better survival rates and quality of life for some patients.
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are testing new drugs and combinations. They aim to find treatments that work better with fewer side effects. Patients in trials might get access to new therapies before they’re widely available. It’s important for those with bile duct cancer to talk to their doctors about trial options.
| Clinical Trial Focus | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|
| Targeted Therapies | Precision treatment based on genetic markers |
| Combination Approaches | Enhanced effectiveness through synergistic treatments |
| Novel Drug Delivery | Improved drug absorption and reduced side effects |
Emerging Therapies
Scientists are working on targeted therapies that target specific genetic mutations in bile duct cancers. These new treatments might slow tumor growth and improve outcomes. Also, new radiation methods and minimally invasive procedures are giving more options to patients who can’t have traditional surgery.
As research keeps going, the outlook for bile duct cancer patients is getting better. Advances in immunotherapy, clinical trials, and new therapies offer hope for better treatments and survival.
Managing Side Effects During Treatment
Dealing with side effects is a big part of bile duct cancer treatment. Patients often face challenges like fatigue, nausea, and skin reactions. Effective symptom management can improve quality of life and treatment outcomes.
Supportive care is key in addressing these issues. Doctors and nurses work closely with patients to develop personalized strategies for managing side effects. This may include medication adjustments, lifestyle changes, or complementary therapies.
Communication is key in successful side effect management. Patients should report any new or worsening symptoms to their healthcare team promptly. This allows for timely interventions and adjustments to the treatment plan.
| Common Side Effect | Management Strategy |
|---|---|
| Fatigue | Regular light exercise, balanced diet, adequate rest |
| Nausea | Anti-nausea medications, small frequent meals, ginger tea |
| Skin reactions | Gentle skin care, moisturizers, avoiding sun exposure |
Patients can take an active role in their care by keeping a symptom diary. This helps track side effects over time and provides valuable information to the healthcare team. With proper supportive care and open communication, many side effects can be effectively managed. This allows patients to focus on their treatment and recovery.
Nutrition and Lifestyle Changes
When facing bile duct cancer, making positive lifestyle changes can improve your quality of life. Focus on nutrition, exercise, and stress management. These can help you feel better and possibly improve treatment outcomes.
Dietary Recommendations
A balanced diet is key for staying strong during cancer treatment. Eating nutrient-rich foods can manage side effects and support health. Choose lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Avoid high-fat foods to ease digestion.
Stay hydrated and eat smaller, more frequent meals. This can help with nausea and appetite loss.
Exercise Guidelines
Regular physical activity boosts energy and mood. Start with gentle exercises like short walks or light stretching. Gradually increase intensity as you feel able.
Always check with your healthcare team before starting any new exercise. Aim for 30 minutes of moderate activity most days. But rest when your body needs it.
Stress Management
Coping with cancer can be tough. Use stress management techniques to improve mental well-being. Try deep breathing, meditation, or gentle yoga.
Engage in hobbies or join support groups to reduce anxiety. Remember, it’s okay to ask for help when you need it.
By focusing on nutrition, exercise, and stress management, you can actively participate in your treatment. These lifestyle changes can make you feel more in control. Always work with your healthcare team to tailor these recommendations to your needs and monitor any changes in your symptoms or overall health.
Support Resources and Patient Communities
Facing bile duct cancer can feel overwhelming, but you’re not alone. Support groups offer a safe space to share experiences and find comfort. These gatherings, both in-person and online, connect you with others who truly understand your journey. Patient communities provide a wealth of knowledge, from treatment tips to coping strategies.
Emotional support is key during cancer treatment. Many organizations offer counseling services tailored to cancer patients and their families. These professionals can help you navigate complex feelings and find strength in challenging times. Remember, reaching out for help is a sign of courage, not weakness.
Educational resources abound for those seeking to learn more about bile duct cancer. The Cholangiocarcinoma Foundation and the American Cancer Society offer reliable information and patient-friendly guides. These materials can empower you to make informed decisions about your care. By tapping into these support networks, you’ll find a community ready to stand by your side every step of the way.
FAQ
Q: What is bile duct cancer?
A: Bile duct cancer, also known as cholangiocarcinoma, is a rare cancer. It happens in the bile ducts, which carry bile from the liver to the small intestine. It can occur in different parts of the bile duct system. There are three types: intrahepatic, perihilar, and distal cholangiocarcinoma.
Q: What are the early warning signs of bile duct cancer?
A: Early signs include jaundice (yellow skin and eyes), abdominal pain, and unexplained weight loss. You might also notice changes in stool or urine color and fever. These symptoms can be subtle and may not show up until the cancer is advanced.
Q: Who is at risk for developing bile duct cancer?
A: People over 50 are at higher risk. Certain liver diseases, like primary sclerosing cholangitis, increase risk. Chronic inflammation of the bile ducts and exposure to chemicals also play a role. Genetic conditions, obesity, and smoking can raise your risk too.
Q: How is bile duct cancer diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis involves blood tests for tumor markers and imaging studies like CT scans and MRIs. Cholangiograms and endoscopic procedures are also used. A biopsy confirms the presence of cancer cells.
Q: What treatment options are available for bile duct cancer?
A: Treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy. The choice depends on the cancer’s stage, location, and your health. Palliative care is also important for managing symptoms.
Q: Can bile duct cancer be cured?
A: Bile duct cancer can be cured in some cases, mainly when caught early. Surgery offers the best chance for cure. Even in advanced stages, treatments can extend life and improve quality of life.
Q: What is the survival rate for bile duct cancer?
A: Survival rates vary by stage and location at diagnosis. Five-year survival rates range from 2% to 30%. But, these rates are improving with better treatments and earlier detection.
Q: Are there any clinical trials for bile duct cancer?
A: Yes, there are ongoing clinical trials for bile duct cancer. They explore new treatments like targeted therapies and immunotherapies. These trials offer hope for better outcomes, even after standard treatments.
Q: How can I manage side effects during treatment?
A: Managing side effects requires working with your healthcare team. This can include medications for nausea or pain, dietary changes, exercise, and rest. Supportive care and complementary therapies can also help.
Q: Are there support groups for people with bile duct cancer?
A: Yes, there are support groups for bile duct cancer. You can find them online or through cancer centers. They offer emotional support, practical advice, and a chance to connect with others facing similar challenges.
Go to the full page to view and submit the form.