Prostate cancer is a serious health issue that affects many men globally. This guide aims to enlighten you about the condition, its signs, and risk factors. By knowing prostate cancer signs and risk factors, men can take early steps towards detection and treatment.
We’ll cover the basics of prostate cancer, including symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options. Our aim is to give clear, easy-to-understand information to help men make informed health decisions. Whether you’re worried about symptoms or want to know your risk factors, this guide offers valuable insights into prostate cancer and men’s health.
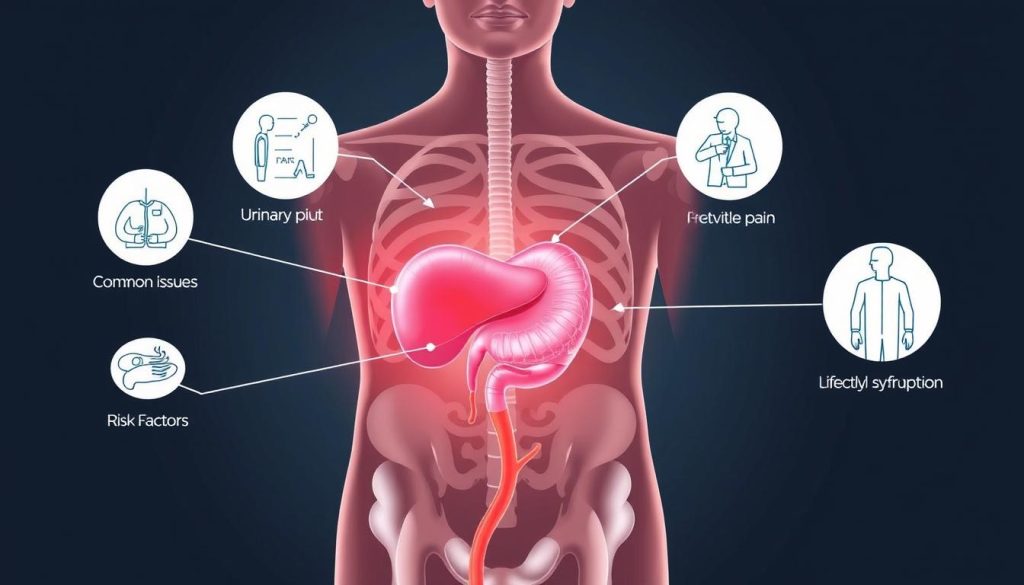
What Is Prostate Cancer And Symptoms
Prostate cancer is a serious health issue for men. It happens when cells in the prostate gland grow too much. Knowing the signs can help find it early and improve treatment.
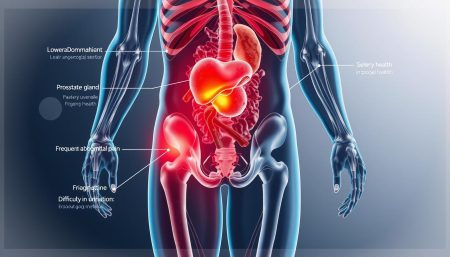
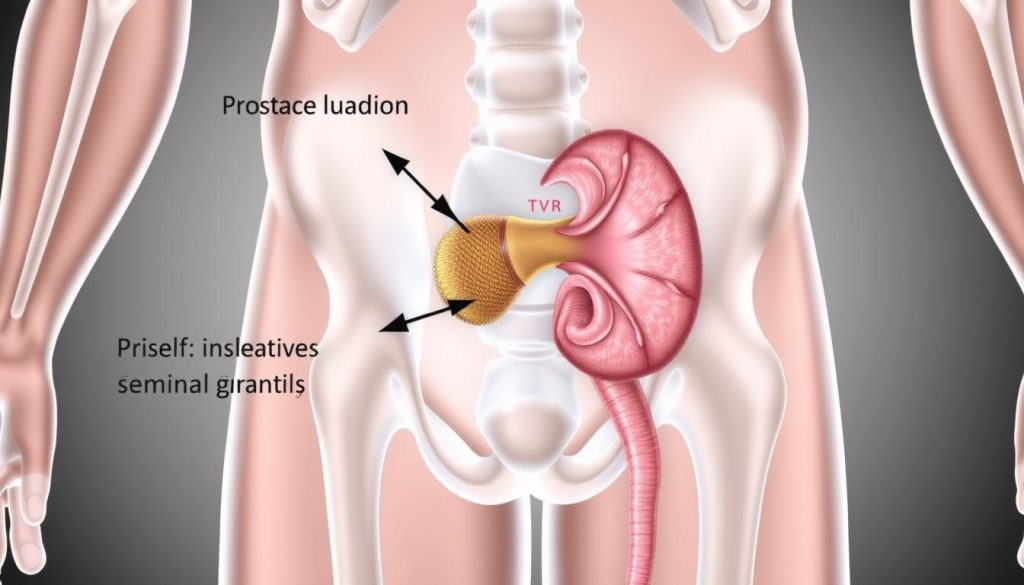
Understanding The Prostate Gland Function
The prostate is a small gland in men that makes seminal fluid. This fluid helps sperm grow and move. It’s located below the bladder and surrounds part of the urethra, the tube for urine.
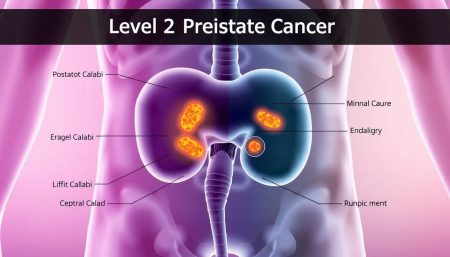
Early Warning Signs Of Prostate Cancer
It’s important to spot prostate cancer signs early. Some common signs include:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination
- Weak or interrupted urine flow
- Blood in urine or semen
- Discomfort in the pelvic area
Common Symptoms In Different Stages
Symptoms change with the cancer’s stage. Early stages might show few signs. But, later stages can cause bone pain, weight loss, or tiredness.
| Stage | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Early Stage | Urinary changes, mild discomfort |
| Localized | Erectile dysfunction, pelvic pain |
| Advanced | Bone pain, weight loss, fatigue |
If you notice any symptoms, see your doctor. Finding prostate cancer early can greatly improve treatment chances.
Risk Factors And Prevention Strategies
Knowing about prostate cancer risk factors is key to catching it early. We’ll look at what increases the risk and how to lower it.
Age And Family History Considerations
Men’s risk of prostate cancer goes up with age. Family history also matters a lot. If your relatives had prostate cancer, you’re at higher risk.
Getting regular check-ups is important, especially after 50. Or even earlier if you have a family history.

Lifestyle And Environmental Factors
Some lifestyle choices can raise your risk. Eating a lot of red meat and not enough fruits and veggies is bad. Being overweight and not exercising also increases risk.
Exposure to certain chemicals might also play a part in getting prostate cancer.
Preventive Measures And Screening Guidelines
There are steps you can take to lower your risk. Exercise, eat well, and keep a healthy weight. Screening guidelines suggest talking to your doctor about PSA tests by 50. Or sooner if you’re at high risk.
| Risk Factor | Impact Level | Preventive Measure |
|---|---|---|
| Age (over 50) | High | Regular screenings |
| Family History | High | Early and frequent screenings |
| Diet (high in red meat) | Moderate | Increase plant-based foods |
| Obesity | Moderate | Maintain healthy weight |
| Lack of Exercise | Moderate | Regular physical activity |
While some risks can’t be changed, a healthy lifestyle and screenings can help a lot. Stay informed and take care of your health to lower your risk of prostate cancer.
Diagnostic Methods For Prostate Cancer
Several tests and procedures help find prostate cancer. Doctors use these to detect and stage the disease. This guides treatment choices.
The first test is often the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test. High PSA levels might mean cancer, but other issues can also cause it. A digital rectal exam (DRE) lets doctors feel the prostate for any problems.
If tests show concerns, a prostate biopsy is usually next. This involves taking small tissue samples for a closer look. The biopsy results show if cancer is there and how aggressive it is.
“Early detection through proper screening can significantly improve prostate cancer outcomes.”
Imaging tests are key for figuring out how far the cancer has spread. These include:
- Transrectal ultrasound
- MRI scans
- Bone scans
- CT scans
Knowing the cancer stage is important for planning treatment. The TNM system looks at tumor size, lymph node involvement, and if it has spread. Regular screening helps catch cancer early, making treatment more effective.
| Prostate Cancer Stage | Description | 5-Year Survival Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Stage I | Cancer confined to prostate | Nearly 100% |
| Stage II | Cancer still in prostate, more advanced | Nearly 100% |
| Stage III | Cancer spread beyond prostate | Nearly 100% |
| Stage IV | Cancer spread to distant parts of body | 30% |
Accurate diagnosis and staging help doctors and patients make the best treatment choices. This ensures the most effective approach for each case.
Treatment Options And Their Effectiveness
Prostate cancer treatment options depend on the disease’s stage and how aggressive it is. Knowing these choices helps patients make informed decisions about their care.
Surgery and Radiation Therapy
For localized prostate cancer, surgery and radiation therapy are common prostate cancer treatment options. Surgery removes the prostate gland. Radiation uses high-energy beams to kill cancer cells. Both can be effective but may cause side effects like urinary incontinence or erectile dysfunction.
Hormone Therapy Approaches
Hormone therapy is used for advanced prostate cancer. It lowers testosterone levels, which can slow cancer growth. This treatment may be used alone or with other therapies.
Emerging Treatment Technologies
New technologies are expanding treatment possibilities. These include targeted drug therapies, immunotherapy, and precision radiation techniques. These innovations aim to improve outcomes while minimizing side effects.
Active Surveillance Protocol
For some men with low-risk prostate cancer, active surveillance might be recommended. This approach involves regular monitoring through PSA tests and biopsies, delaying active treatment until necessary.
| Treatment | Best For | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Surgery | Localized cancer | Incontinence, erectile dysfunction |
| Radiation | Localized or advanced cancer | Fatigue, urinary issues |
| Hormone Therapy | Advanced prostate cancer | Hot flashes, loss of libido |
| Active Surveillance | Low-risk cancer | Anxiety, risk of progression |
Choosing the right treatment plan involves weighing the benefits and risks of each option. Patients should discuss their individual case with healthcare providers to determine the most suitable approach for their prostate cancer.
Living With Prostate Cancer: Survival And Quality Of Life
Life after a prostate cancer diagnosis can be tough, but many men find joy in living. Thanks to early detection, survival rates have gone up. For those with advanced cancer, new treatments bring hope and better results.
Dealing with prostate cancer is not just about medical treatment. Support groups and counseling help men and their families with the emotional side. Many find comfort in sharing their stories with others who understand. Staying active and eating well can also improve health during and after treatment.
Survivors need to keep up with regular health checks and watch for signs of cancer coming back. Some may deal with side effects like changes in how they pee or have sex. Talking openly with doctors is important to find ways to manage these issues. With the right care and support, many men with prostate cancer can live well and look forward to the future.
FAQ
Q: What are the early warning signs of prostate cancer?
A: Early signs of prostate cancer can be hard to spot. They might include needing to pee a lot, especially at night. You might also have trouble starting or stopping urination, or feel like your urine flow is weak.
Other signs are blood in your urine or semen, and pain or burning when you pee. But, many men with early prostate cancer don’t show any symptoms at all.
Q: Who is at higher risk for developing prostate cancer?
A: Some men are more likely to get prostate cancer. This includes men over 50, those with a family history of it, and African Americans. Certain genetic mutations also raise the risk.
What you eat and how active you are can also play a part. Eating a lot of red meat and fatty foods, being overweight, and not exercising can increase your risk.
Q: How is prostate cancer diagnosed?
A: Doctors use several tests to find prostate cancer. These include a PSA blood test and a digital rectal exam (DRE). They might also do a biopsy and use imaging tests like MRI or CT scans.
If cancer is thought to be present, a biopsy is done. This confirms the diagnosis and shows how aggressive the cancer is.
Q: What are the stages of prostate cancer?
A: Prostate cancer is staged from I to IV. Stage I is early and the cancer is only in the prostate. Stage II is also in the prostate but might be more aggressive.
Stage III means the cancer has spread to nearby tissues. Stage IV is the worst, with cancer in distant parts of the body like bones or lymph nodes.
Q: What treatment options are available for prostate cancer?
A: Treatment choices depend on the cancer’s stage and the patient’s health. Options include active surveillance, surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and chemotherapy for advanced cases.
New treatments like immunotherapy and targeted therapy are also being used for some cases.
Q: What is active surveillance, and when is it recommended?
A: Active surveillance means watching low-risk, slow-growing prostate cancer closely. It’s for men with early-stage, low-grade cancer. This approach avoids immediate treatment.
It involves regular PSA tests, DREs, and biopsies to check if the cancer is growing.
Q: What are the survival rates for prostate cancer?
A: Survival rates for prostate cancer are good, especially if caught early. The 5-year survival rate for early cancer is nearly 100%. For cancer that has spread, it’s about 30%.
But, many men with prostate cancer live a long time, thanks to better treatments.
Q: How can I maintain my quality of life after a prostate cancer diagnosis?
A: Keeping a good quality of life after a diagnosis involves several steps. Joining support groups and staying healthy with exercise and a balanced diet are key. Managing treatment side effects is also important.
Don’t forget to talk to your partner about any changes in sexual function or continence issues caused by treatment.