Prostate cancer is a big health worry for men everywhere. Spotting prostate cancer early can save lives. This article looks at the key signs and symptoms that every man should be aware of.
Finding prostate cancer early can greatly improve treatment results. Knowing the symptoms helps men take care of their health. Let’s explore the early signs of prostate cancer and why seeing a doctor quickly is so important.
Understanding Prostate Cancer and Its Impact on Men’s Health
Prostate cancer is a big worry for men’s health. It hits the prostate gland, a key part of the male body. We’ll look at how this gland works, how common prostate cancer is, and why catching it early is crucial.
How the Prostate Gland Functions
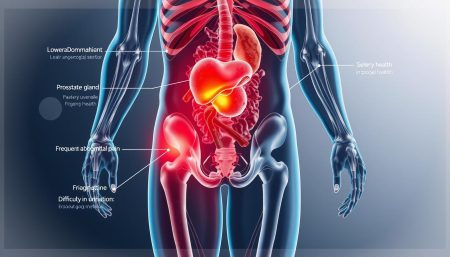
The prostate gland is vital for male fertility. It makes fluid that helps and protects sperm. This small organ is below the bladder and around the urethra. When it’s healthy, it helps with urine control and sex.
The Prevalence of Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is a common cancer in men. It grows slowly and is more common with age. Risk factors include family history and, with Black men at higher risk.
Why Early Detection Matters
Finding prostate cancer early is key. Early-stage cancer often has no symptoms, making regular checks important. Early detection means better treatment chances, leading to better life quality.
“Early detection of prostate cancer can save lives. Regular check-ups are a man’s best defense.”
Understanding prostate cancer and its impact on men’s health is the first step in fighting this disease. By knowing the facts, men can take charge of their health and make informed decisions about screenings and care.
What Are The Signs of Prostate Cancer
Spotting prostate cancer early can make a big difference. Men should know the signs that might show they have this disease.
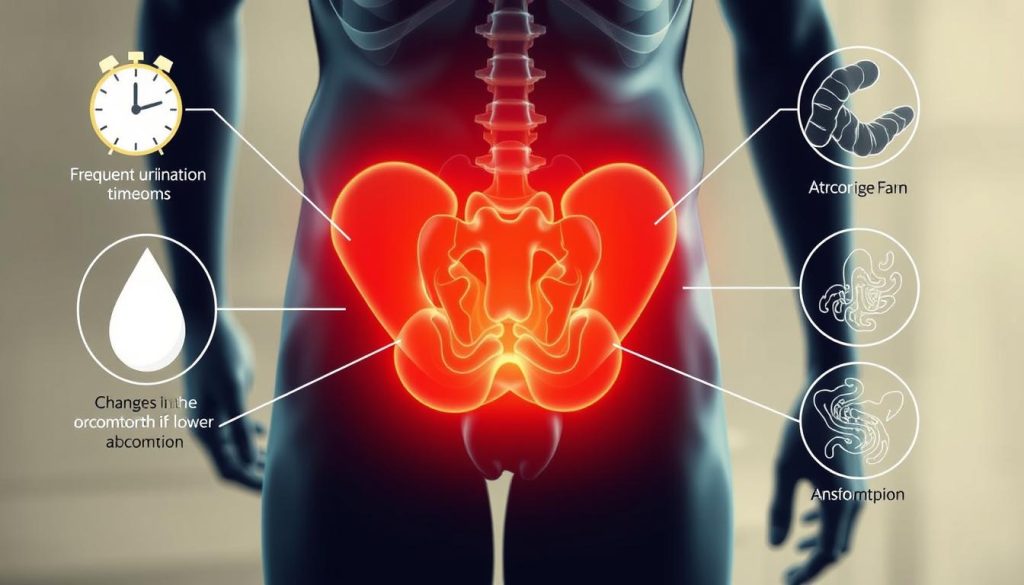
Common Physical Symptoms
Prostate cancer grows slowly, and symptoms come on gradually. Urinary changes are common early signs. These include:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Weak or interrupted urine flow
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination
- Burning sensation during urination
Urinary Changes and Warning Signs
Urinary issues are often the first signs of prostate cancer. Blood in urine or semen is a big warning sign. Some men also feel a sudden need to urinate or feel their bladder isn’t empty.
Pain and Discomfort Indicators
As the disease gets worse, men may feel pain or discomfort in different areas:
- Lower back pain
- Hip or pelvic discomfort
- Pain during ejaculation
Advanced Stage Symptoms
In later stages, symptoms can get worse:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Erectile dysfunction | Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection |
| Bone pain | Persistent pain in bones, especially the spine |
| Unexplained weight loss | Significant weight loss without diet changes |
| Fatigue | Persistent tiredness and lack of energy |
If you notice any of these symptoms, see your doctor right away. Early detection can greatly improve treatment results.
Risk Factors and High-Risk Groups
Knowing about prostate cancer risk factors is key to catching it early. Age is a big factor, with men over 50 at higher risk. If a close relative had prostate cancer, your risk goes up too.
Race also plays a part. African American men face a higher risk of aggressive prostate cancer. Their risk is almost double that of other races.
What you eat and how active you are can affect your risk. Eating a lot of red meat and dairy might up your risk. But, eating fruits and veggies and staying active can help lower it.
| Risk Factor | Impact Level |
|---|---|
| Age (over 50) | High |
| Family History | High |
| Race (African American) | High |
| Diet (High in red meat) | Moderate |
| Lack of Exercise | Moderate |
Men with several risk factors are in high-risk groups. If you’re over 50, have a family history, or are African American, get screened regularly. Talk to your doctor about your risk to make a plan for screenings.
Having risk factors doesn’t mean you’ll definitely get prostate cancer. It just means you should watch your prostate health more closely. Regular check-ups and a healthy lifestyle can help prevent and catch it early.
Diagnostic Methods and Screening Tests
Prostate cancer screening is key to catching it early. Doctors use different ways to find this disease.
Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Testing
The PSA test checks PSA levels in blood. High levels might mean cancer, but can also show other issues. Doctors often suggest this test for men over 50.
Digital Rectal Exam (DRE)
A DRE lets a doctor feel the prostate gland through the rectum. This hands-on method can spot problems with the prostate’s size, shape, or feel.
Advanced Imaging Techniques
If tests show something odd, doctors might use MRI or CT scans. These scans give clear pictures of the prostate and nearby areas. They help find tumors or other issues.
Biopsy Procedures
A biopsy is usually the last step to confirm cancer. It takes small tissue samples from the prostate for lab tests. Though it’s invasive, a biopsy can show if cancer cells are present.
| Diagnostic Method | Purpose | Invasiveness |
|---|---|---|
| PSA Test | Measure PSA levels in blood | Minimally invasive |
| Digital Rectal Exam | Physical examination of prostate | Minimally invasive |
| Advanced Imaging | Detailed images of prostate | Non-invasive |
| Prostate Biopsy | Tissue sample analysis | Invasive |
Using these methods early can lead to better treatment results. Men should talk to their doctors about their risk and screening choices.
Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Doctors and patients team up to find the best treatment for prostate cancer. They look at surgery, radiation, and hormone therapy. These methods aim to get rid of the tumor and keep quality of life high. Immunotherapy is also being explored to help the body fight cancer cells.
How to manage prostate cancer depends on the stage and the person. For small cancers, watching and waiting might be suggested. This means regular check-ups and tests. But, for bigger cancers, a mix of treatments might be needed. Blood tests help decide on treatments and check how well they’re working.
Choosing a treatment for prostate cancer is a big decision. Patients think about their age, health, and what they prefer. Support groups and counseling can help with these choices. Remember, managing prostate cancer is an ongoing effort. Regular check-ups and changes in treatment are often needed for the best results.
FAQ
Q: What are the most common signs of prostate cancer?
A: Signs of prostate cancer include frequent urination, especially at night. You might also notice weak or interrupted urine flow. Difficulty starting or stopping urination is another symptom. Blood in urine or semen and pain or burning during urination are also signs.
But, early-stage prostate cancer often doesn’t show symptoms. That’s why regular screenings are key.
Q: At what age should men start getting screened for prostate cancer?
A: Men at average risk should talk to their doctor about screening at age 50. If you’re African American or have a family history, start the conversation at 45 or earlier.
Q: What is a PSA test?
A: A PSA test measures the PSA protein in your blood. High levels can mean prostate cancer, but other issues can also raise PSA. It’s a common screening tool to detect cancer early.
Q: Are there any risk factors for prostate cancer that I can control?
A: Some risk factors like age and family history can’t be changed. But, lifestyle choices can help. Eating well, staying active, keeping a healthy weight, and not smoking may lower your risk.
Q: What is a digital rectal exam (DRE)?
A: A DRE is a physical exam where a doctor checks the prostate gland through the rectum. It’s quick and helps find any abnormalities that might indicate cancer. It might be uncomfortable, but it’s an important part of screening.
Q: If I’m diagnosed with prostate cancer, what treatment options are available?
A: Treatment options depend on the cancer’s stage, your health, and what you prefer. Options include active surveillance, surgery, radiation, hormone therapy, and sometimes chemotherapy or immunotherapy. Your healthcare team will help choose the best plan for you.
Q: Can prostate cancer be cured?
A: Early detection often means prostate cancer can be treated and cured. The 5-year survival rate for early-stage cancer is nearly 100%. But, advanced cancer is harder to treat. That’s why early screening is so important.
Q: What is active surveillance?
A: Active surveillance is for low-risk, slow-growing cancers. Instead of immediate treatment, the cancer is monitored closely. If it starts to grow, treatment begins. This approach avoids unnecessary treatment and its side effects.