Prostate cancer is a common disease that affects many men around the world. It’s important to know what causes it and how to prevent it. This guide will look at the different things that can lead to prostate cancer, like genetics and lifestyle.
We’ll dive into how prostate cancer works, share important statistics, and talk about its symptoms. Our goal is to help you understand more about prostate cancer and how to spot it early.
If you’re worried about your health or someone you care about, this guide is for you. It offers a detailed look at prostate cancer risk factors and why regular check-ups are key.
Understanding Prostate Cancer: A Comprehensive Overview
Prostate cancer is a complex disease that affects millions of men worldwide. To grasp its impact, we need to explore the prostate gland’s structure, cancer development, and key statistics.
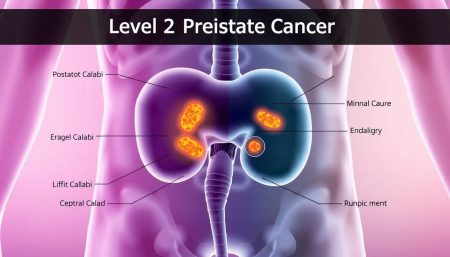
Anatomy of the Prostate Gland
The prostate is a walnut-sized gland located below the bladder. It produces fluid that nourishes and protects sperm. As men age, the prostate can enlarge, leading to various health issues.
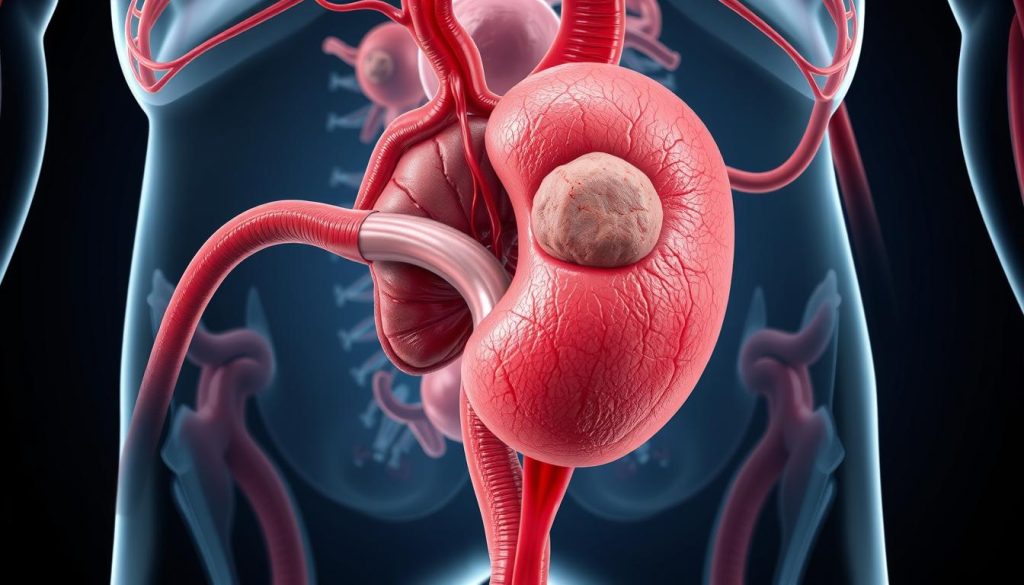
How Cancer Develops in the Prostate
Cancer starts when cells in the prostate begin to grow uncontrollably. These abnormal cells can form tumors and spread to other parts of the body. Early prostate cancer screening is crucial for timely detection and treatment.
Key Statistics and Prevalence
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men globally. Understanding its prevalence helps emphasize the importance of regular check-ups and early intervention.
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Annual new cases worldwide | 1.4 million |
| Lifetime risk for men | 1 in 8 |
| 5-year survival rate (localized) | Nearly 100% |
Prostate cancer treatment options vary based on the cancer’s stage and the patient’s overall health. From active surveillance to surgery and radiation therapy, each approach targets different prostate cancer stages. Regular prostate cancer screening remains a cornerstone in early detection and improved outcomes.
What Causes of Prostate Cancer: Primary Risk Factors
Knowing what causes prostate cancer is key to preventing and catching it early. Prostate cancer risk factors include things we can and can’t control. Let’s look at the main factors that raise your risk.
Age is a big factor in prostate cancer. Men over 50 are more at risk, and the risk grows with age. Race also matters, with African American men facing a higher risk of aggressive prostate cancer.
Family history is another important factor. If your relatives have had prostate cancer, you’re more likely to get it too. Genetic mutations, like BRCA1 and BRCA2, also raise your risk.
What you eat and how active you are can also affect your risk. Eating a lot of red meat and dairy might increase your risk. But eating fruits and veggies and staying active might help protect you. Being overweight and not exercising can lead to more aggressive cancer.
| Risk Factor | Impact Level | Controllable? |
|---|---|---|
| Age (over 50) | High | No |
| Race (African American) | High | No |
| Family History | Moderate to High | No |
| Diet | Moderate | Yes |
| Obesity | Moderate | Yes |
Research is always finding new things about prostate cancer. Some studies say inflammation in the prostate and certain infections might raise your risk. They’re also looking into how chemicals in the environment might affect it.
“While we can’t control all risk factors, understanding them empowers us to make informed decisions about our health.”
It’s important to get regular check-ups and screenings, especially if you have risk factors. Early detection is key, just like with other cancers. It can make a big difference in treatment outcomes.
Age-Related Risk Factors and Family History
Knowing the risk factors for prostate cancer is key for early detection. Age and family history are big factors in who gets this disease.
Age as a Critical Factor
Prostate cancer risk goes up with age. Most men are diagnosed over 50, with an average age of 66. This shows why older men need regular screenings.

Genetic Predisposition
Some genes raise the risk of prostate cancer. Men with BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes are more likely to get aggressive cancer. Testing can find these genes, helping doctors plan better.
Family History Patterns
A family history of prostate cancer raises the risk. Men with a dad or brother who had it are twice as likely. This risk grows with more relatives or early cases.
| Family History | Relative Risk | Recommended Screening Age |
|---|---|---|
| No family history | 1x | 50 years |
| One first-degree relative | 2x | 45 years |
| Multiple relatives or early-onset cases | 3-4x | 40 years |
Grasping these risk factors is vital for better screening programs. It helps in catching prostate cancer early, boosting survival rates.
Lifestyle and Environmental Risk Factors
Knowing how our daily habits and surroundings affect prostate health is key for preventing prostate cancer. Let’s look at how our choices and environment can change our risk levels.
Dietary Influences
What we eat greatly affects our prostate health. Eating a lot of red meat and dairy might raise your risk. But, foods like tomatoes, broccoli, and green tea, which are full of antioxidants, can help protect you.
Physical Activity Impact
Regular exercise is vital for staying healthy and might lower your prostate cancer risk. Men who exercise often have less aggressive prostate cancer. Try to do at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise every day to help prevent prostate cancer.
Environmental Exposures
Some environmental factors can raise your risk of prostate cancer. Being around chemicals like pesticides or heavy metals can be harmful. While we can’t always avoid these, knowing about them helps us make better choices and get screened early. This is important for catching and treating prostate cancer early.
FAQ
Q: What are the primary risk factors for prostate cancer?
A: Prostate cancer risk factors include age over 50, family history, and being African American. Genetic mutations also play a role. Lifestyle choices like eating red meat, being obese, and not exercising can increase risk.
Q: Can prostate cancer be prevented?
A: Preventing prostate cancer is not guaranteed. But, a healthy lifestyle can lower your risk. Eat fruits and veggies, exercise, stay fit, and avoid tobacco. Regular check-ups are key for early detection.
Q: What are the early symptoms of prostate cancer?
A: Early prostate cancer might not show symptoms. But, as it grows, you might have trouble urinating or feel pain in your pelvic area. These signs can also mean other health issues. Always see a doctor for a proper check-up.
Q: How is prostate cancer diagnosed?
A: Doctors use tests like a digital rectal exam (DRE) and a PSA blood test to find prostate cancer. Imaging studies like MRI might also be used. A biopsy confirms the diagnosis and how aggressive the cancer is.
Q: What treatment options are available for prostate cancer?
A: Treatment choices depend on the cancer’s stage and your health. Options include active surveillance, surgery, radiation, hormone therapy, and more. Your healthcare team will help pick the best treatment for you.
Q: How does age affect prostate cancer risk?
A: Age is a big risk factor for prostate cancer. The risk jumps after 50, with most cases in men over 65. But, younger men with a family history or other risk factors can also get it.
Q: What role does genetics play in prostate cancer?
A: Genetics are important in prostate cancer risk. Men with a family history of prostate cancer are at higher risk. Certain genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2 can also increase risk. Genetic testing might be suggested for those with a strong family history.
Q: How effective is prostate cancer screening?
A: Screening with PSA tests and DREs can find cancer early. But, there’s debate over overdiagnosis and overtreatment. The American Cancer Society advises talking to your doctor about screening, starting at 50 for average-risk men.
Q: What are the survival rates for prostate cancer?
A: Survival rates for prostate cancer are high, especially if caught early. The 5-year survival rate for all stages is about 98%. For early-stage cancer, it’s nearly 100%. Early detection is key for better survival rates.
Q: How does diet affect prostate cancer risk?
A: Diet may impact prostate cancer risk, though more research is needed. Eating red meat and dairy might increase risk, while fruits, veggies, and whole grains might lower it. Foods like fish and tomatoes may also help. Eating well is good for prostate health.