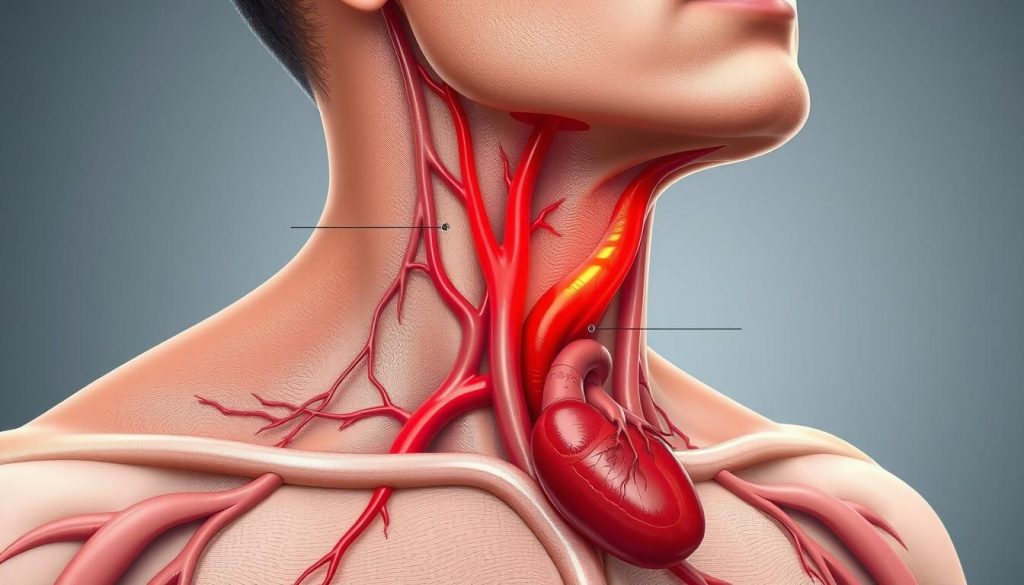
Keeping an eye on vascular health is key to catching circulatory problems early. Raised jugular venous pressure (JVP) is a sign often missed but very important for heart health. Spotting high JVP can help catch and treat serious conditions before they get worse.
Learning about raised jugular venous pressure signs is important. It helps us see when there might be circulatory issues under the surface. This knowledge helps start medical care early, reducing risks to heart health.
Understanding raised jugular venous pressure signs is a skill for both doctors and patients. It helps spot health dangers early. Knowing these signs lets people get medical help fast, leading to better health and care.
What is Raised Jugular Venous Pressure?
Raised Jugular Venous Pressure (JVP) is key to checking the heart’s health. It shows the pressure in the right atrium’s veins. This helps doctors spot heart problems.
Defining Jugular Venous Pressure (JVP)
The JVP’s role is to show how the jugular vein works. When its pressure goes up, it means the body’s blood flow might be off. Doctors then check the heart more closely.
Physiology Behind JVP Elevation
Anything that blocks blood flow can raise JVP. This includes a big heart, too much fluid, or bad valves. Knowing this helps doctors catch problems early.
Doctors can then suggest ways to fix or prevent JVP issues. This helps avoid serious health problems.
Causes of Raised Jugular Venous Pressure
Understanding why JVP increases is key for doctors. It helps them find and treat the root cause of the problem. High JVP can signal heart disease or even kidney failure. Each cause needs a different approach to care.
Cardiac Conditions Leading to Elevated JVP
Heart disease is a top reason for high JVP. Problems like heart failure, tricuspid valve stenosis, and constrictive pericarditis make it hard for the heart to pump. This leads to blood building up in the veins, showing up in the jugular veins.
Non-Cardiac Factors Influencing JVP
Other health issues can also raise JVP. For example, kidney failure causes fluid buildup, putting extra pressure on the heart. The kidneys can’t handle fluid balance well, leading to more blood in the veins. Respiratory problems and some abdominal issues also raise pressure in the chest, affecting JVP.
| Condition | Effect on JVP |
|---|---|
| Heart Failure | Increase due to impaired cardiac pumping |
| Tricuspid Valve Stenosis | Raised JVP from obstructed blood flow |
| Renal Failure | Fluid overload leading to increased venous pressure |
| Respiratory Conditions | Increased thoracic pressure elevating JVP |
Recognizing the Signs of Elevated Jugular Venous Pressure
Spotting the signs of high jugular venous pressure (JVP) is key to checking heart health. Doctors use clinical assessment and JVP physical exam to get better at finding high JVP. They look at how veins look and measure them to catch heart problems early.
Physical Examination Techniques
Checking JVP needs knowing how to look at veins and how to position patients. It helps doctors see if veins are too full, which might mean heart trouble. This is done in a quiet place to get the best precise JVP measurement.
Visual Assessment and Measurement
Doctors look at JVP by having patients sit at a 45-degree angle. They watch the neck veins for any signs of trouble. By comparing vein heights to the chest, doctors get a clear picture of venous pressure, which helps in making accurate diagnoses.
| Technique | Significance | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Inspection | Visual assessment of neck veins | Detects abnormalities in JVP height |
| Positioning | Patient at 45-degree | Optimizes visibility and accuracy |
| Measurement | Comparison against sternal angle | Provides quantitative data on venous pressure |
Doctors need to be good at these checks to measure JVP right. Using these methods helps doctors find high JVP better. This makes patient care and treatment more accurate.
Raised Jugular Venous Pressure: Clinical Implications
The clinical significance of raised JVP is very important. It is linked to venous congestion and bad heart health implications. Knowing about raised JVP can help doctors act fast and save lives.
High JVP can mean serious heart problems are coming. Venous congestion shows too much pressure in veins. If not fixed, it can harm organs and lower quality of life. Watching and treating raised JVP is key to keeping the heart healthy.
- Indication of right heart dysfunction
- Marker for fluid status and blood volume in the body
- Significant role in diagnosing heart failure
| Indicator | Implication | Associated Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Increased JVP | Higher risk of heart failure | Progressive venous congestion |
| Persistent elevation | Potential for organ damage | Increased morbidity and mortality |
Managing clinical significance of raised JVP needs careful plans. This includes medicines and lifestyle changes. Early treatment of venous congestion can prevent serious heart health implications.
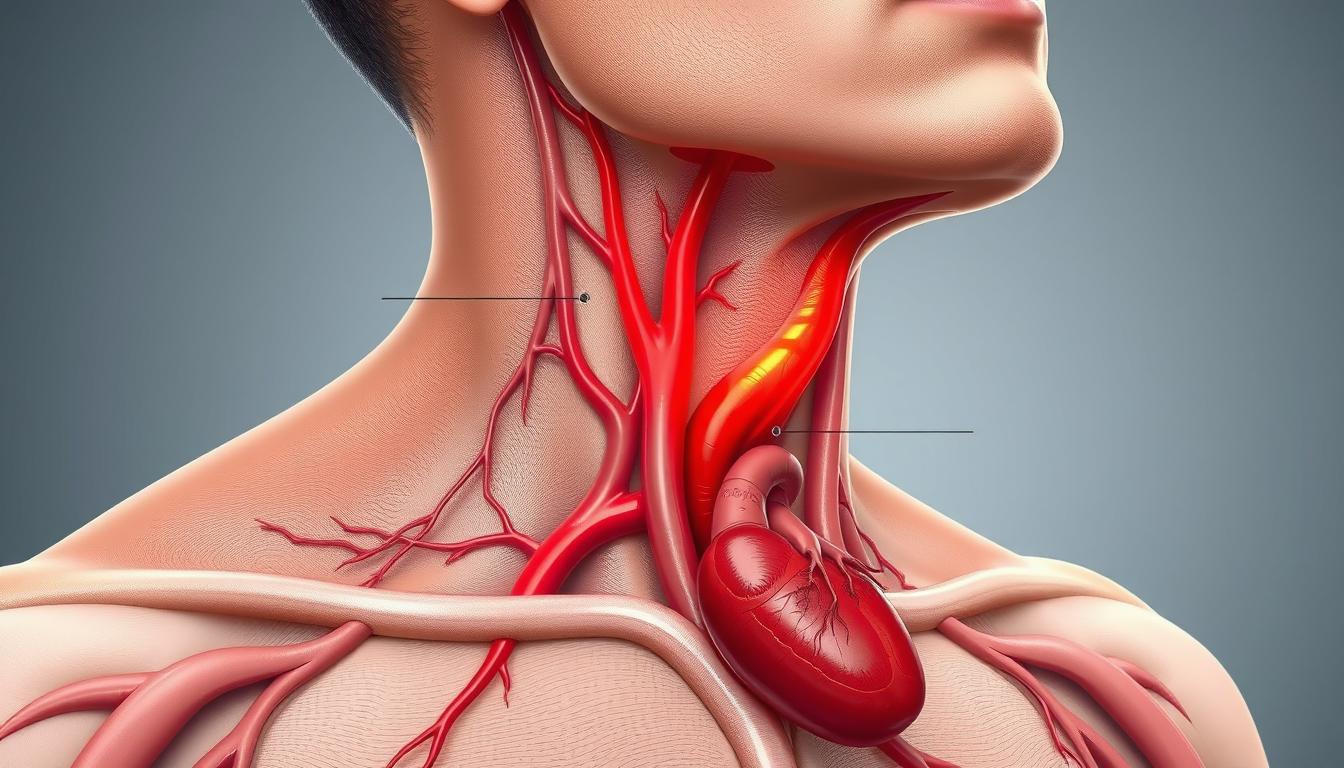
Health Risks Associated with Raised JVP
Persistent high Jugular Venous Pressure (JVP) signals heart problems and broader health risks. It’s key to understand these risks to manage and prevent severe complications.
Potential Complications of Long-Term Elevated JVP
Long-term high JVP often leads to congestive heart failure. This makes it hard for the heart to pump blood. It can cause organ congestion and harm the heart’s function.
It also causes fluid retention. This shows as swelling in legs, belly, and lungs. It worsens the health situation and lowers quality of life.
The Link Between Raised JVP and Systemic Health
Raised JVP affects more than just the heart and fluid balance. It poses big systemic health risks. These risks can lead to further health problems if not treated quickly.
It’s vital to watch and manage raised JVP. This helps avoid these systemic issues and improves health outcomes.
| Health Complication | Related to Congestive Heart Failure | Related to Fluid Retention |
|---|---|---|
| Hepatic Congestion | Yes | Moderate |
| Pulmonary Edema | Severe | Mild |
| Peripheral Edema | No | Severe |
| Renal Impairment | Yes | No |
Diagnosing Raised Jugular Venous Pressure
In the world of medical diagnostics, precision and accuracy are key. Finding elevated Jugular Venous Pressure (JVP) needs advanced tests. These tests use cardiac imaging and hemodynamic measurements to fully understand a patient’s health.
Tools and Tests for Detecting JVP Elevation
Diagnosing raised JVP starts with cardiac imaging like echocardiography and MRI scans. These tools help see the heart and blood vessels. They show if blood flow is blocked. Hemodynamic measurements also play a big role. They give real-time data on vein blood pressure, showing if JVP is high.
Interpreting Diagnostic Results
Understanding test results is very important. Doctors look for signs of heart problems or valve issues. The data from diagnostic testing helps decide the best treatment. It’s all about matching the treatment to the patient’s specific needs.
| Diagnostic Tool | Purpose | Key Measurements |
|---|---|---|
| Echocardiogram | To visualize heart function and structure | Chamber size, valve function |
| MRI | To assess both structure and detailed heart functionality | Cross-sectional heart images |
| Hemodynamic Monitoring | To measure blood flow and pressure in the cardiovascular system | Pressure within the veins |
JVP Measurement: A Step-by-Step Guide
Knowing how to measure jugular venous pressure (JVP) is key for checking a patient’s heart health. To do this right, follow a set of steps. This guide will show you how to measure JVP correctly.
First, make sure the patient is lying down with their upper body up at a 45-degree angle. This makes the jugular vein easier to see and helps with the measurement.
- Position the patient with the head slightly turned away from the side you are observing.
- Identify the sternocleidomastoid muscle, which will help in locating the jugular vein.
- Observe the highest point of the vein’s pulsation, which is your reference point for JVP.
- Use a centimeter scale to measure straight down from the sternal angle (also known as the Angle of Louis), to the level of the highest visible pulsation.
Step-by-step JVP measurement needs focus on these key points for accuracy. The table below explains the measurement spots and why they matter in JVP assessment.
| Position | Description | Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| 45-degree angle | Patient lying back with support | Optimal visibility of the jugular vein and pulsation |
| Head turned slightly | Helps to expose the neck area for easier viewing | Enhances accuracy in identifying the vein’s position |
| Measure from sternal angle | Measurement starts from this fixed bone landmark to the highest pulsation point | Standardizes the measurement for consistency and comparison |
This guide on how to measure JVP helps healthcare workers do accurate and consistent JVP assessments. Using the right method is important for diagnosing and keeping track of heart health in patients.
Management Strategies for Elevated Jugular Venous Pressure
Managing elevated JVP is key to better patient outcomes and quality of life. Medical treatments and lifestyle changes are both important. They work together to care for the patient fully.
Medications and Treatments
For elevated JVP, doctors often start with medicines. Diuretics and vasodilators help lower venous volume and pressure. In serious cases, surgery might be needed to fix structural issues.
Lifestyle Modifications and Patient Education
Changing your lifestyle is vital for managing JVP. It’s important to eat less salt, balance fluids, and keep a healthy weight. Teaching patients about their condition helps them stick to treatment plans.
- Limiting sodium intake to less than 2,000 mg a day can significantly decrease the burden on the heart and blood vessels.
- Regular physical activity tailored to patient-specific needs helps improve cardiovascular health without overexertion.
- Regular monitoring of weight and symptoms to detect any early signs of fluid retention or worsening JVP.
| Treatment | Description | Impact on JVP |
|---|---|---|
| Diuretics | Helps reduce fluid accumulation | Decreases venous pressure |
| Vasodilators | Expands blood vessels easing blood flow | Reduces workload on the heart |
| Lifestyle Changes | Incorporates diet, exercise, and fluid management | Long-term effectiveness in JVP management |
Prognosis for Patients with Raised JVP
The long-term outlook for patients with raised jugular venous pressure (JVP) depends on many factors. These include the condition’s severity, any other health issues, and how well treatment works. A big part of managing this condition is keeping up with patient follow-up and cardiac monitoring.
Factors Impacting Patient Outcomes
Several elements affect the prognosis for patients with elevated JVP:
- Severity of the Initial Diagnosis: More severe cases need more intense and longer treatments.
- Presence of Comorbidities: Other health problems can make treatment harder and outcomes worse.
- Quality of Care: Getting good healthcare and following recommended treatments greatly improves chances of better outcomes.
Monitoring and Follow-up Care Needs
Managing raised JVP well needs careful follow-up care. This is to adjust treatments as needed and watch for any changes in the condition:
- Regular Health Assessments: Regular check-ups are key to keeping track of health and making treatment changes.
- Continuous Cardiac Monitoring: Keeping an eye on the heart helps spot any issues that need quick action.
- Patient Education: Teaching patients about their condition and how to manage symptoms at home is important. It helps with self-care and lowers the risk of emergencies.
Improving long-term outcomes for patients with raised JVP requires a detailed, ongoing care plan. This plan should include regular medical checks, patient education, and cardiac monitoring.
Educating Patients on the Significance of Raised JVP
Teaching patients about raised Jugular Venous Pressure (JVP) is key for better health literacy. It helps them take a more active role in their health. When they understand JVP and its effects, they’re more likely to follow treatment plans and make lifestyle changes.
One important part of patient education is making complex medical terms easy to grasp. Healthcare providers should use simple language instead of jargon. This makes messages more relatable and easier to understand.
- Explanation of the condition: What raised JVP indicates about heart health.
- Connection to symptoms: How elevated JVP might affect daily life and symptom recognition.
- Treatment implications: Importance of following medical advice to manage the condition.
- Monitoring techniques: Teaching patients how to monitor their own JVP at home.
Visual aids and practical demonstrations during consultations also help a lot. They make complex ideas easier to understand.
Customizing the learning experience to fit each patient’s needs is also important. It helps address different learning styles and abilities. Using a mix of verbal information, written handouts, and digital resources can meet various learning preferences and reinforce the information.
The main goal of health literacy in the context of raised JVP is to empower patients. It gives them the confidence to make informed health decisions. This not only benefits individual health outcomes but also helps reduce healthcare costs by lowering hospital visits and complications through better self-management.
The Role of Technology in Monitoring JVP
The growth of medical technology innovation has changed how doctors diagnose and manage raised Jugular Venous Pressure (JVP). New tech plays a big role in the daily lives of patients through non-invasive monitoring.
New JVP tech advancements give doctors tools to measure JVP easily and accurately without invasive methods. This shift focuses on the patient, making care less painful and safer.
Innovations in Non-Invasive Measurement
Wearable devices now let doctors monitor JVP continuously. These devices provide real-time data for quick decisions. They show how far non-invasive tech has come, making patients feel more in control and comfortable.
Data-Driven Management Approaches
Today’s devices use advanced algorithms to give insights into patient health. This helps doctors predict and improve treatments. By using early detection, treatments can be adjusted to better outcomes and use resources wisely.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Real-time monitoring | Immediate data for urgent care decisions |
| Data accuracy | Reliable readings reduce diagnostic errors |
| User-friendliness | Simple operation for patients |
| Integration with healthcare systems | Seamless communication of data with medical teams |
The world of medical technology innovation is growing fast. It’s changing how we manage conditions like raised JVP. Now, non-invasive monitoring is becoming the norm in patient care.
Facing the Challenges of Heart Health: Elevated JVP Prospects
Exploring Jugular Venous Pressure (JVP) and its effects on heart health is key. It’s vital to spot early signs of heart conditions. Early detection can stop serious health problems from getting worse. Learn more about cardiovascular disease warning signs for better prevention.
The Importance of Early Detection and Intervention
Preventative care is the best way to fight health issues caused by high JVP. Early action can stop heart problems from getting worse. It also makes complications less severe. So, knowing the signs early is very important for better health outcomes.
Community Health Initiatives and Resources
Community wellness programs are vital for heart health education. Community health resources help teach people how to prevent and manage heart issues early. These resources give support and info to help people take care of their health before problems start.
| Resource | Description | Impact on Early Detection |
|---|---|---|
| Mobile Health Clinics | Deliver medical services directly to underserved areas. | Increases access to early screening for heart conditions. |
| Educational Workshops | Workshops focusing on lifestyle changes and health education. | Raises awareness of key early signs and effective management. |
| Collaborative Care Programs | Partnerships between hospitals and local communities. | Helps with ongoing monitoring and management, lowering late-stage complications. |
Working together, community involvement and medical progress lead to strong prevention. This ensures everyone gets the care they need.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Raised Jugular Venous Pressure
Knowing when to get medical help for raised jugular venous pressure (JVP) is important. Look for signs like neck vein swelling. Also, watch for symptoms like tiredness, shortness of breath, dizziness, or chest pain. These signs mean you should see a doctor right away.
Raised JVP might not always be serious, but it can be a sign of heart problems. If your symptoms get worse or come on suddenly, get help fast. Also, watch for swelling in your legs or sudden weight gain. These could mean fluid buildup due to heart issues.
If you’re at risk for heart problems or have a family history, be careful. Watch for symptoms and get medical help if you notice anything off. Early action can help prevent serious problems with raised JVP. So, listen to your body and know when to go to the doctor.
FAQ
Q: What is raised jugular venous pressure and why is it important?
A: Raised jugular venous pressure (JVP) means the veins in your neck have too much pressure. It shows problems with your heart and blood flow. Doctors use it to find heart and blood vessel issues.
Q: How does elevated JVP affect cardiac function?
A: High JVP means your heart’s right side is under too much pressure. It shows your heart might not be pumping well. This could be because of many different health problems.
Q: What are the primary cardiac conditions that lead to an increase in JVP?
A: Heart failure, constrictive pericarditis, and tricuspid valve stenosis can raise JVP. These are heart problems that make it hard for the heart to pump blood.
Q: Can elevated JVP be caused by non-cardiac factors?
A: Yes, non-heart factors can also raise JVP. This includes too much fluid from kidney problems or lung issues that increase chest pressure.
Q: How is raised JVP diagnosed during a physical examination?
A: Doctors check for raised JVP by looking at your neck veins and measuring their pressure. They use a vertical scale for this.
Q: What are the clinical implications of an elevated JVP?
A: High JVP for a long time can cause blood to back up in your veins. This can harm your heart and even increase your risk of dying if you have heart problems.
Q: What health risks are associated with long-term elevated JVP?
A: Long-term high JVP can lead to heart failure, liver problems, swelling in your legs, and other serious health issues.
Q: What diagnostic tests are used to detect elevated JVP?
A: Doctors use echocardiography, MRI, and special devices to check JVP. These tests help find out how serious the problem is and what’s causing it.
Q: What is involved in a step-by-step JVP measurement?
A: To measure JVP, you need to be in the right position. Doctors look for certain spots and use a centimeter scale to measure the pressure.
Q: What are the management strategies for raised JVP?
A: Treatment includes medicines like diuretics and vasodilators, surgery, changes in your lifestyle, and teaching you about your condition. This helps you follow your treatment plan and take care of your health.
Q: How does the prognosis for patients with raised JVP vary?
A: How well you do depends on the cause, how well treatment works, if you follow your plan, and the care you get after treatment.
Q: Why is patient education on raised JVP critical?
A: Teaching patients about raised JVP is key. It helps them understand their condition and why they need to take care of their health. This makes them more likely to follow their treatment plan.
Q: How is technology improving the monitoring of JVP?
A: New technology lets doctors monitor JVP without invasive methods. It makes tracking changes in JVP easier and more accurate.
Q: What initiatives can help with early detection and management of elevated JVP?
A: Community programs, access to resources, and education are important. They help prevent and manage heart problems related to raised JVP.
Q: When should someone seek medical attention for raised JVP?
A: If you notice your neck veins are swollen, you’re tired all the time, or you can’t breathe well, see a doctor. These signs can mean serious heart problems.
Go to the full page to view and submit the form.