Prostate cancer is a serious health concern for men worldwide. Knowing the early signs can greatly improve treatment outcomes. This guide explores the prostate cancer signs and indicators. It helps men take charge of their health.
From small changes in urinary habits to noticeable prostate tumor symptoms, we’ll cover it all. Understanding these signs helps men get medical help early. This can catch prostate cancer in its early stages.
Let’s look at the key symptoms, risk factors, and diagnostic procedures for prostate cancer. With this knowledge, you can protect your prostate health and overall well-being.
Understanding Prostate Cancer and Its Impact on Men’s Health
Prostate cancer is a big health worry for men everywhere. Spotting signs early can make a big difference. Let’s look at what this disease is and how it affects men’s health.
The Role of the Prostate Gland
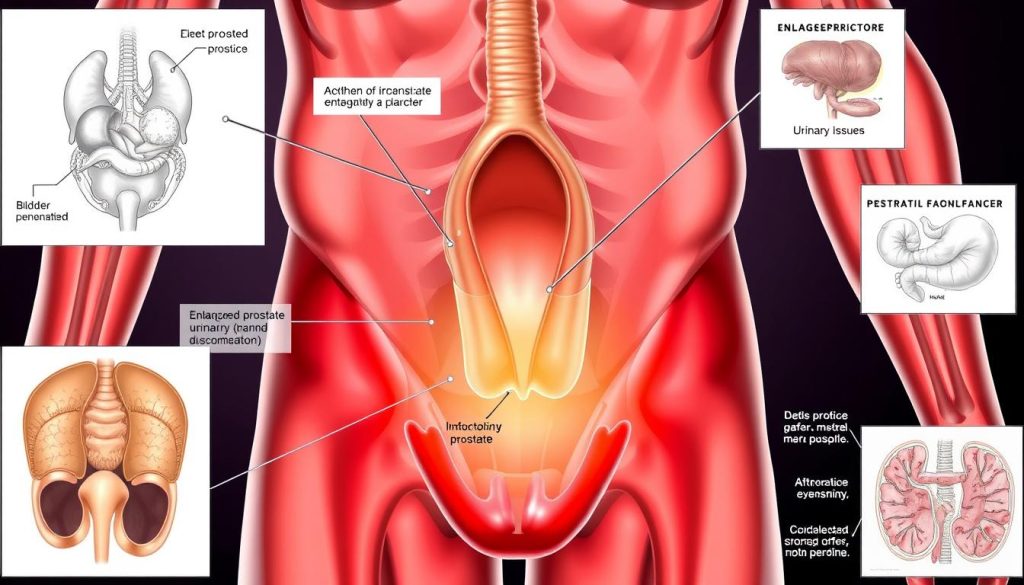
The prostate gland is key for men’s reproductive health. It makes seminal fluid, which helps and protects sperm. If cancer grows here, it can mess with normal functions and show warning signs.
Risk Factors and Age-Related Concerns
Age is a big risk for prostate cancer. Men over 50 face a higher chance. Other risks include family history, race, and diet. Knowing these can help men watch for prostate problems.
Global Statistics and Prevalence
Prostate cancer is a top cancer for men worldwide. Its spread changes by region and race. Knowing these numbers shows why regular check-ups and early detection are key.
| Region | Incidence Rate (per 100,000) | Mortality Rate (per 100,000) |
|---|---|---|
| North America | 73.7 | 10.1 |
| Europe | 62.1 | 11.3 |
| Asia | 11.5 | 4.5 |
| Africa | 26.6 | 14.9 |
By knowing about prostate cancer, men can spot warning signs early. This can lead to better treatment and outcomes.
What Are Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
Spotting prostate cancer early is key to better treatment. Men should know about body changes that could mean they have this disease.
Urinary Changes and Warning Signs
Urinary symptoms are often the first signs of prostate cancer. These include:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination
- Weak or interrupted urine flow
- Burning sensation during urination
Sexual Function Changes
Prostate cancer can also impact a man’s sex life. Look out for:
- Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection
- Painful ejaculation
- Decreased libido
Pain and Discomfort Indicators
As the disease gets worse, pain may show up. Common symptoms include:
- Lower back pain
- Hip or pelvic discomfort
- Unexplained weight loss
Remember, these symptoms can also mean other health issues. If you notice any, see your doctor right away for a check-up.
| Symptom Category | Early Stage | Advanced Stage |
|---|---|---|
| Urinary | Frequent urination, weak flow | Urinary retention, blood in urine |
| Sexual | Erectile difficulties | Painful ejaculation, reduced libido |
| Pain | Mild pelvic discomfort | Severe bone pain, fatigue |
Early Detection Signs That Shouldn’t Be Ignored
Spotting early signs of prostate cancer is key for quick action and better treatment. Men should watch for small changes in their body. These could mean prostate disease is starting.
Changes in urination are big warning signs. If you pee more often, especially at night, or have trouble starting or stopping, see a doctor. These could be signs of prostate cancer or other issues.
Pain or discomfort in the pelvic area, lower back, or hips is not normal. It could mean prostate disease and needs a doctor’s check.
“Don’t ignore persistent changes in your body. Early detection can make a significant difference in prostate cancer treatment and outcomes.”
Sexual function changes can also point to prostate problems. Trouble getting or keeping an erection, or pain during ejaculation, need a doctor’s look.
Blood in urine or semen is rare but serious. It could mean prostate cancer or other serious conditions.
- Increased urinary frequency or urgency
- Difficulty starting or stopping urine flow
- Pelvic, lower back, or hip pain
- Changes in sexual function
- Blood in urine or semen
These signs don’t always mean cancer, but they’re worth checking. Finding prostate disease early can lead to better treatment and health.
Advanced Prostate Cancer Symptoms and Manifestations
Prostate cancer can get worse and cause more severe symptoms. It’s key to know the signs of advanced prostate cancer to get help early. Let’s look at the main symptoms that show up in later stages.
Bone Pain and Metastasis Signs
Advanced prostate cancer often spreads to the bones. This can cause ongoing pain in the hips, back, or chest. Some men might even get fractures from weak bones. These symptoms can get worse and make it hard to move around.

Systemic Symptoms
As cancer gets worse, it can affect the whole body. This can include:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue and weakness
- Anemia (low red blood cell count)
- Swelling in the legs or feet
Some men might also notice changes in bowel habits, like those seen in colon cancer. This highlights the need for thorough health checks.
Quality of Life Impact
Advanced prostate cancer symptoms can really change daily life. Pain and tiredness might stop you from doing things you love. Urinary and sexual issues often get worse. Some men also feel emotionally down because of these changes.
Talking to healthcare providers about these issues is crucial. They can help find ways to manage symptoms and keep your quality of life as good as possible.
Diagnostic Procedures for Prostate Cancer Symptoms
Finding prostate cancer early is key to treating it well. Doctors use different methods to spot signs of this disease. Let’s look at how they check for prostate cancer.
PSA Testing and Digital Rectal Examination
The PSA blood test and digital rectal exam are main screening tools. The PSA test checks for prostate-specific antigen in the blood. The digital rectal exam lets doctors feel the prostate for any oddities. These tests are often the first signs of prostate cancer.
Imaging Studies and Biopsy Options
If tests show possible prostate cancer, doctors might suggest more imaging. MRI scans give detailed prostate images, spotting suspicious spots. A prostate biopsy is the best way to confirm cancer, by taking tissue samples for a microscope check.
Regular Screening Recommendations
How often to get screened for prostate cancer depends on your risk and age. Mayo Clinic experts say talk to your doctor about screening, especially if you’re over 50 or have a family history of prostate cancer.
| Age Group | Screening Recommendation | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 40-49 | Discuss with doctor if high risk | As advised |
| 50-69 | Regular screening | Every 1-2 years |
| 70+ | Individual assessment | Based on health status |
Early detection of prostate cancer can greatly improve treatment results. If you have concerns or notice any symptoms, talk to your healthcare provider.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Prostate Symptoms
It’s important to know the signs of prostate health problems early. Look out for changes in how you pee or have sex. These could be signs of prostate cancer that need a doctor’s check.
Don’t ignore issues like needing to pee a lot, a weak stream, or trouble starting or stopping. These could mean you have a prostate problem. Also, if you have trouble getting or keeping an erection, it’s a red flag.
Pain in your lower back, hips, or pelvis is not normal. It could mean your prostate cancer is advanced. If you’re over 50 or have a family history of prostate cancer, see a doctor fast.
Not all prostate symptoms are cancer, but it’s better to check. Regular visits and talking openly with your doctor can help catch problems early. Don’t be scared or shy – your health is important.
FAQ
Q: What are the most common symptoms of prostate cancer?
A: Common symptoms include frequent urination, especially at night. You might also have trouble starting or stopping urination. Weak or interrupted urine flow is another sign.
Painful or burning urination, blood in urine or semen, and erectile dysfunction are symptoms too. But, early prostate cancer often doesn’t show symptoms.
Q: At what age should men start getting screened for prostate cancer?
A: Men should talk to their doctor about screening at 50. If you’re African American or have a family history, start at 45. This is to catch prostate cancer early.
Q: Can prostate cancer cause back pain?
A: Yes, advanced prostate cancer can cause back pain. This happens when cancer spreads to the bones, especially the spine. It’s a sign of advanced cancer.
But, back pain can have many causes. It doesn’t always mean prostate cancer.
Q: Are there any early warning signs of prostate cancer?
A: Early prostate cancer often doesn’t show symptoms. But, changes in urination habits might be a sign. This includes more frequent or urgent urination, or a weak stream.
These symptoms can also mean non-cancerous conditions like BPH. So, it’s important to get checked.
Q: How is prostate cancer diagnosed?
A: Doctors use tests to diagnose prostate cancer. These include a digital rectal exam (DRE), a PSA blood test, and imaging studies like MRI or CT scans. A prostate biopsy might also be needed.
The tests used depend on your situation and initial results.
Q: Can prostate cancer affect sexual function?
A: Yes, prostate cancer and its treatments can affect sex. The cancer itself might cause erectile dysfunction. Treatments like surgery, radiation, or hormone therapy can also lead to side effects.
These include erectile dysfunction and reduced libido. Talk to your doctor about these risks.
Q: What are the risk factors for developing prostate cancer?
A: Risk factors include age, race, family history, and genetic mutations. Diet and obesity might also play a role. But, their exact impact is still being studied.
Q: How often should I get my prostate checked?
A: How often you need a prostate check depends on your age, risk level, and test results. Men should talk to their doctor about screening at 50 (or earlier for high-risk groups).
Your doctor will recommend a screening schedule based on your situation.
Q: What’s the difference between BPH and prostate cancer?
A: BPH is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate. It’s common in older men. Prostate cancer, on the other hand, is a cancer that can grow in the prostate.
While both can cause similar symptoms, BPH doesn’t increase cancer risk. But, it’s possible to have both. So, getting a proper medical evaluation is key.
Q: Can prostate cancer be prevented?
A: There’s no sure way to prevent prostate cancer. But, making healthy lifestyle choices can help. Eating a diet rich in fruits and vegetables, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight are good choices.
Avoiding smoking is also important. Some studies suggest that foods high in lycopene and selenium might help. But, more research is needed to confirm these benefits.