Colon cancer, also known as colorectal or bowel cancer, is a serious health concern in the US. This guide explores the nature of this disease and its impact on public health. We’ll also look at early warning signs and how to prevent it.
Understanding cancer symptoms and prevention is key to taking control of your health. This information is for health-conscious adults and those affected by cancer. Let’s learn more about colon cancer and how to protect ourselves and our loved ones.
What Is Colon Cancer and Its Impact on Public Health
Colon cancer is a serious disease that affects the large intestine. It starts with small growths called polyps. If not treated, it can spread to other parts of the body. This disease has a big impact on public health in the United States.
Definition and Basic Understanding
Colorectal cancer forms in the colon or rectum. It often starts as benign polyps that can turn cancerous over time. Regular screenings can catch these growths early, making prevention and treatment more effective.
Statistics and Prevalence in the United States
Colon cancer is the third most common cancer in the US. Each year, thousands of people are diagnosed with this disease. Early detection through screening has helped lower death rates, but it remains a significant health concern.
| Year | New Cases | Deaths |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 147,950 | 53,200 |
| 2021 | 149,500 | 52,980 |
| 2022 | 151,030 | 52,580 |
Demographics Most Affected
While colon cancer can affect anyone, some groups face higher risks. Men, African Americans, and people over 50 are more likely to develop this disease. Family history and certain lifestyle factors also play a role in determining who might be at greater risk for colorectal cancer.
Early Warning Signs of Colorectal Cancer
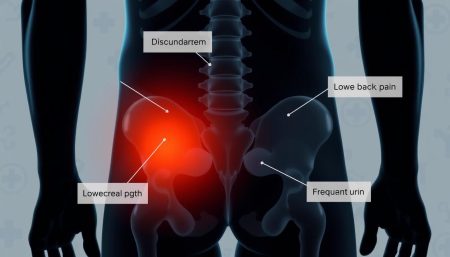
It’s key to spot the early signs of colorectal cancer to get timely treatment. Many ignore small symptoms, thinking they’re not serious. Knowing these signs can help you get medical help sooner.
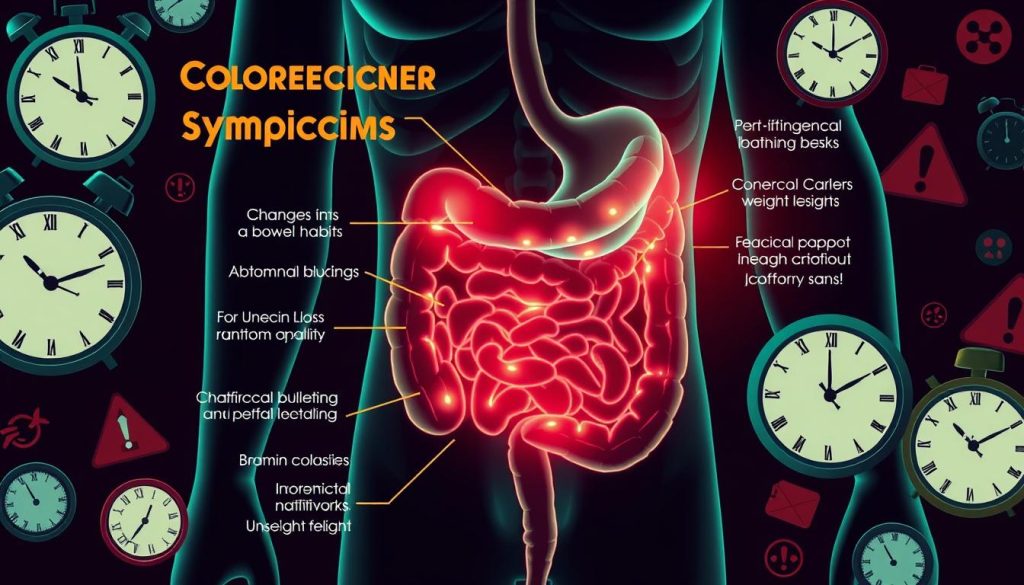
- Changes in bowel habits lasting more than a few days
- Rectal bleeding or blood in the stool
- Persistent abdominal discomfort, such as cramps or gas
- Feeling that your bowel doesn’t empty completely
- Weakness or fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
These symptoms can also mean other health issues. If you keep feeling these signs, see your doctor for a check-up.
| Symptom | Possible Indication | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Blood in stool | Potential colorectal cancer | Immediate medical attention |
| Persistent abdominal pain | Advanced colorectal cancer | Consult doctor promptly |
| Unexplained weight loss | Various cancers, including colorectal | Schedule check-up |
Spotting cancer symptoms early can greatly help treatment. Regular screenings are vital, more so if you’re at risk due to age, family history, or lifestyle. Always talk to your healthcare provider about any worries.
Common Risk Factors for Developing Colon Cancer
Knowing the risk factors for colon cancer is key to preventing and catching it early. These factors include genetics, lifestyle, and medical conditions. They all play a part in how likely someone is to get this disease.
Genetic and Family History
Genetics are a big deal when it comes to colon cancer. If your family has a history of it, you might be at higher risk. Some inherited syndromes like Lynch syndrome and familial adenomatous polyposis really up the risk.
Lifestyle-Related Risk Factors
Our lifestyle choices can also affect our risk. For example:
- Being overweight or obese
- Not being active enough
- Smoking
- Drinking too much alcohol
- Eating a lot of red and processed meats
Choosing healthier habits can lower your risk of getting colorectal cancer.
Medical Conditions That Increase Risk
Some medical conditions also raise your risk. These include:
| Medical Condition | Increased Risk |
|---|---|
| Type 2 diabetes | 20-40% higher risk |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | 2-3 times higher risk |
| History of colorectal polyps | Up to 6 times higher risk |
Getting regular screenings and managing these conditions well is important for preventing colon cancer.
The Importance of Regular Colon Cancer Screening
Regular screening is key to preventing and catching colon cancer early. It helps find problems before they get worse. This way, you have a better chance of successful treatment and recovery.
Different Types of Screening Tests
There are several effective ways to detect colon cancer:
- Colonoscopy: A thorough check of the whole colon
- Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT): Finds hidden blood in stool
- Stool DNA Test: Looks for genetic signs of colon cancer
- Virtual Colonoscopy: Uses CT scans to see the colon in 3D
When to Start Screening
The American Cancer Society suggests starting colonoscopy screening at 45 for those at average risk. If you have a family history or other risk factors, you might need to start earlier.
Frequency Recommendations
The timing of screenings depends on the test and your risk:
| Screening Method | Recommended Frequency |
|---|---|
| Colonoscopy | Every 10 years |
| FIT | Annually |
| Stool DNA Test | Every 3 years |
| Virtual Colonoscopy | Every 5 years |
These are general guidelines. Your doctor might suggest a different schedule based on your health and risk. Don’t delay talking to your healthcare provider about your screening options. Regular screenings are essential for preventing colon cancer.
Understanding Different Stages of Colon Cancer
Colon cancer goes through different stages. Each stage affects treatment choices and how well a patient might do. Knowing these stages helps doctors and patients plan the best treatment.
The staging system for colorectal cancer uses numbers 0 to 4. This shows how far the disease has spread. Here’s a quick look at each stage:
| Stage | Description | 5-Year Survival Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Cancer in earliest stage, found in innermost lining of colon | 90% |
| 1 | Cancer has grown into the inner wall of the colon | 87% |
| 2 | Cancer has grown through the wall of the colon | 80% |
| 3 | Cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes | 71% |
| 4 | Cancer has spread to distant parts of the body | 14% |
Finding colon cancer early is key to better treatment results. Regular screenings can catch it early. As cancer grows, treatments like surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation might be needed.
Knowing about these stages helps patients make better choices about their care. It’s important to work with healthcare providers. They can help decide the best treatment based on the cancer’s stage and details.
The Role of Colonoscopy in Cancer Prevention
Colonoscopy screening is key in preventing cancer. It lets doctors find and remove growths that could turn cancerous. Let’s look at how colonoscopy works and why it’s important for your colon health.
Preparation Guidelines
Getting ready for a colonoscopy is important. Your doctor will tell you what to do. You’ll likely need to:
- Stick to a clear liquid diet the day before
- Use laxatives to clean your colon
- Avoid solid foods and some medicines
These steps help your doctor see your colon clearly during the test.
What to Expect During the Procedure
You’ll be sedated during the colonoscopy for your comfort. A thin, flexible tube with a camera will be inserted into your rectum. The doctor will look for any issues and remove polyps if needed. The whole process usually takes 30-60 minutes.
Recovery and Follow-up Care
After the colonoscopy, you’ll need someone to drive you home because of the sedation. You might feel some cramping or bloating. Your doctor will talk about the results and any polyps removed. They’ll also tell you when to have your next screening, which is important for keeping cancer at bay.
| Colonoscopy Benefit | Impact on Cancer Prevention |
|---|---|
| Early Detection | Identifies precancerous polyps |
| Polyp Removal | Prevents cancer from developing |
| Regular Screening | Reduces colon cancer risk by up to 90% |
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Colon Cancer Risk
Making smart lifestyle choices is key to preventing colon cancer. Healthy habits can lower your risk of colorectal cancer and boost your health.
Keeping a healthy weight is important. Too much body fat, around the waist, can lead to inflammation and hormone changes that promote cancer. Regular exercise helps control weight, improves bowel function, and cuts down inflammation.
Drinking less alcohol is also critical. Too much alcohol can harm cells in the colon and rectum, raising the risk of colorectal cancer. It’s best to drink in moderation or avoid it.
Quitting smoking is essential. Smoking introduces harmful chemicals that can damage DNA and cause cancer in the colon and rectum.
| Lifestyle Change | Impact on Colon Cancer Risk |
|---|---|
| Maintain healthy weight | Reduces inflammation and harmful hormone levels |
| Regular physical activity | Improves bowel function and reduces inflammation |
| Limit alcohol consumption | Decreases cell damage in colon and rectum |
| Quit smoking | Eliminates exposure to cancer-causing chemicals |
By making these lifestyle changes, you can actively prevent colon cancer and enhance your health. Remember, even small changes can significantly reduce your risk of colorectal cancer.
Dietary Guidelines for Colon Cancer Prevention
A healthy diet is key in fighting cancer, including colon cancer. By choosing the right foods, you can lower your risk and stay healthy.
Foods to Include
Include these foods in your diet to fight colon cancer:
- Fiber-rich fruits and vegetables
- Whole grains
- Lean proteins like fish and poultry
- Beans and legumes
- Garlic and onions
Foods to Avoid
Stay away from these foods to lower colon cancer risk:
- Processed meats
- Red meat
- Sugary drinks
- Alcohol
- Highly processed foods
Nutritional Supplements
Some supplements can help fight colon cancer:
| Supplement | Potential Benefit | Recommended Daily Intake |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D | May reduce colon cancer risk | 600-800 IU |
| Calcium | Might lower risk of colorectal cancer | 1000-1200 mg |
| Folate | May help prevent DNA mutations | 400 mcg |

These dietary tips are part of a bigger plan to prevent colon cancer. Don’t forget regular check-ups and a healthy lifestyle too.
Treatment Options for Colon Cancer
Colon cancer treatment has made great strides, giving patients many ways to fight the disease. The right treatment depends on the cancer’s stage, location, and the patient’s health.
Surgery is often the first choice for most colon cancer cases. Doctors remove the tumor and nearby lymph nodes to stop it from spreading. For cancers caught early, surgery might be all that’s needed.
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells everywhere in the body. It’s often used after surgery to get rid of any cancer left behind. For more advanced cancers, chemo can make tumors smaller and ease symptoms.
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to target cancer cells. It’s not as common for colon cancer but might be used to shrink tumors before surgery or to ease symptoms in advanced cases.
Targeted therapies aim at specific genes or proteins that help cancer grow. These drugs are often more effective and have fewer side effects than traditional chemo.
| Treatment Type | When Used | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Surgery | Early to mid-stage colorectal cancer | Pain, infection risk |
| Chemotherapy | Advanced colon cancer, post-surgery | Nausea, hair loss, fatigue |
| Radiation | Pre-surgery, symptom relief | Skin irritation, fatigue |
| Targeted Therapy | Advanced colorectal cancer | Skin problems, high blood pressure |
Your doctor will tailor a treatment plan just for you. Remember, catching colon cancer early through screenings can lead to better treatment results.
Advanced Diagnostic Methods and Technologies
Modern medicine has brought us advanced tools for finding and treating colon cancer. These tools help doctors spot colorectal cancer early. This leads to better treatment results.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging is key in finding colon cancer. CT colonography makes detailed 3D images of the colon. This lets doctors see small growths.
MRI scans give clear pictures of soft tissues. They help doctors know how far the cancer has spread. PET scans show where cancer is by highlighting active areas.
Laboratory Tests
Blood tests are important for colon cancer screening and tracking. The fecal immunochemical test (FIT) looks for hidden blood in stool. Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) levels help see how cancer is growing and if treatments are working.
Circulating tumor DNA tests find genetic changes in cancer cells from a blood sample. This is a simple way to check for cancer.
Genetic Testing
Genetic tests are changing how we treat colon cancer. They find inherited mutations that raise cancer risk, like Lynch syndrome. Tumor profiling shows specific genetic changes in cancer cells.
This helps doctors pick the best treatments for each patient. It makes treatment more personal.
| Diagnostic Method | Purpose | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| CT Colonography | Detect polyps and tumors | Non-invasive, quick procedure |
| Fecal Immunochemical Test | Screen for hidden blood in stool | Easy to perform at home |
| Tumor Profiling | Identify genetic mutations in cancer cells | Guides personalized treatment plans |
Recovery and Support After Colon Cancer Treatment
Recovering from colon cancer treatment is a journey that needs patience, support, and dedication. Survivors face unique challenges as they adjust to life after cancer treatment. Physical rehabilitation, emotional support, and lifestyle changes are key to healing and preventing recurrence.
Physical rehabilitation is vital for recovery. Many survivors feel tired, weak, and have digestive issues after treatment. Working with a physical therapist can help rebuild strength and improve fitness. Occupational therapy may also help with daily activities.
Emotional support is also important. Cancer survivors often feel anxious, depressed, and fear recurrence. Support groups, counseling, and connecting with other survivors offer emotional help. Many hospitals and cancer centers have programs for colon cancer survivors.
Lifestyle changes are important for long-term health and cancer prevention. Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is key. Regular exercise, managing stress, and avoiding tobacco and too much alcohol are also essential.
| Recovery Aspect | Recommended Actions |
|---|---|
| Physical | Physical therapy, gradual exercise, balanced nutrition |
| Emotional | Support groups, counseling, mindfulness practices |
| Lifestyle | Healthy diet, regular exercise, stress reduction |
Ongoing medical follow-ups are key for monitoring health and catching any signs of recurrence early. Regular screenings and check-ups help in early detection and prompt treatment. Survivors should work closely with their healthcare team to create a personalized follow-up care plan.
Latest Research and Medical Breakthroughs
Colon cancer research is moving fast, bringing new hope to patients. Scientists are looking into new ways to treat colorectal cancer. These could change how we care for patients.
Immunotherapy is a big hope for colon cancer treatment. It uses the body’s immune system to attack cancer cells. Early trials show some patients are staying cancer-free for a long time.
Precision medicine is another exciting area. It uses genetic info to make treatments just for each patient. This could lead to better results and fewer side effects.
| Research Area | Potential Benefits | Current Status |
|---|---|---|
| Immunotherapy | Long-term remission | Clinical trials ongoing |
| Precision Medicine | Personalized treatment | Implemented in some centers |
| Liquid Biopsies | Early detection | Research phase |
New screening methods are being developed too. Liquid biopsies, which check blood for cancer signs, might be a better choice than old methods. They’re less invasive.
These new findings in colon cancer research give us hope. They could lead to better ways to prevent, find, and treat cancer. As research goes on, patients might get more effective and tailored care soon.
Insurance Coverage and Financial Considerations
Dealing with colon cancer can be tough. But knowing about your insurance can help. We’ll look at how insurance can cover cancer treatment and colonoscopy costs.
Medicare and Medicaid Coverage
Medicare helps with colon cancer screening and treatment. If you’re 50 or older, Medicare Part B covers colonoscopies for free. Medicaid’s coverage varies by state, but it often helps with cancer services for those who qualify.
Private Insurance Options
Most private insurance plans cover colon cancer screenings and treatments. Talk to your provider about what’s covered for colonoscopies and other cancer services. Early screenings can lead to better treatment options.
Financial Assistance Programs
If money is tight, there’s hope. Many groups offer financial help for colon cancer patients. They can cover treatment costs, medication, and even travel for care. Contact cancer support groups or hospital social workers to find these resources.
FAQ
Q: What is colon cancer?
A: Colon cancer starts in the large intestine (colon). It often begins with small, noncancerous clumps called polyps. Over time, some polyps can turn cancerous.
Q: What are the early warning signs of colon cancer?
A: Signs include changes in bowel habits and rectal bleeding. You might also feel persistent abdominal discomfort or unexplained weight loss. Fatigue is another symptom. But, many people don’t show symptoms early on, making regular screening key.
Q: Who is at risk for developing colon cancer?
A: Anyone can get colon cancer, but some are at higher risk. This includes being over 50, having a family history, or certain genetic syndromes. Inflammatory bowel diseases, a sedentary lifestyle, obesity, smoking, and a diet high in red and processed meats also increase risk.
Q: How often should I get screened for colon cancer?
A: If you’re at average risk, start screening at 45. The frequency varies by test: colonoscopy every 10 years, or annual fecal immunochemical tests (FIT). Those at higher risk may need to start earlier and more often.
Q: What is a colonoscopy and how does it help prevent colon cancer?
A: A colonoscopy lets doctors check the colon for polyps or cancer. They can remove precancerous polyps, preventing cancer. This makes colonoscopy a tool for both diagnosis and prevention.
Q: Can lifestyle changes reduce the risk of colon cancer?
A: Yes, making healthy lifestyle choices can lower your risk. Stay at a healthy weight, exercise, and eat lots of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit red and processed meats, avoid too much alcohol, and don’t smoke.
Q: What are the treatment options for colon cancer?
A: Treatment varies by cancer stage and includes surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation. Targeted and immunotherapy may also be used. The best treatment is based on the cancer’s specifics and your health.
Q: Are there any new breakthroughs in colon cancer treatment?
A: Yes, there are new treatments like immunotherapy and precision medicine. These target specific genetic mutations in tumors. Ongoing clinical trials aim to find and improve new therapies.
Q: How does colon cancer staging work?
A: Staging shows how far the cancer has spread. It ranges from stage I (local) to stage IV (distant). Staging helps choose the best treatment and gives insight into the prognosis.
Q: What dietary guidelines should I follow to help prevent colon cancer?
A: Eat a diet full of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Cut down on red and processed meats and alcohol. Some studies suggest calcium and vitamin D are also beneficial.