Uterine cancer is a serious gynecologic cancer that affects many women each year. This guide aims to explain its complexities, from early signs to new treatments. Whether you’re dealing with a diagnosis or just want to learn, we’re here to guide you through uterine cancer.
Endometrial cancer, the most common type, starts in the uterus lining. We’ll look at its symptoms, risk factors, and the latest care advancements. Our aim is to give you the information you need, supporting you every step of the way.
This guide covers everything from diagnostic procedures to treatment options. Our goal is to offer clarity and hope. Let’s start this journey together, exploring uterine cancer’s complexities and helping you make informed decisions for better outcomes.
What Is Uterine Cancer and Its Types
Uterine cancer starts in the uterus, a key part of a woman’s reproductive system. This cancer type has two main forms that affect different parts of the uterus.
Endometrial Cancer: The Most Common Type
Endometrial cancer grows in the lining of the uterus. It’s the most frequent type of uterine cancer. Women often spot this cancer early due to unusual bleeding, which can lead to quicker treatment.
Uterine Sarcoma: Understanding Rare Forms
Uterine sarcoma is less common. It starts in the muscle wall or supporting tissues of the uterus. This type is harder to find early and can spread faster than endometrial cancer.
Differences Between Uterine and Cervical Cancer
People often mix up uterine and cervical cancer. While both affect the female reproductive system, they are distinct:
- Uterine cancer forms in the uterus
- Cervical cancer grows in the cervix, which connects the uterus to the vagina
- Cervical cancer often links to HPV, while uterine cancer usually doesn’t
- Screening tests differ for each cancer type
Knowing these differences helps women understand their health risks and symptoms better. Regular check-ups are key for catching any gynecological cancers early.
Risk Factors and Causes of Uterine Cancer
Uterine cancer is a complex gynecologic cancer with various risk factors. Understanding these can help women take proactive steps in their health journey. Let’s explore the key elements that may increase the likelihood of developing this condition.
Genetic and Hereditary Factors
Some women carry genes that make them more susceptible to uterine cancer. Lynch syndrome, a hereditary condition, significantly raises the risk. If you have close relatives with uterine or colorectal cancer, your chances may be higher.

Lifestyle and Environmental Influences
Your daily habits play a role in uterine cancer risk. Obesity is a major factor, as excess fat tissue can increase estrogen levels in the body. Lack of physical activity and a diet high in animal fats may also contribute to risk.
Medical Conditions That Increase Risk
Certain health issues can elevate uterine cancer risk. These include:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Endometrial hyperplasia
- Type 2 diabetes
- Estrogen-only hormone replacement therapy
| Risk Factor | Impact Level | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Obesity | High | Maintain healthy weight |
| Lynch Syndrome | Very High | Genetic counseling |
| PCOS | Moderate | Regular check-ups |
| Sedentary Lifestyle | Moderate | Regular exercise |
By recognizing these risk factors, women can work with their healthcare providers to develop personalized prevention strategies. Regular screenings and lifestyle modifications can make a significant difference in reducing uterine cancer risk.
Early Warning Signs to Watch For
Spotting uterine cancer symptoms early is key to effective treatment. Women should know the important signs that mean they need to see a doctor.
Abnormal vaginal bleeding is often the first sign of uterine cancer. This includes bleeding between periods, after menopause, or heavier than usual. Pelvic pain or pressure is another symptom that should not be ignored.
Other warning signs include:
- Unusual vaginal discharge
- Difficulty or pain when urinating
- Pain during intercourse
- Unexplained weight loss
These symptoms can also be caused by other conditions. If you notice any of these signs, like abnormal bleeding or persistent pelvic pain, see your healthcare provider right away.
| Warning Sign | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Abnormal vaginal bleeding | Bleeding between periods or after menopause | Consult doctor immediately |
| Pelvic pain | Persistent discomfort or pressure in pelvic area | Schedule medical evaluation |
| Unusual discharge | Watery or blood-tinged vaginal discharge | Discuss with healthcare provider |
Early detection of uterine cancer symptoms can greatly improve outcomes. Stay alert and look after your health by getting medical advice when necessary.
Recognizing Common Symptoms of Uterine Cancer
Uterine cancer symptoms can be hard to spot at first. This makes it very important to catch them early. Women should know about certain body changes that might mean they have this disease.
Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding Patterns
The most common sign of uterine cancer is abnormal vaginal bleeding. This can include:
- Bleeding between periods
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
- Bleeding after menopause
Pelvic Pain and Discomfort
Pelvic pain is another sign of uterine cancer. Women might feel:
- A feeling of pressure in the pelvic area
- Pain during intercourse
- Unexplained lower back pain
Changes in Urinary Habits
Uterine cancer can also change how you pee. You might notice:
- Frequent urination
- Difficulty emptying the bladder
- Pain or burning sensation while urinating

| Symptom | Description | When to Seek Medical Attention |
|---|---|---|
| Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding | Bleeding between periods or after menopause | Immediately |
| Pelvic Pain | Persistent discomfort or pressure in the pelvic area | If lasting more than two weeks |
| Urinary Changes | Increased frequency or pain during urination | If accompanied by other symptoms |
If you notice any of these symptoms, like abnormal bleeding or pelvic pain, see your doctor right away. Catching it early can really help with treatment.
Diagnostic Procedures and Testing
Diagnosing uterine cancer involves several tests to confirm its presence. This usually starts when a woman notices unusual symptoms or during a routine check-up.
A pelvic exam is often the first step. The doctor checks for abnormalities in the uterus and surrounding areas. If concerns arise, further tests are ordered.
Transvaginal ultrasound is a common imaging test. It uses sound waves to create pictures of the uterus. This helps detect tumors or other irregularities.
- Endometrial biopsy: A small tissue sample is taken from the uterine lining
- Hysteroscopy: A thin, lighted tube is used to examine the uterus
- Dilation and curettage (D&C): A procedure to remove tissue for examination
In some cases, additional imaging tests like CT scans or MRIs may be needed. These provide detailed views of the pelvic area. They help in diagnosing uterine cancer.
Blood tests can check for tumor markers, substances that may indicate cancer. CA-125 is one such marker often used in gynecologic cancer screening.
The diagnostic journey can be overwhelming. It’s important to communicate openly with your healthcare team throughout the process. They can explain each test and what the results mean for your health.
Understanding Cancer Staging and Grading
Doctors use staging and grading to describe uterine cancer when they diagnose it. These systems help decide the best treatment and predict how well you’ll do. Let’s look at how staging and grading work for uterine cancer.
Stage Classifications Explained
Uterine cancer staging shows how far the cancer has spread. Doctors use tests like CT scans and biopsies to find this out. The stages go from I to IV, with I being early-stage cancer in the uterus and IV meaning it has spread to distant organs.
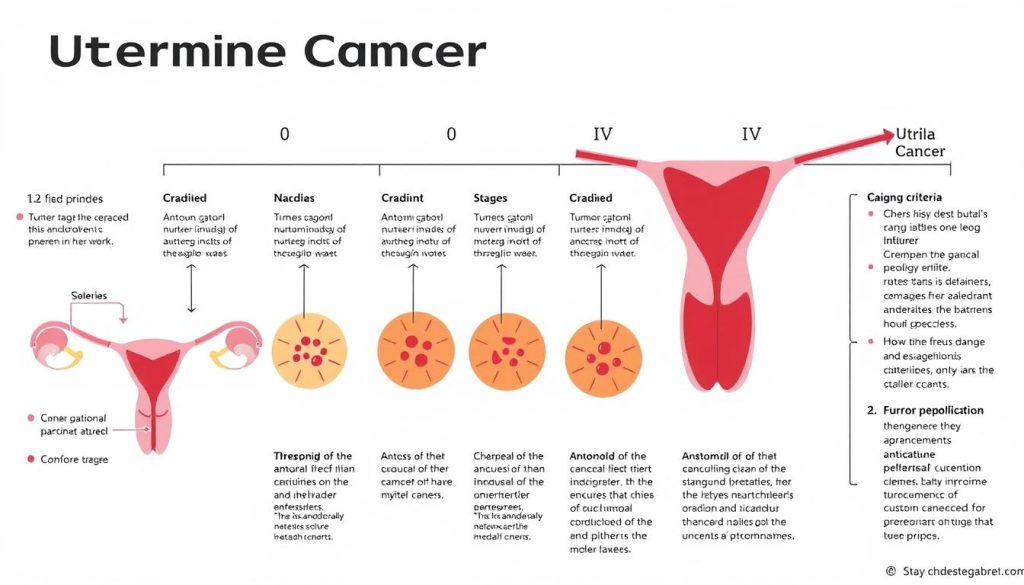
Tumor Grading System
Cancer grading looks at how abnormal tumor cells appear under a microscope. It helps guess how fast the cancer might grow and spread. Grades are from 1 to 3:
- Grade 1: Cells look mostly normal and grow slowly
- Grade 2: Cells look somewhat abnormal
- Grade 3: Cells look very abnormal and tend to grow and spread faster
Impact of Staging on Treatment Choices
The stage and grade of uterine cancer guide treatment choices. Early-stage cancers might need surgery alone, while advanced cases often require a mix of treatments. Your doctor will use this info to create a plan that’s best for you. Remember, each case is unique, and your care team is there to support you through every step.
Treatment Options for Uterine Cancer
Uterine cancer treatment includes various medical options. Doctors consider the cancer stage, your health, and what you prefer. Let’s look at the main ways to fight this disease.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is often the first choice for uterine cancer treatment. A common surgery is a hysterectomy, which removes the uterus. Sometimes, doctors also take out the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and lymph nodes nearby.
Radiation Therapy Approaches
Radiation therapy kills cancer cells with high-energy beams. It can be given from outside or inside the body. External beam radiation hits the tumor from outside. Internal radiation, or brachytherapy, places radioactive material close to the tumor.
Chemotherapy Protocols
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells everywhere in the body. It’s often used after surgery to get rid of any leftover cancer cells. Chemo can be taken by mouth or through an IV, depending on the drugs.
| Treatment | Main Purpose | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Hysterectomy | Remove uterus and possibly other organs | Pain, bleeding, infection |
| Radiation Therapy | Destroy cancer cells with high-energy beams | Fatigue, skin changes, digestive issues |
| Chemotherapy | Kill cancer cells throughout the body | Nausea, hair loss, fatigue |
Your doctor will help choose the best treatments for you. Each treatment is important in fighting uterine cancer and helping patients get better.
Role of Hysterectomy in Treatment
Hysterectomy is key in treating uterine cancer. This surgery removes the uterus and sometimes other organs. For many, it’s the main way to fight uterine cancer.
There are many types of hysterectomies, each for different needs. Simple hysterectomy takes out the uterus. Radical hysterectomy removes more tissues. Sometimes, the ovaries and fallopian tubes are removed too.
The choice of surgery depends on the cancer’s stage and the patient’s health. Options include:
- Abdominal hysterectomy
- Vaginal hysterectomy
- Laparoscopic hysterectomy
- Robotic-assisted surgery
Recovery time varies with the surgery type. Most women can get back to normal in 4-8 weeks. This surgery means you can’t have kids anymore and might start menopause early if ovaries are removed.
Even though it’s a big surgery, hysterectomy is often the best chance for a cure. It’s vital to talk to your doctor about this option to make a good choice.
Radiation and Chemotherapy Protocols
Uterine cancer treatment often includes radiation therapy and chemotherapy. These methods work together to fight cancer cells. They help improve patient outcomes. Let’s look at how they fight this disease.
External Beam Radiation
External beam radiation therapy uses high-energy x-rays to kill cancer cells. A machine sends radiation to certain body areas. Patients get treatment five days a week for weeks.
Brachytherapy Options
Brachytherapy is internal radiation therapy. Doctors put radioactive material near the tumor inside the body. It gives high doses of radiation while protecting healthy tissue.
Brachytherapy can be low-dose-rate or high-dose-rate, based on the patient’s needs.
Combination Therapy Approaches
Many uterine cancer treatments use different therapies together. Doctors might use radiation before surgery to shrink tumors. Or after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells.
Chemotherapy drugs might be used with radiation to make it more effective.
| Treatment Approach | Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| External Beam Radiation | Targets larger areas | Multiple sessions required |
| Brachytherapy | Precise tumor targeting | May require hospital stay |
| Combination Therapy | Improved effectiveness | Potential for increased side effects |
Every patient’s treatment plan is different. Doctors look at the cancer stage, health, and what the patient prefers. They use radiation therapy or chemotherapy for uterine cancer.
Regular check-ups help adjust the treatment as needed. This ensures the best outcome for the patient.
Hormonal Therapy and Targeted Treatments
Hormonal therapy and targeted treatments are key in fighting uterine cancer. They bring new hope to patients, mainly those with hormone-sensitive tumors.
Hormonal therapy blocks or lowers hormones that help cancer grow. For uterine cancer, it often targets estrogen. Doctors might give medications like progestins to slow or stop cancer cell growth.
Targeted treatments aim at specific cancer cell features. They harm cancer cells less than healthy ones. For uterine cancer, treatments might include:
- mTOR inhibitors
- PARP inhibitors
- Immunotherapy drugs
The right treatment depends on the cancer’s stage, grade, and type. Some might need a mix of hormonal therapy and targeted treatments with other options.
These therapies can be effective but might have side effects. Patients should talk to their healthcare team about risks and benefits. This helps find the best treatment for them.
Recovery and Post-Treatment Care
Recovering from uterine cancer is a journey of healing and adjusting. It’s important to focus on post-treatment care for the best results. Let’s look at the main parts of recovery and follow-up care.
Physical Recovery Timeline
Every woman’s recovery from uterine cancer treatment is different. Most regain strength over weeks to months. It’s key to rest and do light activities to heal and avoid problems.
Managing Side Effects
Side effects from treatment can last during recovery. Issues like fatigue, pain, and hormonal changes are common. It’s vital to work with your healthcare team to manage these symptoms for a smoother recovery.
| Side Effect | Management Strategy |
|---|---|
| Fatigue | Balanced rest and exercise |
| Pain | Prescribed medications and relaxation techniques |
| Hormonal changes | Hormone therapy or natural remedies |
Follow-up Care Schedule
Regular check-ups are key to tracking your recovery and catching any recurrence early. Your doctor will set up a schedule based on your needs. These visits will likely decrease if you’re recovering well.
Remember, recovering from uterine cancer takes time and support. Stick to your care plan and keep talking to your healthcare team. This will help you on your path to wellness.
Prevention Strategies and Screening
Uterine cancer prevention starts with knowing your risk factors and making healthy choices. Regular gynecologic cancer screening is key for early detection and better outcomes.

Keeping a healthy weight through diet and exercise can lower your risk of uterine cancer. Eat a balanced diet full of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Try to avoid processed foods and red meat.
Gynecologic cancer screening is vital for catching cancer early. Women should see their healthcare provider regularly and report any unusual symptoms right away. Your doctor will suggest screenings based on your age and risk factors.
| Prevention Strategy | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Maintain healthy weight | Keep BMI within normal range | Reduces risk by up to 40% |
| Regular exercise | 150 minutes moderate activity per week | Lowers risk by 20-30% |
| Balanced diet | High in fruits, vegetables, whole grains | May reduce risk by 15-20% |
| Limit hormone therapy | Discuss risks with healthcare provider | Can significantly decrease risk |
While these strategies can lower your risk, they don’t guarantee you won’t get uterine cancer. Stay informed about symptoms and talk openly with your healthcare provider for the best care.
Living with Uterine Cancer: Emotional Support
Uterine cancer can be tough on your emotions. Women need strong support to get through it. This support can come from family, friends, professional counselors, and support groups.
Coping Mechanisms
There are many ways to cope with cancer. Some find solace in journaling or meditation. Others enjoy exercise or creative activities. It’s vital to find what works for you.
Talking about your feelings with loved ones or a therapist can also help. It’s a way to release emotions and get support.
Support Groups and Resources
Being part of a uterine cancer support group is very helpful. These groups provide a safe place to share and learn from others. Hospitals and cancer centers often host these meetings.
For those who prefer online, there are forums and virtual groups. They offer support from the comfort of your home.
Family Impact Management
Uterine cancer affects the whole family. It’s important to talk openly about it. Involve your loved ones in your care decisions.
Family counseling can help everyone cope with the changes. Remember, asking for help is not a sign of weakness. It’s a key part of healing.
Fighting cancer is a daily battle. Be kind to yourself and seek help when needed. Your mental health is just as important as your physical health in this fight.
Latest Research and Treatment Advances
Uterine cancer research is moving forward, bringing new hope to patients. Scientists are finding new ways to detect and treat this disease more effectively.
Researchers are working on blood tests to catch uterine cancer early. These tests look for genetic markers linked to the disease. This could lead to faster diagnoses and better outcomes.
New treatments for uterine cancer are focused on targeted therapies. These drugs target cancer cells without harming healthy tissue, reducing side effects. Immunotherapy is also promising, helping the body’s immune system fight cancer more effectively.
| Treatment Type | Description | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Targeted Therapy | Drugs that target specific genetic mutations in cancer cells | Fewer side effects, more precise treatment |
| Immunotherapy | Boosts the body’s natural defenses against cancer | Long-lasting remissions, fewer side effects |
| Combination Therapies | Using multiple treatment types together | Enhanced effectiveness, reduced resistance |
Clinical trials are testing these new methods. Patients should talk to their healthcare team about joining. As research advances, the outlook for those with uterine cancer is looking brighter.
Conclusion: Empowering Patients in the Fight Against Uterine Cancer
Knowing about uterine cancer is key to catching it early. Women can protect their health by understanding symptoms and risk factors. Regular check-ups and talking openly with doctors are essential.
Dealing with uterine cancer is tough, but knowing what to do helps. Patients can spot early signs and choose from many treatments. Support groups, advanced care, and research give hope and better results.
Every person’s battle with uterine cancer is different. Staying up-to-date with research and treatments helps patients make informed choices. With more awareness and support, we can fight uterine cancer together, empowering patients at every turn.
FAQ
Q: What are the most common symptoms of uterine cancer?
A: Symptoms of uterine cancer include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, and changes in urination. These signs can also mean other health issues. It’s key to see a doctor for a proper check-up.
Q: How is uterine cancer diagnosed?
A: Doctors use several methods to find uterine cancer. These include pelvic exams, imaging tests, and endometrial biopsies. Sometimes, a hysteroscopy is done to see inside the uterus. A pathologist checks tissue samples for a final diagnosis.
Q: What are the main types of uterine cancer?
A: Uterine cancer has two main types: endometrial and uterine sarcoma. Endometrial cancer is the most common, starting in the uterus lining. Uterine sarcoma is rarer but more aggressive.
Q: What are the risk factors for developing uterine cancer?
A: Risk factors include obesity, never being pregnant, and late menopause. Diabetes, high blood pressure, and family cancer history also increase risk. Long-term use of estrogen-only hormone therapy and Lynch syndrome are other factors.
Q: How is uterine cancer treated?
A: Treatment for uterine cancer may include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and hormonal therapy. The plan depends on the cancer type, stage, and the patient’s health.
Q: What is the survival rate for uterine cancer?
A: Survival rates vary by stage and type of cancer. The 5-year survival rate is about 81%. Early detection (stage I) can raise this rate to 95%. But, individual results can differ.
Q: Can uterine cancer be prevented?
A: Preventing uterine cancer is not guaranteed. But, healthy lifestyle choices can help. These include a healthy weight, exercise, managing health conditions, and discussing hormone therapy with your doctor. Regular check-ups are also key for early detection.
Q: How does uterine cancer differ from cervical cancer?
A: Uterine and cervical cancers are different diseases. Uterine cancer starts in the uterus lining, while cervical cancer begins in the cervix. They have different risk factors, screening methods, and treatments.
Q: What support is available for people diagnosed with uterine cancer?
A: Support for uterine cancer patients includes support groups, counseling, and advocacy organizations. Hospitals offer services for patients and their families. There are also resources for managing side effects and financial help.
Q: Are there any new treatments or research developments for uterine cancer?
A: Research on uterine cancer treatment is ongoing. New areas include targeted therapies, immunotherapy, and personalized medicine. Clinical trials are testing new treatments. Advances in surgery, like minimally invasive and robotic surgeries, also improve outcomes.

















