Cardiovascular disease includes many heart and blood vessel problems. It covers heart disease, stroke, and heart attacks. These issues are big threats to our health worldwide. Knowing about them helps keep our hearts healthy and avoid serious problems.
Heart disease often starts quietly over years. It can take many forms, like coronary artery disease or heart valve issues. Spotting early signs is key to getting help fast.
Strokes and heart attacks are emergencies that need quick action. They can come from long-term heart issues or happen suddenly in healthy people. Knowing the warning signs, like chest pain or sudden weakness, can save lives.
Learning about cardiovascular disease helps us protect our heart health. It also lowers the risk of these serious conditions.
Understanding What Is Considered Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) refers to many heart and blood vessel problems. It’s important to know about CVD to understand its big impact on health worldwide.
Definition and Basic Concepts
CVD includes heart and circulatory system issues. It includes heart disease, which affects the heart, and vascular diseases that affect blood vessels. Cardiovascular disease can cause serious health problems if not treated.
Major Types of CVD
There are many conditions under the CVD umbrella:
- Coronary artery disease
- Congestive heart failure
- Heart valve disorders
- Arrhythmias
- Stroke
Coronary artery disease, or heart disease, is the most common. It happens when plaque builds up in arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart.
Global Impact and Statistics
CVD has a big impact on health and the economy worldwide. Here are some important stats:
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Annual global deaths from CVD | 17.9 million |
| Percentage of all deaths caused by CVD | 31% |
| Premature deaths (under 70) due to CVD | 38% |
| Global economic cost of CVD (2010) | $863 billion |
These numbers show we need to work harder on preventing, detecting, and treating CVD worldwide.
Common Types of Heart Disease and Their Symptoms
Heart disease includes many conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels. Spotting symptoms early can save lives. Let’s look at some common heart issues and their warning signs.
Coronary artery disease can lead to heart attacks. Symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, and feeling tired. During a heart attack, you might feel intense chest pressure, arm pain, or nausea.
Strokes happen when blood flow to the brain stops. Look out for sudden numbness, confusion, severe headache, or trouble speaking. Quick action is key for stroke recovery.
Arrhythmias are irregular heartbeats that can feel like fluttering or racing. Some people say it’s like their heart skipping beats. Severe arrhythmias may cause dizziness or fainting.
Heart valve problems can cause shortness of breath, swelling in legs, and feeling tired. You might hear a heart murmur during a checkup, signaling valve issues.
“Knowing the signs of heart disease can make all the difference. Don’t ignore unusual symptoms – they could be your body’s way of alerting you to a serious problem.”
Remember, symptoms can vary from person to person. If you notice any concerning signs, get medical help right away. Early detection and treatment can greatly improve heart disease outcomes.
Coronary Artery Disease: The Leading Cardiovascular Condition
Coronary artery disease is the top heart disease. It happens when arteries to the heart get narrowed or blocked. Knowing how it starts, what increases the risk, and how to treat it is key for heart health.
Atherosclerosis Development
Atherosclerosis is the main cause of coronary artery disease. It happens when plaque builds up in artery walls, blocking blood flow. If not treated, it can cause a heart attack.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Many things can raise your risk of coronary artery disease:
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
To prevent it, focus on lifestyle changes. Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and managing stress are important.
Treatment Options
Treatment for coronary artery disease depends on how severe it is. Options include:
- Medications to control blood pressure and cholesterol
- Angioplasty to open blocked arteries
- Coronary artery bypass surgery for severe blockages
- Lifestyle changes to slow disease progression
Early detection and treatment can greatly lower heart attack risk and improve heart health.
Heart Attack and Stroke: Emergency Cardiovascular Events
Heart attacks and strokes are serious emergencies that need quick action. They can happen suddenly, without warning. Knowing the signs and acting fast is critical to save lives.
A heart attack happens when blood flow to the heart is blocked. This is usually due to plaque buildup in the arteries. Symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, and discomfort in the upper body.
Strokes occur when blood flow to the brain is cut off. This can be due to a clot or a ruptured blood vessel. Signs include sudden numbness, confusion, and trouble speaking or walking.
Both heart attacks and strokes are signs of cardiovascular disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, obesity, and diabetes. Some groups are at higher risk.
“Time is muscle in heart attacks and time is brain in strokes. Every minute counts when it comes to saving lives and preventing long-term damage.”
Getting immediate medical help is vital for both conditions. For heart attacks, treatments may include medications or procedures to open blocked arteries. Stroke treatment depends on the type but can involve clot-busting drugs or surgery.
| Condition | Key Symptoms | Immediate Action |
|---|---|---|
| Heart Attack | Chest pain, shortness of breath, upper body discomfort | Call 911, chew aspirin if advised |
| Stroke | Sudden numbness, confusion, speech difficulty | Call 911, note time symptoms started |
Preventing these emergencies is key. Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and managing stress can lower your risk. Being prepared and acting fast can save lives in cardiovascular emergencies.
Understanding Heart Rhythm Disorders and Arrhythmias
Heart rhythm disorders, or arrhythmias, are common in cardiovascular disease. They affect the heart’s electrical system, leading to irregular beats. Knowing about arrhythmias is key to understanding their impact and treatment.
Types of Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias vary in how they affect the heart:
- Tachycardia: Rapid heartbeat (over 100 beats per minute)
- Bradycardia: Slow heartbeat (under 60 beats per minute)
- Atrial fibrillation: Irregular and rapid heart rhythm
- Ventricular fibrillation: Rapid, chaotic heartbeat in the lower chambers
Diagnosis Methods
Special tests are needed to find arrhythmias:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Records electrical signals of the heart
- Holter monitor: Portable ECG device worn for 24-48 hours
- Event recorder: Similar to a Holter monitor but used for longer periods
- Echocardiogram: Uses sound waves to create heart images
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for heart rhythm disorders varies by type and severity. Options include:
- Medications to control heart rate or rhythm
- Cardioversion to restore normal heart rhythm
- Catheter ablation to destroy problematic heart tissue
- Implantable devices like pacemakers or defibrillators
Understanding arrhythmias is vital for managing cardiovascular health. If you experience symptoms like palpitations, dizziness, or shortness of breath, consult a healthcare provider promptly.
Heart Valve Diseases and Their Impact
Heart valve problems are a big part of cardiovascular disease. They make it hard for the heart to pump blood well. This can cause many health issues. It’s important to know about heart valve diseases early to treat them.
Heart valves are key for blood to flow right through the heart. If they don’t work right, it can cause two main problems:
- Stenosis: Narrowing of the valve, restricting blood flow
- Regurgitation: Leaking of the valve, allowing blood to flow backward
These issues can make the heart work too hard. If not treated, they can lead to serious heart disease. Symptoms like shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain, and irregular heartbeats may appear slowly.
There are different ways to treat heart valve problems. Doctors might use medicine or surgery. Sometimes, the heart needs a new valve to work right again.
| Treatment Option | Description | Suitable For |
|---|---|---|
| Medication | Manage symptoms and prevent complications | Mild cases or those unsuitable for surgery |
| Valve Repair | Surgical correction of damaged valve | Suitable candidates with repairable valves |
| Valve Replacement | Replacement of faulty valve with artificial one | Severe cases or irreparable valve damage |
Getting heart valve problems treated early can really help. Regular health checks and knowing the symptoms are important. This way, people can manage their heart disease better.
Congestive Heart Failure: Causes and Management
Congestive heart failure is a serious disease that affects millions. It happens when the heart can’t pump blood well. This leads to fluid buildup in the lungs and other parts of the body.
Types of Heart Failure
Heart failure is divided into two types: systolic and diastolic. Systolic failure means the heart can’t pump blood out. Diastolic failure means the heart can’t fill with blood.
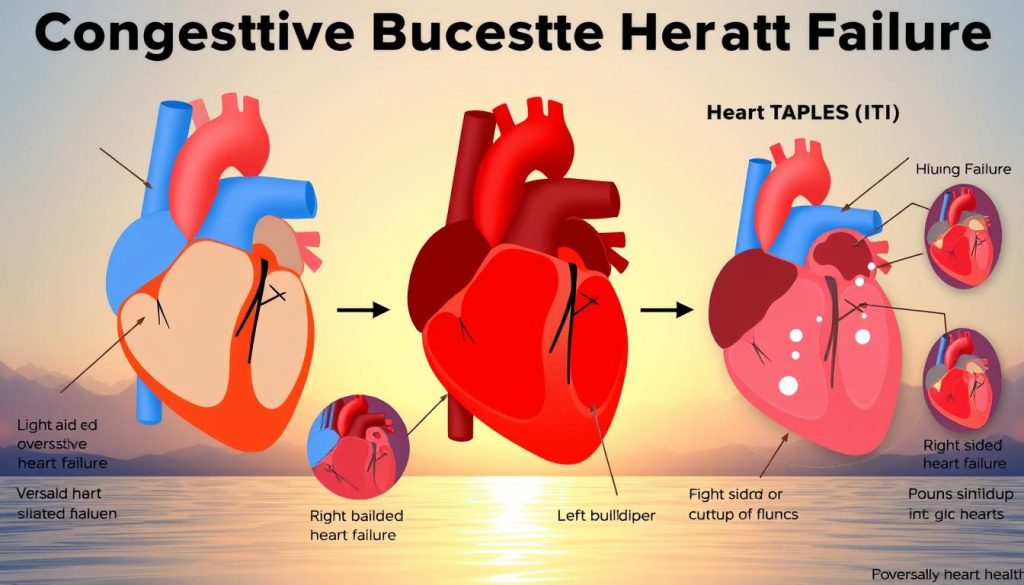
Warning Signs
It’s important to know the warning signs of congestive heart failure. Common symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath, often when lying down
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet
- Persistent coughing or wheezing
- Fatigue and weakness
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
Treatment Strategies
Managing congestive heart failure involves lifestyle changes and medical treatments. Treatment strategies include:
- Medications to help the heart function better and reduce fluid
- Dietary changes, like eating less salt
- Regular exercise, as advised by a doctor
- Quitting smoking and drinking less alcohol
- In severe cases, surgery or device implantation may be needed
Early detection and proper management can greatly improve life quality. Regular health check-ups are key for those at risk of heart disease.
Pericardial and Aortic Diseases: Lesser-Known Conditions
Many people know about common heart issues, but pericardial and aortic diseases are not as well-known. These conditions are serious and need quick medical help.
Pericardial disease affects the sac around the heart. It can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, and fever. There are different types, including:
- Pericarditis (inflammation)
- Pericardial effusion (fluid buildup)
- Constrictive pericarditis (scarring)
Aortic diseases affect the main artery in the body. They can be very dangerous if not treated. Common issues include:
- Aortic aneurysm
- Aortic dissection
- Aortic valve disease
It’s important to catch these diseases early. Doctors use tests like echocardiograms and CT scans to find them. Treatment varies but might include medicine, surgery, or changes in lifestyle.
| Condition | Symptoms | Diagnosis | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pericardial Disease | Chest pain, fever, fatigue | ECG, echocardiogram | Anti-inflammatories, drainage |
| Aortic Disease | Back pain, shortness of breath | CT scan, MRI | Surgery, medication |
Knowing about these heart diseases can help you spot symptoms early. Regular health checks and a healthy lifestyle can prevent many heart problems.
Prevention Strategies for Cardiovascular Health
It’s important to take care of your heart to avoid cardiovascular disease. Making good choices can lower your risk and improve your health. Let’s look at some effective ways to prevent cardiovascular disease.
Lifestyle Modifications
Small changes can make a big difference. Quitting smoking and drinking less alcohol are key steps. Also, managing stress, getting enough sleep, and keeping a healthy weight are important for your heart.
Diet and Exercise
Eating well is essential for a healthy heart. Focus on fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid too much saturated fat, salt, and sugar. Regular exercise, like walking or cycling, strengthens your heart and improves blood flow.
Regular Health Screenings
Don’t miss out on check-ups! Regular tests can spot problems early. Keep an eye on your blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar. These tests offer insights into your heart health and help you stay on track.
FAQ
Q: What is considered cardiovascular disease?
A: Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a group of conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels. It includes heart disease, stroke, and coronary artery disease. Other conditions like heart valve problems and arrhythmias also fall under CVD.
Q: What are the most common types of cardiovascular disease?
A: The most common types are coronary artery disease, heart failure, and arrhythmias. Valve disorders, stroke, peripheral artery disease, and aortic diseases are also significant.
Q: What are the main symptoms of a heart attack?
A: Symptoms of a heart attack include chest pain or discomfort. You might also feel short of breath or experience pain in the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach. Women may have less typical symptoms like fatigue, nausea, or dizziness.
Q: How is coronary artery disease diagnosed?
A: Coronary artery disease is diagnosed through a review of your medical history and physical exam. Tests like electrocardiograms (ECG), stress tests, and coronary angiograms are used. Cardiac CT scans may also be part of the diagnosis.
Q: What’s the difference between a heart attack and stroke?
A: A heart attack occurs when blood flow to the heart is blocked. This causes damage to the heart muscle. A stroke happens when blood flow to the brain is interrupted. This deprives brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients.
Q: What are arrhythmias and how are they treated?
A: Arrhythmias are abnormal heart rhythms. Treatment options include medications, lifestyle changes, and medical procedures. Devices like pacemakers or implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) may also be used, depending on the type and severity.
Q: How does congestive heart failure affect the body?
A: Congestive heart failure happens when the heart can’t pump blood well. This leads to fluid buildup in the lungs and other tissues. Symptoms include shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling in the legs and ankles.
Q: What are the risk factors for cardiovascular disease?
A: Risk factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and smoking. Obesity, diabetes, and physical inactivity are also major risks. An unhealthy diet, excessive alcohol, age, gender, and family history also play a role.
Q: Can cardiovascular disease be prevented?
A: While some risk factors can’t be changed, many cardiovascular diseases can be prevented or managed. Lifestyle changes like a healthy diet, regular exercise, not smoking, and managing stress are key.
Q: What are pericardial diseases?
A: Pericardial diseases affect the pericardium, the protective sac around the heart. Conditions include pericarditis (inflammation), pericardial effusion (fluid buildup), and constrictive pericarditis.